|
Franciszek Kareu (1731-1802)
Franciszek Kareu (10 December 1731, Orsza – 11 August 1802, Polotsk) was a Polish-Welsh Jesuit priest, architect, missionary and teacher in the region of modern day Belarus. During the worldwide Suppression of the Society of Jesus, with the exception of the territory of the Russian Empire, he was elected Temporary Vicar General of the Society of Jesus in Russia from 1799 to 1801. His careful management of this precarious institutional challenge facilitated a transition leading to the universal restoration of the order in the early 19th-century. Early years and formation Born of a noble Wales, Welsh family (Carew), settled in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, he followed the conventional course of studies available to sons of the landowning class. These included humanities and philosophy, in Orsza (in present day Belarus), before joining the Jesuit order. As all candidates of the time, Kareu joined the Jesuits in Vilnius, where he completed two years of novitiate (1754–56). There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franciszek Kareu (1731-1802)
Franciszek Kareu (10 December 1731, Orsza – 11 August 1802, Polotsk) was a Polish-Welsh Jesuit priest, architect, missionary and teacher in the region of modern day Belarus. During the worldwide Suppression of the Society of Jesus, with the exception of the territory of the Russian Empire, he was elected Temporary Vicar General of the Society of Jesus in Russia from 1799 to 1801. His careful management of this precarious institutional challenge facilitated a transition leading to the universal restoration of the order in the early 19th-century. Early years and formation Born of a noble Wales, Welsh family (Carew), settled in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, he followed the conventional course of studies available to sons of the landowning class. These included humanities and philosophy, in Orsza (in present day Belarus), before joining the Jesuit order. As all candidates of the time, Kareu joined the Jesuits in Vilnius, where he completed two years of novitiate (1754–56). There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particular, rites of sacrifice to, and propitiation of, a deity or deities. Their office or position is the 'priesthood', a term which also may apply to such persons collectively. A priest may have the duty to hear confessions periodically, give marriage counseling, provide prenuptial counseling, give spiritual direction, teach catechism, or visit those confined indoors, such as the sick in hospitals and nursing homes. Description According to the trifunctional hypothesis of prehistoric Proto-Indo-European society, priests have existed since the earliest of times and in the simplest societies, most likely as a result of agricultural surplus and consequent social stratification. The necessity to read sacred texts and keep temple or church rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicar General
A vicar general (previously, archdeacon) is the principal deputy of the bishop of a diocese for the exercise of administrative authority and possesses the title of local ordinary. As vicar of the bishop, the vicar general exercises the bishop's Ordinary (church officer), ordinary executive (government), executive power over the entire diocese and, thus, is the highest official in a diocese or other particular church after the diocesan bishop or his equivalent in canon law. The title normally occurs only in Western Christian churches, such as the Latin Church of the Catholic Church and the Anglican Communion. Among the Eastern churches, the Mar Thoma Syrian Church of Kerala uses this title and remains an exception. The title for the equivalent officer in the Eastern churches is syncellus and protosyncellus. The term is used by many religious orders of men in a similar manner, designating the authority in the Order after its Superior General. Ecclesiastical structure In the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Poland and Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Lithuania