|
Fourier-transform Mass Spectrometry
Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry is a type of mass analyzer (or mass spectrometer) for determining the mass-to-charge ratio (''m''/''z'') of ions based on the ion cyclotron resonance, cyclotron frequency of the ions in a fixed magnetic field. The ions are trapped in a Penning trap (a magnetic field with electric trapping plates), where they are excited (at their resonant cyclotron frequencies) to a larger cyclotron radius by an oscillating electric field orthogonal to the magnetic field. After the excitation field is removed, the ions are rotating at their cyclotron frequency in phase (as a "packet" of ions). These ions induce a charge (detected as an image current) on a pair of electrodes as the packets of ions pass close to them. The resulting signal is called a free induction decay (FID), transient or interferogram that consists of a superposition of sine waves. The useful signal is extracted from this data by performing a Fourier transform to give a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) is one of the United States Department of Energy national laboratories, managed by the Department of Energy's (DOE) Office of Science. The main campus of the laboratory is in Richland, Washington. Originally named the Pacific Northwest Laboratory, PNL was established in 1965 when research and development at the Hanford Site was separated from other Hanford operations. In 1995, the laboratory was renamed the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory also known as PNNL. Facilities PNNL houses several scientific user facilities and research facilities. Scientific user facilities The Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory (EMSL) is a U.S. Department of Energy national scientific user facility. EMSL provides researchers around the world with integrated capabilities in oxide and mineral interface chemistry, high-performance computing and computational chemistry software, mass spectrometry, high-field magnetic resonance, and sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Physics Letters
''Chemical Physics Letters'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in chemical physics and physical chemistry. It was established in 1967 and is published by Elsevier. The editors-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The highest-ranking editor of a publication may also be titled editor, managing ... are David C. Clary, B. Dietzek, K-L. Han, anA. Karton External links * Chemical physics journals Publications established in 1967 Elsevier academic journals English-language journals {{chem-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal-to-noise Ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power, often expressed in decibels. A ratio higher than 1:1 (greater than 0 dB) indicates more signal than noise. SNR, bandwidth, and channel capacity of a communication channel are connected by the Shannon–Hartley theorem. Definition Signal-to-noise ratio is defined as the ratio of the power of a signal (meaningful input) to the power of background noise (meaningless or unwanted input): : \mathrm = \frac, where is average power. Both signal and noise power must be measured at the same or equivalent points in a system, and within the same system bandwidth. Depending on whether the signal is a constant () or a random variable (), the signal-to-noise ratio for random noise becomes: : \mathrm = \frac where E refers to the expected value, i.e. in this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time-of-flight
