|
Fort Drum (El Fraile Island)
Fort Drum, also known as El Fraile Island (), is a heavily fortified island situated at the mouth of Manila Bay in the Philippines, south of Corregidor Island. Nicknamed a "concrete battleship", the reinforced concrete sea fort, shaped like a battleship, was built by the United States in 1909 as one of the harbor defenses at the wider South Channel entrance to the Bay during the American colonial period. It was unique among forts built by the United States between the American Civil War and early World War II, as it was a sea fort with turrets. It was captured and occupied by the Japanese during World War II, and was recaptured after U.S. forces ignited petroleum and gasoline in the fort, the conflagration killing 68 Japanese soldiers and leaving it permanently out of commission. Due to the high temperature caused by the conflagration, it took five days before U.S. soldiers could enter the fortress. The fort, now abandoned, was named after Brigadier General Richard C. Drum, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harbor Defenses Of Manila And Subic Bays
The Harbor Defenses of Manila and Subic Bays ("Coast Defenses of Manila and Subic Bays" until 1925) (a.k.a. CD/HD Manila Bay) were a United States Army Coast Artillery Corps harbor defense command, part of the Philippine Department of the United States Army from circa 1910 through early World War II. The command primarily consisted of four forts on islands at the entrance to Manila Bay and one fort on an island in Subic Bay.McGovern and Berhow 2003, pp. 7-12 Background and construction The United States acquired the Philippines as a territory as a result of the Spanish–American War in 1898. The Taft Board of 1905 recommended extensive, then-modern fortifications at the entrance to Manila Bay. The islands there had been declared military reservations on 11 April 1902. Accordingly, El Fraile, Carabao, Corregidor, Grande, and Caballo Islands in the Philippines were to be fortified and incorporated into the harbor defenses of Manila and Subic Bays, protecting the bases of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil or simply oil, is a naturally occurring, yellowish-black liquid chemical mixture found in geological formations, consisting mainly of hydrocarbons. The term ''petroleum'' refers both to naturally occurring unprocessed crude oil, as well as to petroleum products that consist of refining, refined crude oil. Petroleum is a fossil fuel formed over millions of years from anaerobic decay of organic materials from buried prehistoric life, prehistoric organisms, particularly planktons and algae, and 70% of the world's oil deposits were formed during the Mesozoic. Conventional reserves of petroleum are primarily recovered by oil drilling, drilling, which is done after a study of the relevant structural geology, sedimentary basin analysis, analysis of the sedimentary basin, and reservoir characterization, characterization of the petroleum reservoir. There are also unconventional (oil & gas) reservoir, unconventional reserves such as oil sands and oil sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Of Fortifications
Several boards have been appointed by US presidents or Congress to evaluate the US defensive fortifications, primarily coastal defenses near strategically important harbors on the US shores, its territories, and its protectorates. Endicott Board In 1885, US President Grover Cleveland appointed a joint Army, Navy and civilian board, headed by Secretary of War William Crowninshield Endicott, known as the Board of Fortifications (now usually referred to simply as the Endicott Board). The findings of the Board in its 1886 report illustrated a grim picture of neglect of America's coast defenses and recommended a massive $127 million construction program for a series of new forts with breech-loading cannons, mortars, floating batteries, and submarine mines for some 29 locations on the US coast. Coast Artillery fortifications built between 1885 and 1905 are often referred to as Endicott Period fortifications. The first board consisted of the following officers and civilians: * Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Drum Before
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ("strong") and ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley Civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large cyclopean stone walls fitted without mortar had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae. A Greek '' phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the Roman castellum or fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Though smaller than a real fortress, they acted as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
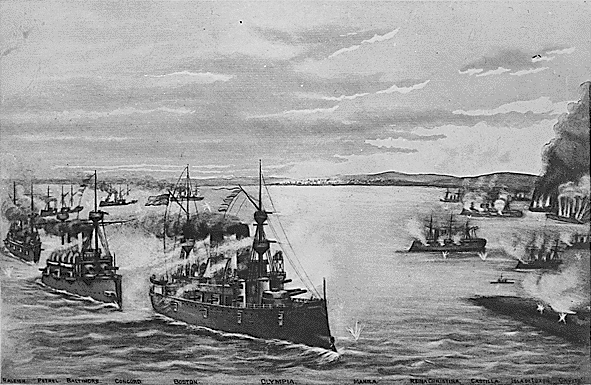
Battle Of Manila Bay
The Battle of Manila Bay (; ), also known as the Battle of Cavite, took place on May 1, 1898, during the Spanish–American War. The American Asiatic Squadron under Commodore George Dewey engaged and destroyed the Spanish Pacific Squadron under ''Contraalmirante'' (Rear admiral) Patricio Montojo. The battle took place in Manila Bay in the Philippines, and was the first major engagement of the Spanish–American War. The battle was one of the most decisive naval battles in history and marked the end of the Spanish colonial period in Philippine history. Tensions between Spain and the United States worsened over the Spanish conduct during their efforts to quell the Cuban War of Independence, with many Americans being agitated by largely falsified reports of Spanish atrocities against the Cuban population. In January 1898, fearing the fate of American interests in Cuba due to the war, the cruiser was dispatched to protect them. Less than a month later, the cruiser explo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunboat
A gunboat is a naval watercraft designed for the express purpose of carrying one or more guns to bombard coastal targets, as opposed to those military craft designed for naval warfare, or for ferrying troops or supplies. History Pre-steam era In the age of sail, a gunboat was usually a small undecked vessel carrying a single smoothbore cannon in the bow, or just two or three such cannons. A gunboat could carry one or two masts or be oar-powered only, but the single-masted version of about length was most typical. Some types of gunboats carried two cannon, or else mounted a number of swivel guns on the railings. The small gunboat had advantages: if it only carried a single cannon, the boat could manoeuvre in shallow or restricted areas – such as rivers or lakes – where larger ships could sail only with difficulty. The gun that such boats carried could be quite heavy; a 32-pounder for instance. As such boats were cheap and quick to build, naval forces favoured swarm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QF 4