ruled by a common Monarchy, monarch in real union, who was both King of Poland and List of Lithuanian monarchs, Grand Duke of Lithuania. It was one of the largest and most populous countries of 16th- to 17th-century Europe. At its largest territorial extent, in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth covered almost and as of 1618 sustained a multi-ethnic population of almost 12 million. Polish language, Polish and Latin were the two co-official languages. The Commonwealth was established by the Union of Lublin in July 1569, but the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania had been in a ''de facto'' personal union since 1386 with the marriage of the Polish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and shares Borders of Russia, land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than List of countries and territories by land borders, any other country but China. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's ninth-most populous country and List of European countries by population, Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city is Moscow, the List of European cities by population within city limits, largest city entirely within E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orsha
Orsha ( be, О́рша, Во́рша, Orša, Vorša; russian: О́рша ; lt, Orša, pl, Orsza) is a city in Belarus in the Vitebsk Region, on the fork of the Dnieper and Arshytsa rivers. History Orsha was first mentioned in 1067 as Rsha, making it one of the oldest towns in Belarus. The town was named after the river, which was originally also named Rsha, probably from a Baltic root *''rus'' 'slowly flowing.' In 1320, Orsha became a part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Between 1398–1407, the Orsha castle was built. On 8 September 1514 the famous Battle of Orsha occurred, between allied Grand Duchy of Lithuania with Kingdom of Poland and Muscovite army. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanislaus Czerniewicz
Stanislaw Czerniewicz (15 August 1728 in Kaunas – 7 July 1785) was a Lithuanian-Polish Jesuit priest. He was Rector of the Jesuit College in Polotsk when the Society of Jesus was suppressed in 1773; in 1782, he was elected vicar general for the Jesuits in Russia in 1782 and ''de facto'' Superior General of the Society of Jesus. Early career After his Jesuit training in Lithuania – philosophy (1747–50) and theology (1753–57) at Academy of Vilnius – Czerniewicz taught grammar and poetry in the Kražiai College (1750–53) before being called to Rome where he was secretary for the Polish Assistancy of the Society of Jesus (1759–68). There he got familiarised with the governance of the society. He returned to his country where he was made rector of the Jesuit College in Polotsk (now in Belarus) in 1770. After the suppression of the Society of Jesus The brief of Clement XIV suppressing the Society (July 1773) could not be promulgated in the Jesuit houses of the Rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesuit College In Polotsk
The Jesuit College in Polotsk ( lat, Collegium Polocense) was a college established by the Jesuit Order in Polotsk, then part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and later occupied by the Russian Empire, and now in Belarus. It was established in 1580 and continued to function until 1820 when Jesuits were banished from the Russian Empire. History Polish King Stephen Báthory captured Polotsk in 1579 during the Livonian War and invited Jesuits to the city in hopes to lessen the influence of the Eastern Orthodox Church. The Jesuits established a college (equivalent to a secondary school), modeled after the Jesuit Academy in Vilnius, in 1580. Its first rector was Piotr Skarga. A faculty of philosophy was added in 1649 and a faculty of theology in 1737. After the first partition of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1772, Polotsk became part of the Russian Empire. That saved the college from the suppression of the Jesuits as Russian Empress Catherine the Great did not follow papa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabriel Lenkiewicz
