|
Fossatum Africae
''Fossatum Africae'' ("African ditch") is one or more linear defensive structures (sometimes called ''limes'') claimed to extend over or more in northern Africa constructed during the Roman Empire to defend and control the southern borders of the Empire in Africa. It is considered to be part of the greater frontier system in Roman Africa. It is considered to have many similarities of construction to Hadrian's Wall, one of the northern borders of the Empire in Britain. History The Fossa regia was the first frontier line to be built in Roman Africa, used to initially divide the Berber kingdom of Numidia from the territory of Carthage that was conquered by the Romans in the second century, but this is considered to be independent of the Fossatum Africae. There is only a single mention of the Fossatum (as such) in historical literature prior to the 20th century. This occurs in a letter written by the co-emperors Honorius and Theodosius II to Gaudentius, the ''vicarius Africae' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in the west, to Egypt's Suez Canal. Varying sources limit it to the countries of Algeria, Libya, Morocco, and Tunisia, a region that was known by the French during colonial times as "''Afrique du Nord''" and is known by Arabs as the Maghreb ("West", ''The western part of Arab World''). The United Nations definition includes Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt, Sudan, and the Western Sahara, the territory disputed between Morocco and the Sahrawi Republic. The African Union definition includes the Western Sahara and Mauritania but not Sudan. When used in the term Middle East and North Africa (MENA), it often refers only to the countries of the Maghreb. North Africa includes the Spanish cities of Ceuta and Melilla, and plazas de s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banu Hilal
The Banu Hilal ( ar, بنو هلال, translit=Banū Hilāl) was a confederation of Arabian tribes from the Hejaz and Najd regions of the Arabian Peninsula that emigrated to North Africa in the 11th century. Masters of the vast plateaux of the Najd, they enjoyed a somewhat infamous reputation, possibly owing to their relatively late (for the Arabian tribes) conversion to Islam and accounts of their campaigns in the borderlands between Iraq and Syria. When the Fatimid Caliphate became masters of Egypt and the founders of Cairo in 969, they hastened to confine the unruly Bedouin in the south before sending them to Central North Africa (Libya, Tunisia and Algeria) and then to Morocco. Origin According to Arab genealogists, the Banu Hilal were a sub-tribe of the Mudar tribal confederation, specifically of the Amir ibn Sa'sa'a, and their progenitor was Hilal. According to traditional Arab sources, their full genealogy was the following: Hilāl ibn ''ʿ''Āmir ibn Ṣaʿ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterscarp
A scarp and a counterscarp are the inner and outer sides, respectively, of a ditch or moat used in fortifications. Attackers (if they have not bridged the ditch) must descend the counterscarp and ascend the scarp. In permanent fortifications the scarp and counterscarp may be encased in stone. In less permanent fortifications, the counterscarp may be lined with paling fence set at an angle so as to give no cover to the attackers but to make advancing and retreating more difficult. If an attacker succeeds in breaching a wall a coupure can be dug on the inside of the wall to hinder the forlorn hope, in which case the side of the ditch farthest from the breached wall and closest to the centre of the fortification is also called the counterscarp. Counterscarp gallery These are tunnels or "galleries" that have been built behind the counterscarp wall inside the moat or ditch. Each gallery is pierced with loopholes for musketry, so that attacking forces that enter the moat can be dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
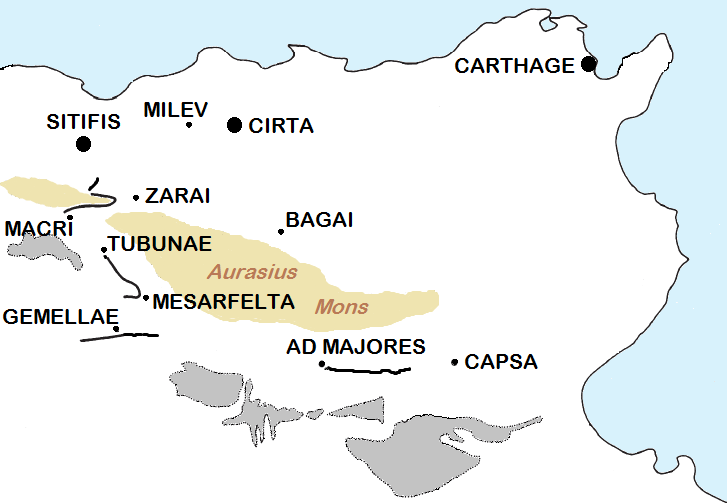
Gemellae
Gemellae was a Roman fort and associated camp on the fringe of the Sahara Desert in what is today part of Algeria. It is now an archaeological site, 25 km south and 19 km west of Biskra, and 5 km southwest of the present-day village of M'Lili with which it probably shares an original Berber name. It was connected by military Roman road to Castellum Dimmidi and Capsa. History Apparently there was a fortification at Gemellae prior to the coming of the Romans. Pliny the Elder recounts that when Lucius Cornelius Balbus celebrated his victory over the Garamantes of the Sahara in 19 BC, one of the conquests feted in the parade through Rome was that of Milgis Gemmella, described as an ''oppidum'' (usually meaning fortified settlement). The Romans seem to have then occupied the site and made it one of the southernmost outposts, marking the ''limes'' or boundary of the Roman Empire. The earliest epigraph retrieved from the site is an inscription for a statue of Emperor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurès Mountains
The Aures Mountains ( ar, جبال الأوراس) are an eastern prolongation of the Atlas Mountain System that lies to the east of the Saharan Atlas in northeastern Algeria and northwestern Tunisia, North Africa. The mountain range gives its name to the mountainous natural and historical region of the Aures. Geography The Aures mountains are the eastern continuation of the Saharan Atlas. They are located at a lower elevation than the High Atlas mountains of Morocco. The highest peak in the Aurès mountain range is Djebel Chélia in Khenchela Province, which sits at . The Belezma Range is a northwestern prolongation of the Aures Mountains located where the Tell Atlas and the Saharan Atlas come together. Its main summits are high Djebel Refaâ and high Djebel Tichaou. The Atlas chain of mountains extends over 1000 kilometers in total over Northern Africa. History Historically, the Aures served as a refuge and bulwark for the Berber tribes, forming a base of resistance again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubunae
Tobna (), also known by the ancient names of Tubunae or Thubunae, is a ruined former city in Batna Province of Algeria, located just south of the modern city of Barika. From this position, it once controlled the eastern part of the Hodna region, while M'Sila did the west. It flourished from the time of the Roman Empire through the Islamic Middle Ages, until it was sacked and destroyed by the Banu Hilal in the 11th century, after which it was finally abandoned. Poorly documented by archaeologists today, Tobna's ruins occupy an extensive area and include the remains of a Byzantine fortress as well as the traces of a wall covering a 950 m by 930 m area. History The site of Tobna is poorly studied by archaeologists as of 2019. The same is true of the surrounding Hodna region in general. Jean Baradez's aerial surveys in Algeria, published in 1949, provided the first aerial images of the site. From this data, he worked on reconstructing the Roman road network surrounding the city. Onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauretania Sitifensis
Mauretania Sitifensis was a Roman province in Northwest Africa. The capital was Setifis. History In the later division of the Roman Empire under the Emperor Diocletian, the eastern part of Mauretania Caesariensis, from Saldae to the river Ampsaga, was split into a new province, and called Mauretania Sitifensis named after the inland town of Setifis ( Setif in modern Algeria). At the time of Constantine the Great, Mauretania Sitifensis was assigned to the administrative Diocese of Africa, under the Praetorian prefecture of Italy. The new province had a huge economic development in the 4th century, until the conquest by the Vandals. In this province, the Christian denomination known as Donatism challenged the Roman Church (which was the main local religion after Constantine), while Setifis was a center of Mithraism. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, certain areas of Mauretania Sitifensis were under Vandal and later Byzantine control, but most of the province (until 578 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numidia
Numidia ( Berber: ''Inumiden''; 202–40 BC) was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians located in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up modern-day Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisia, Libya, and some parts of Morocco. The polity was originally divided between the Massylii in the east and the Masaesyli in the west. During the Second Punic War (218–201 BC), Masinissa, king of the Massylii, defeated Syphax of the Masaesyli to unify Numidia into one kingdom. The kingdom began as a sovereign state and later alternated between being a Roman province and a Roman client state. Numidia, at its largest extent, was bordered by Mauretania to the west, at the Moulouya River, Africa Proconsularis to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the north, and the Sahara to the south. It was one of the first major states in the history of Algeria and the Berbers. History Independence The Greek historians referred to these peoples as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transhumance
Transhumance is a type of pastoralism or nomadism, a seasonal movement of livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures. In montane regions (''vertical transhumance''), it implies movement between higher pastures in summer and lower valleys in winter. Herders have a permanent home, typically in valleys. Generally only the herds travel, with a certain number of people necessary to tend them, while the main population stays at the base. In contrast, ''horizontal transhumance'' is more susceptible to being disrupted by climatic, economic, or political change. Traditional or fixed transhumance has occurred throughout the inhabited world, particularly Europe and western Asia. It is often important to pastoralist societies, as the dairy products of transhumance flocks and herds (milk, butter, yogurt and cheese) may form much of the diet of such populations. In many languages there are words for the higher summer pastures, and frequently these words have been used as place names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zaraï
Zaraï was a Berber, Carthaginian, and Roman town at the site of present-day Aïn Oulmene, Algeria. Under the Romans, it formed part of the province of Numidia. Name The Punic name for the town was (). Zarai is mentioned in the ''Antonine Itinerary'' and in the ''Tabula Peutingeriana''. Ptolemy calls it Zaratha and wrongly places it in Mauretania Caesariensis. It is probably the Apuleius's Zaratha. These two forms and the term "Zaraitani" found in an inscription seem to indicate that the name Zaraï which appears on another inscriptionCorp. Inscript. 2532. must have lost a final letter. Geography The ruins of Zaraï are called "Henshir Zraïa" and are found inside the municipality of Ain Oulmene. They lie to the south-east of Setif in Algeria, crowning an eminence which overlooks all the country on the left bank of the Oued Taourlatent, known to the medieval Arabs as Oued Zaraoua. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rommel
Johannes Erwin Eugen Rommel () (15 November 1891 – 14 October 1944) was a German field marshal during World War II. Popularly known as the Desert Fox (, ), he served in the ''Wehrmacht'' (armed forces) of Nazi Germany, as well as serving in the ''Reichswehr'' of the Weimar Republic, and the army of German Empire, Imperial Germany. Rommel was a highly decorated officer in World War I and was awarded the ''Pour le Mérite'' for his actions on the Italian Front (World War I), Italian Front. In 1937, he published his classic book on military tactics, ''Infantry Attacks'', drawing on his experiences in that war. In World War II, he commanded the 7th Panzer Division (Wehrmacht), 7th Panzer Division during the Battle of France, 1940 invasion of France. His leadership of German and Italian forces in the North African campaign established his reputation as one of the ablest tank commanders of the war, and earned him the nickname ''der Wüstenfuchs'', "the Desert Fox". Among hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |