|
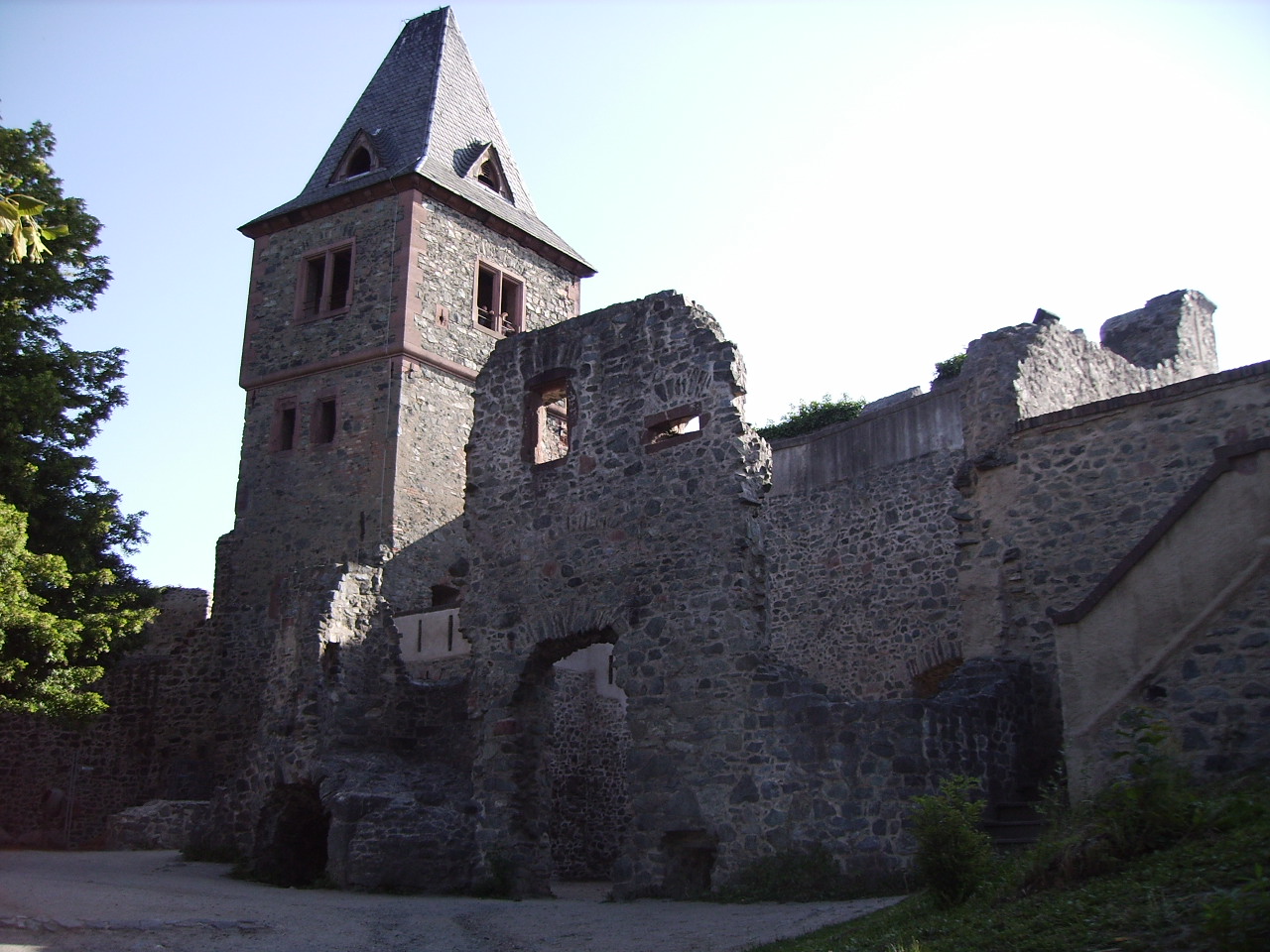
Frankenstein Castle
Frankenstein Castle (german: Burg Frankenstein) is a hilltop castle in the Odenwald overlooking the city of Darmstadt in Germany. This castle may have been an inspiration for Mary Shelley when she wrote her 1818 Gothic novel ''Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus''. Location Frankenstein Castle is in southern Hesse, Germany, on the spurs of the Odenwald mountain range at an elevation of close to the southern outskirts of Darmstadt. It is one of many historic castles along the Hessian Bergstraße Route, also famous for its vineyards and its mild climate. Meaning of "Frankenstein" Frankenstein is a German name consisting of two words: The Franks are a Germanic tribe and "stein" is the German word for "stone". Accordingly, the meaning of Frankenstein is "Stone of the Franks". The word "stein" is common in names of landscapes, places and castles in Germany. Consequently, the term "Frankenstein" is a rather ordinary name for a castle in this region. History Before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Keel
John Alva Keel, born Alva John Kiehle (March 25, 1930 – July 3, 2009) was an Americans, American journalist and influential UFOlogist who is best known as author of ''The Mothman Prophecies''. Early life Keel was born in Hornell, New York, the son of a small-time bandleader. His parents separated and he was raised by his grandparents. He was interested in magic (illusion), magic and had his first story published in a magicians' magazine at age 12. He left school at the age of 16 after taking all the science courses. He worked as a freelance contributor to newspapers, scriptwriter for local radio and television outlets, and author of pulp articles such as "Are You A Repressed Sex Fiend?" He served in the US Army during the Korean War on the staff of the American Forces Network at Frankfurt, Germany. He claimed that while in the Army he was trained in psychological warfare as a propaganda writer. Career After leaving the military he worked as a foreign radio correspondent in Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frankenstein (1931 Film)
''Frankenstein'' is a 1931 American pre-Code science fiction horror film directed by James Whale, produced by Carl Laemmle Jr., and adapted from a 1927 play by Peggy Webling, which in turn was based on Mary Shelley's 1818 novel '' Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus''. The Webling play was adapted by John L. Balderston and the screenplay written by Francis Edward Faragoh and Garrett Fort, with uncredited contributions from Robert Florey and John Russell. ''Frankenstein'' stars Colin Clive as Henry Frankenstein, an obsessed scientist who digs up corpses with his assistant in order to assemble a living being from body parts. The resulting creature, often known as Frankenstein's monster, is portrayed by Boris Karloff. The make-up for the monster was provided by Jack Pierce. Alongside Clive and Karloff, the film's cast also includes Mae Clarke, John Boles, Dwight Frye, and Edward Van Sloan. Produced and distributed by Universal Pictures, the film was a commercial succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine. The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal's body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
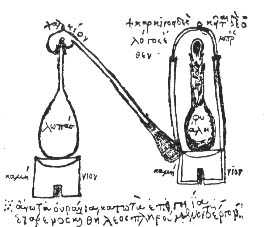
Alchemy