Gabriel Lenkiewicz, actually Gabriel Lenkiewicz-Ipohorski, Kotwicz coat of arms, (15 March 1722, Polotsk – 21 November 1798, Polotsk) was a Polish-Lithuanian Jesuit priest, and ''Temporary Vicar General'' of the Society of Jesus from 1785 until 1798, at a time when under Papal suppression in all Catholic countries, the Society continued in Russia. Early years and formation Lenkiewicz was born in Polotsk, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (today's Belarus), in a noble Polish–Lithuanian family. He joined the Jesuits after completing the 'Humanities'. He did his philosophy (1748–51) in Nieswiez and then studied mathematics, astronomy and architecture in the Academy of Vilnius (1752–54). This was followed by theology in Warsaw (1754–58) where he was ordained priest (1757). After a few years teaching mathematics in Warsaw he was sent to Polish College in Rome for further specialisation in Architecture (1762–65). Career Back in Poland he was appointed to teach science at Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings or other structures. The term comes ; ; . Architectural works, in the material form of buildings, are often perceived as cultural symbols and as works of art. Historical civilizations are often identified with their surviving architectural achievements. The practice, which began in the prehistoric era, has been used as a way of expressing culture for civilizations on all seven continents. For this reason, architecture is considered to be a form of art. Texts on architecture have been written since ancient times. The earliest surviving text on architectural theories is the 1st century AD treatise '' De architectura'' by the Roman architect Vitruvius, according to whom a good building embodies , and (durability, utility, and beauty). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slutsk
Slutsk ( officially transliterated as Sluck, be, Слуцк; russian: Слуцк; pl, Słuck, lt, Sluckas, Yiddish/Hebrew: סלוצק ''Slutsk'') is a city in Belarus, located on the Sluch River south of Minsk. As of 2022, its population is 61,802. Slutsk is the administrative center of Slutsk District. Geography The city is situated in the south-west of its Region, north of Soligorsk. History Slutsk was first mentioned in writing in 1116. It was part of the Principality of Turov and Pinsk, but in 1160 it became the capital of a separate principality. From 1320–1330 it was part of the domain of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Later it was owned by the Olelkovich and Radziwiłł families, which transformed it into a center of the Polish Reformed Church with a gymnasium and a strong fortress. Following the 17th century, the city became famous for manufacturing kontusz belts, some of the most expensive and luxurious pieces of garment of the szlachta. Because of the popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
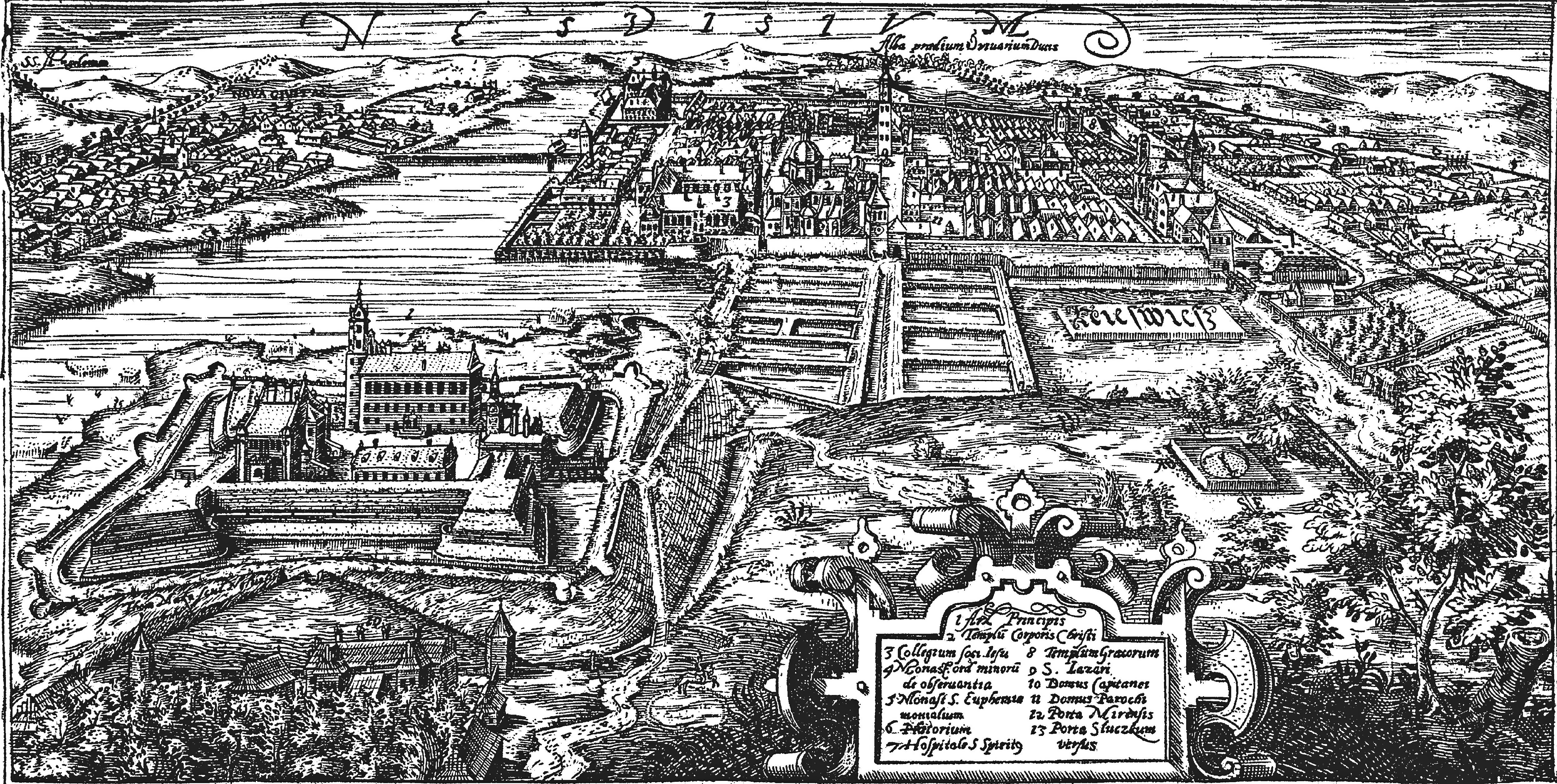
Nieswiez
Nesvizh, Niasviž ( be, Нясві́ж ; lt, Nesvyžius; pl, Nieśwież; russian: Не́свиж; yi, ניעסוויז; la, Nesvisium) is a city in Belarus. It is the administrative centre of the Nyasvizh District (''rajon'') of Minsk Region and site of Niasviž Castle, a World Heritage Site. Its 2009 population is 14,300. History Nesvizh was first documented in 1223. It was part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania until 1793, but the Grand Duchy was part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth since 1569. In the 15th century, while still a minor town, it belonged to the Kiszka family and later to the Radziwiłł family, and remained the family's seat until 1813. In 1561 or 1562 Maciej Kawęczyński founded the print works of the Polish Brethren. The first Belarusian language book printed in Latin script, a catechism by Symon Budny, was published in Nesvizh in 1562. The ''Nieśwież Bible'' ('' Biblia nieświeska''), one of the oldest Polish translations of the Bible, also by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

_(1781).png)