Time of flight (ToF) is the measurement of the time taken by an object, particle or wave (be it acoustic, electromagnetic, etc.) to travel a distance through a medium. This information can then be used to measure velocity or path length, or as a way to learn about the particle or medium's properties (such as composition or flow rate). The traveling object may be detected directly (direct time of flight, dToF, e.g., via an ion detector in mass spectrometry) or indirectly (indirect time of flight, iToF, e.g., by light scattered from an object in laser doppler velocimetry). Overview In electronics, one of the earliest devices using the principle are ultrasonic distance-measuring devices, which emit an ultrasonic pulse and are able to measure the distance to a solid object based on the time taken for the wave to bounce back to the emitter. The ToF method is also used to estimate the electron mobility. Originally, it was designed for measurement of low-conductive thin films, later adju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sector Instrument
A sector instrument is a general term for a class of mass spectrometer that uses a static electric (E) or magnetic (B) sector or some combination of the two (separately in space) as a mass analyzer. Popular combinations of these sectors have been the EB, BE (of so-called reverse geometry), three-sector BEB and four-sector EBEB (electric-magnetic-electric-magnetic) instruments. Most modern sector instruments are double-focusing instruments (first developed by Francis William Aston, Arthur Jeffrey Dempster, Kenneth Bainbridge and Josef Mattauch in 1936) in that they focus the ion beams both in direction and velocity. Theory The behavior of ions in a homogeneous, linear, static electric or magnetic field (separately) as is found in a sector instrument is simple. The physics are described by a single equation called the Lorentz force law. This equation is the fundamental equation of all mass spectrometric techniques and applies in non-linear, non-homogeneous cases too and is an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
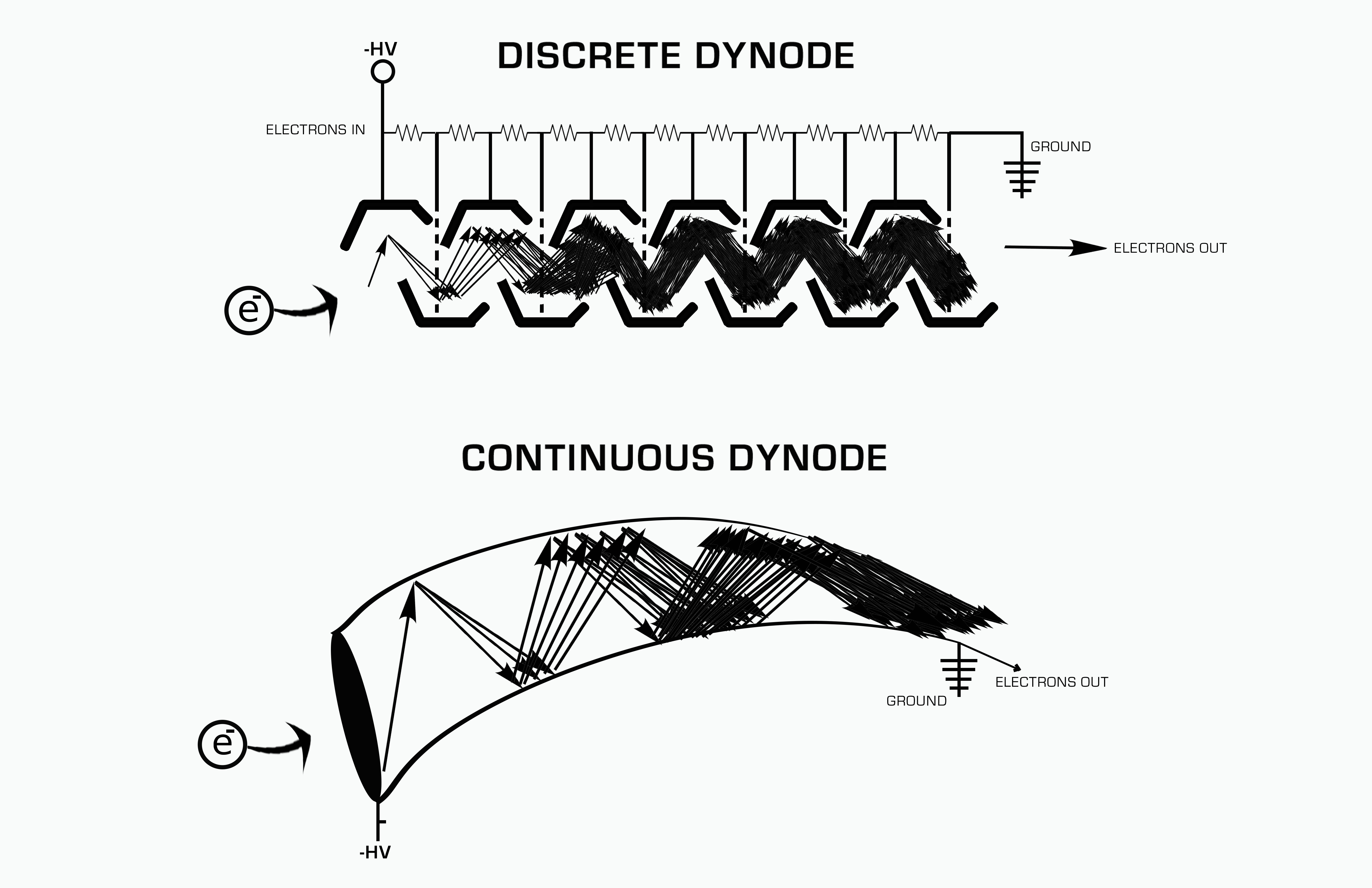
Electron Multiplier
An electron multiplier is a vacuum-tube structure that multiplies incident charges. In a process called secondary emission, a single electron can, when bombarded on secondary-emissive material, induce emission of roughly 1 to 3 electrons. If an electric potential is applied between this metal plate and yet another, the emitted electrons will accelerate to the next metal plate and induce secondary emission of still more electrons. This can be repeated a number of times, resulting in a large shower of electrons all collected by a metal anode, all having been triggered by just one. History In 1930, Russian physicist Leonid Aleksandrovitch Kubetsky proposed a device which used photocathodes combined with dynodes, or secondary electron emitters, in a single tube to remove secondary electrons by increasing the electric potential through the device. The electron multiplier can use any number of dynodes in total, which use a coefficient, σ, and created a gain of σn where n is the nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a '' mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with a beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragments) are then separated acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic Oscillator