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim world, and Europe. In its Western form, alchemy is first attested in a number of pseudepigraphical texts written in Greco-Roman Egypt during the first few centuries AD.Principe, Lawrence M. The secrets of alchemy'. University of Chicago Press, 2012, pp. 9–14. Alchemists attempted to purify, mature, and perfect certain materials. Common aims were chrysopoeia, the transmutation of "base metals" (e.g., lead) into "noble metals" (particularly gold); the creation of an elixir of immortality; and the creation of panaceas able to cure any disease. The perfection of the human body and soul was thought to result from the alchemical ''magnum opus'' ("Great Work"). The concept of creating the philosophers' stone was variously connected with all of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rumour
A rumor (American English), or rumour (British English; see spelling differences; derived from Latin:rumorem - noise), is "a tall tale of explanations of events circulating from person to person and pertaining to an object, event, or issue in public concern." In the social sciences, a rumor involves a form of a statement whose veracity is not quickly or ever confirmed. In addition, some scholars have identified rumor as a subset of propaganda. Sociology, psychology, and communication studies have widely varying definitions of rumor. Rumors are also often discussed with regard to misinformation and disinformation (the former often seen as simply false and the latter seen as deliberately false, though usually from a government source given to the media or a foreign government). Early work French and German social science research on rumor locates the modern scholarly definition of it to the pioneering work of the German William Stern in 1902. Stern experimented on rumor i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dippel's Oil
Dippel's oil (sometimes referred to as bone oil) is a nitrogenous by-product of the destructive distillation of bones. A dark, viscous, tar-like liquid with an unpleasant smell, it is named after its inventor, Johann Konrad Dippel. The oil consists mostly of aliphatic chains, with nitrogen functionalities and includes species such as pyrroles, pyridines and nitriles, as well as other nitrogenous compounds. Dippel's oil had a number of uses which are now mostly obsolete. Its primary use was as an animal and insect repellent. It saw limited use as a chemical warfare harassing agent during the desert campaign of World War II. The oil was used to render wells undrinkable and thus deny their use to the enemy. By not being lethal, the oil was claimed to not be in breach of the Geneva Protocol. See also * Neatsfoot oil, another bone-derived oil * Bone char Bone char ( lat, carbo animalis) is a porous, black, granular material produced by charring animal bones. Its composition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gernsheim
Gernsheim () is a town in Groß-Gerau district and Darmstadt region in Hesse, Germany, lying on the Rhine. Geography Location The ''Schöfferstadt Gernsheim'', as Gernsheim may officially call itself – it was Peter Schöffer's birthplace – lies 18 km southwest of Darmstadt and 16 km northeast of Worms, right on the Rhine's east bank, south of the Old Rhine near Stockstadt am Rhein in the Frankfurt Rhein-Main Region. Neighbouring communities Gernsheim borders in the north on the communities of Biebesheim and Riedstadt, in the east on the town of Pfungstadt and the communities of Bickenbach and Alsbach-Hähnlein (all in Darmstadt-Dieburg), in the south on the town of Bensheim and the communities of Einhausen and Groß-Rohrheim (all in Kreis Bergstraße) and in the west on the community of Hamm (Alzey-Worms). Constituent communities Gernsheim consists of the centres of Allmendfeld, Gernsheim and Klein-Rohrheim. History In the first century, there was Roman s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland , source1_coordinates= , source1_elevation = , source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein , source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland , source2_coordinates= , source2_elevation = , source_confluence = Reichenau , source_confluence_location = Tamins, Graubünden, Switzerland , source_confluence_coordinates= , source_confluence_elevation = , mouth = North Sea , mouth_location = Netherlands , mouth_coordinates = , mouth_elevation = , progression = , river_system = , basin_size = , tributaries_left = , tributaries_right = , custom_label = , custom_data = , extra = The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label= Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label= Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alchemist
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim world, and Europe. In its Western form, alchemy is first attested in a number of pseudepigraphical texts written in Greco-Roman Egypt during the first few centuries AD.Principe, Lawrence M. The secrets of alchemy'. University of Chicago Press, 2012, pp. 9–14. Alchemists attempted to purify, mature, and perfect certain materials. Common aims were chrysopoeia, the transmutation of "base metals" (e.g., lead) into "noble metals" (particularly gold); the creation of an elixir of immortality; and the creation of panaceas able to cure any disease. The perfection of the human body and soul was thought to result from the alchemical ''magnum opus'' ("Great Work"). The concept of creating the philosophers' stone was variously connected with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Konrad Dippel
Johann Konrad Dippel, also spelled Johann Conrad Dippel (10 August 1673 – 25 April 1734), was a German Pietist theologian, physician, alchemist and occultist. Life Dippel was born at Castle Frankenstein near Mühltal and Darmstadt, and therefore once at his school the addendum ''Franckensteinensis'' and once at his university the addendum ''Franckensteina-Strataemontanus'' was used. He studied theology, philosophy and alchemy at the University of Giessen, obtaining a master's degree in theology in 1693. He published many theological works under the name Christianus Demócritus, and most of them are still preserved. Circa 1700, he turned to Hermetic studies and alchemy as a key to nature. Between 1700 and 1702, he engaged in a bitter dispute with the Reformed Court Preacher Conrad Broeske in Offenbach, with whom he shared millenarian hopes for soon-coming renewal in Christendom. He accused Broeske of compromise and collusion with the authorities after Broeske refused to pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defense Media Activity
The Defense Media Activity (DMA) is a United States Department of Defense (DoD) field activity. It provides a broad range of high-quality multimedia products and services to inform, educate, and entertain Department of Defense audiences around the world. The Defense Media Activity is located on Fort Meade, Maryland. DoD field activities are established as DoD components by law, by the President, or by the Secretary of Defense to provide for the performance, on a DoD-wide basis, of a supply or service activity that is common to more than one Military Department when it is determined to be more effective, economical, or efficient to do so. DMA operates as a separate DoD Component under the authority, direction and control of the Assistant to the Secretary of Defense for Public Affairs. History The Defense Media Activity can trace its organizational lineage to the first publication of the '' Stars and Stripes'' newspaper produced by Union soldiers during the Civil War, in 1861. The D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |