|
Fort Knokke
Fort Knokke or Fort de Cnocke or Fort de la Knocque or Fort de Knocke was an important fortification that defended western Flanders from the 1580s until it was demolished in the 1780s. During its 200 year history, the place was held by the Spanish Empire, Kingdom of France, Habsburg Austria and the Dutch Republic. The existing defenses were improved in 1678 by the famous military engineer Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban. The fort was attacked by the Grand Alliance in 1695 during the Nine Years' War but the French garrison successfully held out. It was captured from the French by a ruse in 1712 during the War of the Spanish Succession. Control of the fort and other strong places in the Austrian Netherlands was a key feature of the so-called Barrier Treaty in 1713. The French captured the fort after a two-month siege in 1744 during the War of the Austrian Succession. Emperor Joseph II had the citadel demolished in 1781. The site is on the Yser River about southwest of Diksmuide, Bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lo-Reninge
Lo-Reninge (; vls, Lo-Rênienge) is a city and municipality located in the Belgian province of West Flanders. The municipality comprises the towns of Lo, Noordschote, Pollinkhove and Reninge. On January 1, 2006, Lo-Reninge had a total population of 3,306. The total area is 62.94 km² which gives a population density of 53 inhabitants per km². The Old Town Hall of Lo, built between 1565-1566, and its belfry were inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1999 as part of the Belfries of Belgium and France site. It is the birthplace of Flemish painter Jacques-Albert Senave. Image-City wall - Lo.jpg, The 13th century city wall of Lo, with the Caesar's Tree behind it. Windmolen Margrietmolen, Lo-Reninge (DSCF9531).jpg, The Margriet windmill Sint-Pieterskerk, Lo (DSCF9550).jpg, Sint-Pieter's church in Lo References External links *Official website- Information available in Dutch and limited information available in French, English and German German(s) may refer to: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
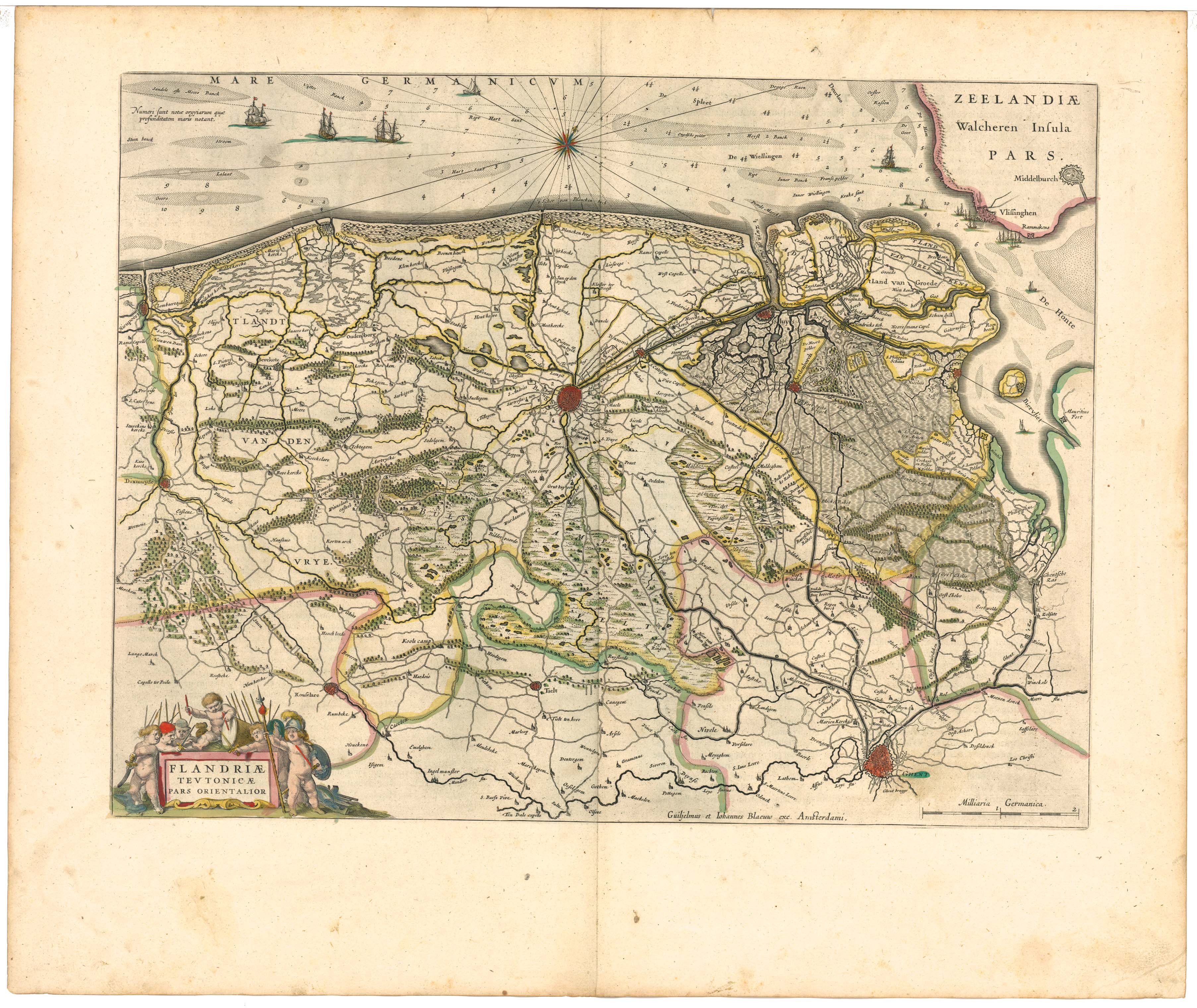
Yser
The Yser ( , ; nl, IJzer ) is a river that rises in French Flanders (the north of France), enters the Belgian province of West Flanders and flows through the '' Ganzepoot'' and into the North Sea at the town of Nieuwpoort. The source of the Yser is in Buysscheure (''Buisscheure''), in the Nord department of northern France. It flows through Bollezeele (''Bollezele''), Esquelbecq (''Ekelsbeke''), and Bambecque (''Bambeke''). After approximately of its course, it leaves France and enters Belgium. It then flows through Diksmuide and out into the North Sea at Nieuwpoort. During the Battle of the Yser in the First World War, by opening the sluices, part of the polder west of the Yser was flooded with seawater between Nieuwpoort and Diksmuide to provide an obstacle to the advancing German Army and keep westernmost Belgium safe from German occupation. The Yser river itself never overflowed its banks.Leper, J., Kunstmatige inundaties in Maritiem Vlaanderen 1316-1945, Michiels, Tong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Aix-la-Chapelle (1668)
__NOTOC__ The Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle or Aachen ended the War of Devolution between France and Spain. It was signed on 2 May 1668 in Aachen (french: Aix-la-Chapelle). Spain acceded on 7 May 1669. The treaty was mediated and guaranteed by the Triple Alliance of the Dutch Republic, England and Sweden at the First Congress of Aix-la-Chapelle. By the terms of the treaty, Louis XIV returned three cities, Cambrai (Kamerijk), Aire (Ariën aan de Leie), and Saint-Omer (Sint-Omaars) to Spain.Phillipson (1916), p. 222. He also returned the province of Franche-Comté. On the other hand, he kept Armentières (Armentiers), Bergues (Sint-Winoksbergen), Charleroi, Courtrai (Kortrijk), Douai (Dowaai), Furnes (Veurne), Lille (Rijsel), Oudenarde (Oudenaarde, Audenarde), and Tournai (Doornik). Lille, Armentières, Bergues and Douai were considered essential to reinforce France's vulnerable northern border and remain French to this day, while the retention of Tournai, Oudenarde, Courtrai, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veurne-Ambacht
Veurne-Ambacht was a viscounty ( ''kasselrij'', ''burggraafschap'') in the County of Flanders. Agriculture contributed mostly to the prosperous area. In the viscountship's capital city Veurne, the ''Landhuis''In the city of Veurne's center, the name ''Landhuis'' (literally: 'country-house') was given assumedly because it served the countryside – as opposed to the adjacent ''Stadhuis'' (literally: 'city-house' though always meaning the City Hall) that served the city. was the seat of the viscountcy. Nowadays Veurne-Ambacht is the name of the northwestern corner of the Belgian province of West Flanders ) , settlement_type = Province of Belgium , image_flag = Flag of West Flanders.svg , flag_size = , image_shield = Wapen van West-Vlaanderen.svg , shield_size = , image_map .... References External links ''Welcome in Veurne'' Website of Veurne City Geography of West Flanders County of Flanders R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castellany
A castellan is the title used in Medieval Europe for an appointed official, a governor of a castle and its surrounding territory referred to as the castellany. The title of ''governor'' is retained in the English prison system, as a remnant of the medieval idea of the castellan as head of the local prison. The word stems from the Latin ''Castellanus'', derived from ''castellum'' "castle". Sometimes also known as a ''constable'' of the castle district, the Constable of the Tower of London is, in fact, a form of castellan, with representative powers in the local or national assembly. A castellan was almost always male, but could occasionally be female, as when, in 1194, Beatrice of Bourbourg inherited her father's castellany of Bourbourg upon the death of her brother, Roger. Similarly, Agnes became the castellan of Harlech Castle upon the death of her husband John de Bonvillars in 1287. Initial functions After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, foreign tribes migrated into w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Ostend
The siege of Ostend was a three-year siege of the city of Ostend during the Eighty Years' War and the Anglo–Spanish War. A Spanish force under Archduke Albrecht besieged the fortress being held initially by a Dutch force which was reinforced by English troops under Francis Vere, who became the town's governor. It was said "the Spanish assailed the unassailable; the Dutch defended the indefensible."Belleroche p 14 The commitment of both sides in the dispute over the only Dutch-ruled area in the province of Flanders, made the campaign continue for more than any other during the war. This resulted in one of the longest and bloodiest sieges in world history: more than 100,000 people were killed, wounded, or succumbed to disease during the siege. Ostend was resupplied via the sea and as a result held out for three years.van Nimwegen pp 171–73 A garrison did a tour of duty before being replaced by fresh troops, normally 3,000 at a time keeping casualties and disease to a minim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostend
Ostend ( nl, Oostende, ; french: link=no, Ostende ; german: link=no, Ostende ; vls, Ostende) is a coastal city and municipality, located in the province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It comprises the boroughs of Mariakerke, Raversijde, Stene and Zandvoorde, and the city of Ostend proper – the largest on the Belgian coast. History Origin to Middle Ages In the Early Middle Ages, Ostend was a small village built on the east-end () of an island (originally called Testerep) between the North Sea and a beach lake. Although small, the village rose to the status of "town" around 1265, when the inhabitants were allowed to hold a market and to build a market hall. The major source of income for the inhabitants was fishing. The North Sea coastline has always been rather unstable due to the power of the water. In 1395 the inhabitants decided to build a new Ostend behind large dikes and further away from the always-threatening sea. 15th to 18th century The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veurne
Veurne (; french: Furnes, italic=no, ) is a city and municipality in the Belgian province of West Flanders. The municipality comprises the town of Veurne proper and the settlements of , , , , , Houtem, , , Wulveringem, and . History Origins up to the 15th century Veurne, in Latin ''Furna'', is first found in 877 as a possession of the Saint Bertin Abbey in Saint-Omer. Around 890 AD, it was noted as a successful fortification against the Viking raids. It soon was placed at the head of the castellany of Veurne, a large territory counting 42 parishes and some 8 half-independent parishes, owing allegiance to the Count of Flanders. Veurne became a city in the 12th century. During the following century, trade with England flourished. In 1270, however, the relations with England came to a standstill and the city's economy went into a long decline; hence the nickname of the Veurne Sleepers. On August 20, 1297, the Battle of Veurne was fought in the ongoing struggle between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Farnese, Duke Of Parma
Alexander Farnese ( it, Alessandro Farnese, es, Alejandro Farnesio; 27 August 1545 – 3 December 1592) was an Italian noble and condottiero and later a general of the Spanish army, who was Duke of Parma, Piacenza and Castro from 1586 to 1592, as well as Governor of the Spanish Netherlands from 1578 to 1592. Thanks to a steady influx of troops from Spain, during 1581–1587 Farnese captured more than thirty towns in the south (now Belgium) and returned them to the control of Catholic Spain. During the French Wars of Religion he relieved Paris for the Catholics. His talents as a field commander, strategist and organizer earned him the regard of his contemporaries and military historians as the first captain of his age. Early life: 1545-1577 Alessandro, born August 27, 1545, was the son of Duke Ottavio Farnese of Parma (a grandchild of Pope Paul III) and Margaret, the illegitimate daughter of the King of Spain and Habsburg Emperor Charles V. He had a twin brother, Carlo, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Reformation, centralisation, taxation, and the rights and privileges of the nobility and cities. After the initial stages, Philip II of Spain, the sovereign of the Netherlands, deployed his armies and regained control over most of the rebel-held territories. However, widespread mutinies in the Spanish army caused a general uprising. Under the leadership of the exiled William the Silent, the Catholic- and Protestant-dominated provinces sought to establish religious peace while jointly opposing the king's regime with the Pacification of Ghent, but the general rebellion failed to sustain itself. Despite Governor of Spanish Netherlands and General for Spain, the Duke of Parma's steady military and diplomatic successes, the Union of Utrecht ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BATTLE OF THE YSER
The Battle of the Yser (french: Bataille de l'Yser, nl, Slag om de IJzer) was a battle of the First World War that took place in October 1914 between the towns of Nieuwpoort and Diksmuide, along a stretch of the Yser River and the Yperlee Canal, in Belgium. The front line was held by a large Belgian force, which halted the German advance in a costly defensive battle. The victory at the Yser allowed Belgium to retain a small strip of territory, with Germany in control of 95 per cent of Belgian territory, which made King Albert a Belgian national hero, sustained national pride and provided a venue for commemorations of heroic sacrifice for the next hundred years. Background German invasion of Belgium On 2 August 1914, the Belgian government refused passage through Belgium to German troops and on the night of the Belgian General Staff ordered the Third Division to Liège to obstruct a German advance. The German army invaded Belgium on the morning of 4 August. Covered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)




.jpg)