In classical mechanics, a harmonic oscillator is a system that, when displaced from its equilibrium position, experiences a restoring force ''F'' proportional to the displacement ''x'': \vec F = -k \vec x, where ''k'' is a positive constant. If ''F'' is the only force acting on the system, the system is called a simple harmonic oscillator, and it undergoes simple harmonic motion: sinusoidal oscillations about the equilibrium point, with a constant amplitude and a constant frequency (which does not depend on the amplitude). If a frictional force ( damping) proportional to the velocity is also present, the harmonic oscillator is described as a damped oscillator. Depending on the friction coefficient, the system can: * Oscillate with a frequency lower than in the undamped case, and an amplitude decreasing with time ( underdamped oscillator). * Decay to the equilibrium position, without oscillations (overdamped oscillator). The boundary solution between an underdamped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Frequency
In physics, angular frequency "''ω''" (also referred to by the terms angular speed, circular frequency, orbital frequency, radian frequency, and pulsatance) is a scalar measure of rotation rate. It refers to the angular displacement per unit time (for example, in rotation) or the rate of change of the phase of a sinusoidal waveform (for example, in oscillations and waves), or as the rate of change of the argument of the sine function. Angular frequency (or angular speed) is the magnitude of the pseudovector quantity angular velocity.(UP1) One turn is equal to 2''π'' radians, hence \omega = \frac = , where: *''ω'' is the angular frequency (unit: radians per second), *''T'' is the period (unit: seconds), *''f'' is the ordinary frequency (unit: hertz) (sometimes ''ν''). Units In SI units, angular frequency is normally presented in radians per second, even when it does not express a rotational value. The unit hertz (Hz) is dimensionally equivalent, but by conventi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field Strength
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, and are created by electric currents such as those used in electromagnets, and by electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function assigning a vector to each point of space, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclotron
A cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator invented by Ernest O. Lawrence in 1929–1930 at the University of California, Berkeley, and patented in 1932. Lawrence, Ernest O. ''Method and apparatus for the acceleration of ions'', filed: January 26, 1932, granted: February 20, 1934 A cyclotron accelerates charged particles outwards from the center of a flat cylindrical vacuum chamber along a spiral path. The particles are held to a spiral trajectory by a static magnetic field and accelerated by a rapidly varying electric field. Lawrence was awarded the 1939 Nobel Prize in Physics for this invention. The cyclotron was the first "cyclical" accelerator. The primary accelerators before the development of the cyclotron were electrostatic accelerators, such as the Cockcroft–Walton accelerator and Van de Graaff generator. In these accelerators, particles would cross an accelerating electric field only once. Thus, the energy gained by the particles was limited by the maximum e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