QF may stand for: Businesses and organisations * Qantas, an Australian airline (IATA:QF) * Qatar Foundation The Qatar Foundation for Education, Science and Community Development () is a state-led non-profit organization in Qatar, founded in 1995 by then-List of emirs of Qatar, emir Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani and his second wife Moza bint Nasser Al-Miss ..., a non-profit * Quiverfull, a Christian movement Military * Quds Force, an Iranian expeditionary unit * Quick-firing gun, an artillery piece * A gun breech that uses metallic cartridges; see British ordnance terms#QF * Q-Fire, a decoy fire site used in World War II Other uses * Quality factor, in physics and engineering, a measure of the "quality" of a resonant system {{disambig fr:QF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Cruiser Don Antonio De Ulloa
''Don Antonio de Ulloa'' was a unprotected cruiser of the Spanish Navy that fought in the Battle of Manila Bay during the Spanish–American War. She was built at La Carraca shipyard, Cadiz, Spain. Her keel was laid in 1883 and the vessel was Ship naming and launching, launched on 23 January 1887. ''Don Antonio de Ulloa'' took an active part in Spanish military action against Philippine insurgents during the "Tagalog Revolt" (1896–1897), the Spanish name for the first two years of the Philippine Revolution. During her overhaul in Manila bay whilst part of the squadron of Rear Admiral Patricio Montojo y Pasarón, the Battle of Manila Bay occurred. With her reduced complement, armament, and inability to maneuver she was sunk with little resistance. Technical characteristics ''Don Antonio de Ulloa'' was built at La Carraca shipyard, Cadiz, Spain. Her keel was laid in 1883 and the vessel was Ship naming and launching, launched on 23 January 1887. The ship was completed in 1889. She ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruiser
A cruiser is a type of warship. Modern cruisers are generally the largest ships in a fleet after aircraft carriers and amphibious assault ships, and can usually perform several operational roles from search-and-destroy to ocean escort to sea denial. The term "cruiser", which has been in use for several hundred years, has changed its meaning over time. During the Age of Sail, the term ''cruising'' referred to certain kinds of missions—independent scouting, commerce protection, or raiding—usually fulfilled by frigates or sloop-of-war, sloops-of-war, which functioned as the ''cruising warships'' of a fleet. In the middle of the 19th century, ''cruiser'' came to be a classification of the ships intended for cruising distant waters, for commerce raiding, and for scouting for the battle fleet. Cruisers came in a wide variety of sizes, from the medium-sized protected cruiser to large armored cruisers that were nearly as big (although not as powerful or as well-armored) as a pre- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Navy
The Spanish Navy, officially the Armada, is the Navy, maritime branch of the Spanish Armed Forces and one of the oldest active naval forces in the world. The Spanish Navy was responsible for a number of major historic achievements in navigation, the most famous being the voyages of Christopher Columbus, discovery of North America and the Magellan's circumnavigation, first global circumnavigation. For several centuries, it played a crucial logistical role in the expansion and consolidation of the Spanish Empire, and defended a vast trade network across the Atlantic Ocean between the Spanish treasure fleet, Americas and Europe, and the Manila Galleon across the Pacific Ocean between the Spanish East Indies, Philippines and the Americas. The Spanish Navy was one of the most powerful maritime forces in the world from the late 15th century to mid-18th century. In the early 19th century, with the Spanish American wars of independence, loss of most of its empire, the Spanish navy trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonzalez Hontoria De 12 Cm Mod 1883
The Gonzalez Hontoria de 12 cm mod 1883 was a Spanish naval gun developed in the late 1800s that armed a variety of warships of the Spanish Navy during the Spanish–American War. History The Hontoria guns were designed by José González Hontoria a Spanish inventor, field marshal of marine infantry and brigadier of the navy. During the 1800s Spain lagged behind other European powers in industrialization and Spain imported weapons from Krupp, Armstrong Whitworth and Schneider et Cie. During the 1860s and 1870s, Hontoria studied explosives, metallurgy, and industrial production with the aim of developing an indigenous arms industry. Construction In 1879 Hontoria designed a series of naval guns ranging from to which would lay the foundation for his later guns. The 1879 series like Ordóñez guns of the same period were breech loading, black powder, built up guns, with steel A tube and cast iron reinforcing hoops. The 1883 series was a step forward in that they were bre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Dewey
George Dewey (December 26, 1837January 16, 1917) was Admiral of the Navy, the only person in United States history to have attained that rank. He is best known for his victory at the Battle of Manila Bay during the Spanish–American War, with the loss of only a single crewman on the American side. Dewey was born in Montpelier, Vermont. At age 15, Dewey's father enrolled him at Norwich University in Northfield, Vermont. Two years later Norwich expelled him for drunkenness and herding sheep into the barracks. Summarily, he entered the United States Naval Academy in 1854. He graduated from the academy in 1858 and was assigned as the executive lieutenant of at the beginning of the American Civil War, Civil War. He participated in the capture of New Orleans and the Siege of Port Hudson, helping the Union (American Civil War), Union take control of the Mississippi River. By the end of the war, Dewey reached the rank of Lieutenant commander (United States), lieutenant commander. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |