|
Forms Processing
Forms processing is a process by which one can capture information entered into data fields and convert it into an electronic format. This can be done manually or automatically, but the general process is that hard copy data is filled out by humans and then "captured" from their respective fields and entered into a database or other electronic format. Overview In the broadest sense, forms processing systems can range from the processing of small application forms to large scale survey forms with multiple pages. There are several common issues involved in forms processing when done manually. These are a lot of tedious human efforts put in, the data keyed in by the user may result in typos, and many hours of labor result from this lengthy process. If the forms are processed using computer software driven applications these common issues can be resolved and minimized to great extent. Most methods for forms processing address the following areas. Manual data entry This method of data p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Copy
''Hard Copy'' is an American tabloid television show that ran in syndication from 1989 to 1999. ''Hard Copy'' was aggressive in its use of questionable material on television, including gratuitous violence. The original hosts of ''Hard Copy'' were Alan Frio and Terry Murphy. Frio left the series after the 1990–91 season and was succeeded by Barry Nolan in the fall of 1991. Nolan and Murphy would stay until after the 1997–98 season, when they both departed. In the show's final season, Kyle Kraska took over as the sole host. ''Hard Copy'' was produced and distributed by Paramount Domestic Television and, for much of its time on air, was often aired with its sister show, the Hollywood news program '' Entertainment Tonight'' as part of an hour-long programming block sold to local stations. Overview ''Hard Copy'' was a tabloid show that aired footage and news about celebrities and everyday people. Also featured were interviews with various newsmakers. 1992 Elton John lawsui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleaved 2 Of 5
Interleaved 2 of 5 (ITF) is a continuous two-width barcode symbology encoding digits. It is used commercially on 135 film, for ITF-14 barcodes, and on cartons of some products, while the products inside are labeled with UPC or EAN. ITF encodes pairs of digits; the first digit is encoded in the five bars (or black lines), while the second digit is encoded in the five spaces (or white lines) interleaved with them. Two out of every five bars or spaces are wide (hence exactly 2 of 5). The digits are encoded to symbols as follows: where "n" is a narrow line (bar or space) and "W" a wide line (2.0 to 3.0 times the width of a narrow line). The wide lines form a two-out-of-five code with consecutive values of 1, 2, 4, 7, and 0, where the code 0 has a value of 11. This is similar to the POSTNET bar code. Before the actual pairs there is a start code consisting of nnnn (narrow bar - narrow space - narrow bar - narrow space), and after all symbols there is the stop code consisting of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quotation Mark
Quotation marks (also known as quotes, quote marks, speech marks, inverted commas, or talking marks) are punctuation marks used in pairs in various writing systems to set off direct speech, a quotation, or a phrase. The pair consists of an opening quotation mark and a closing quotation mark, which may or may not be the same character. Quotation marks have a variety of forms in different languages and in different media. History The single quotation mark is traced to Ancient Greek practice, adopted and adapted by monastic copyists. Isidore of Seville, in his seventh century encyclopedia, , described their use of the Greek ''diplé'' (a chevron): 3⟩ Diplé. Our copyists place this sign in the books of the people of the Church, to separate or to indicate the quotations drawn from the Holy Scriptures. The double quotation mark derives from a marginal notation used in fifteenth-century manuscript annotations to indicate a passage of particular importance (not necessar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed Case
Capitalization (American English) or capitalisation (British English) is writing a word with its first letter as a capital letter (uppercase letter) and the remaining letters in lower case, in writing systems with a case distinction. The term also may refer to the choice of the casing applied to text. Conventional writing systems (orthographies) for different languages have different conventions for capitalization, for example, the capitalization of titles. Conventions also vary, to a lesser extent, between different style guides. In addition to the Latin script, capitalization also affects the Armenian, Cyrillic, Georgian and Greek alphabets. The full rules of capitalization in English are complicated. The rules have also changed over time, generally to capitalize fewer words. The conventions used in an 18th-century document will be unfamiliar to a modern reader; for instance, many common nouns were capitalized. The systematic use of capitalized and uncapitalized words in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European English (other)
The English language in Europe, as a native language, is mainly spoken in the United Kingdom and Ireland. Outside of these states, it has official status in Malta, the Crown Dependencies (the Isle of Man, Jersey and Guernsey), Gibraltar and the Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia (two of the British Overseas Territories). In the Kingdom of the Netherlands, English has an official status as a regional language on the isles of Saba and Sint Eustatius (located in the Caribbean). In other parts of Europe, English is spoken mainly by those who have learnt it as a second language, but also, to a lesser extent, natively by some expatriates from some countries in the English-speaking world. The English language is the de facto official language of England, the sole official language of Gibraltar and of Akrotiri and Dhekelia, and one of the official languages of the Republic of Ireland, Malta, Northern Ireland, Scotland, Wales, the Isle of Man, Jersey, Guernsey and the Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Currency Sign
A currency symbol or currency sign is a graphic symbol used to denote a currency unit. Usually it is defined by the monetary authority, like the national central bank for the currency concerned. In formatting, the symbol can use various formattings: before, between or after the numeric amounts: , and , for example; this positioning is determined by national convention. The symbol is not defined or listed by ISO 4217: that only assigns three-letter codes to currencies (like for Azerbaijani manat) and special cases like gold and silver ( and respectively) that are used as financial instruments. Usage When writing currency amounts, the location of the symbol varies by language. Many currencies in English-speaking countries and Latin America (except Haiti) place it before the amount (e.g., R$50,00). The Cape Verdean escudo (like the Portuguese escudo, to which it was formerly pegged) places its symbol in the decimal separator position (e.g. 20$00). Banco de Cabo Verde.Moedas." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Ink Character Recognition
Magnetic ink character recognition code, known in short as MICR code, is a character recognition technology used mainly by the banking industry to streamline the processing and clearance of cheques and other documents. MICR encoding, called the ''MICR line'', is at the bottom of cheques and other vouchers and typically includes the document-type indicator, bank code, bank account number, cheque number, cheque amount (usually added after a cheque is presented for payment) and a control indicator. The format for the bank code and bank account number is country-specific. The technology allows MICR readers to scan and read the information directly into a data-collection device. Unlike barcode and similar technologies, MICR characters can be read easily by humans. MICR encoded documents can be processed much faster and more accurately than conventional OCR encoded documents. Pre-Unicode standard representation The ISO standard ISO 2033:1983, and the corresponding Japanese Industrial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barcode
A barcode or bar code is a method of representing data in a visual, machine-readable form. Initially, barcodes represented data by varying the widths, spacings and sizes of parallel lines. These barcodes, now commonly referred to as linear or one-dimensional (1D), can be scanned by special optical scanners, called barcode readers, of which there are several types. Later, two-dimensional (2D) variants were developed, using rectangles, dots, hexagons and other patterns, called ''matrix codes'' or ''2D barcodes'', although they do not use bars as such. 2D barcodes can be read using purpose-built 2D optical scanners, which exist in a few different forms. 2D barcodes can also be read by a digital camera connected to a microcomputer running software that takes a photographic image of the barcode and analyzes the image to deconstruct and decode the 2D barcode. A mobile device with an inbuilt camera, such as smartphone, can function as the latter type of 2D barcode reader using special ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligent Character Recognition
In computer science, intelligent character recognition (ICR) is an advanced optical character recognition (OCR) or — rather more specific — handwriting recognition system that allows fonts and different styles of handwriting to be learned by a computer during processing to improve accuracy and recognition levels. Capabilities Most ICR software has a self-learning system referred to as a neural network, which automatically updates the recognition database for new handwriting patterns. It extends the usefulness of scanning devices for the purpose of document processing, from printed character recognition (a function of OCR) to hand-written matter recognition. Because this process is involved in recognising hand writing, accuracy levels may, in some circumstances, not be very good but can achieve 97%+ accuracy rates in reading handwriting in structured forms. Often to achieve these high recognition rates several read engines are used within the software and each is given electiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
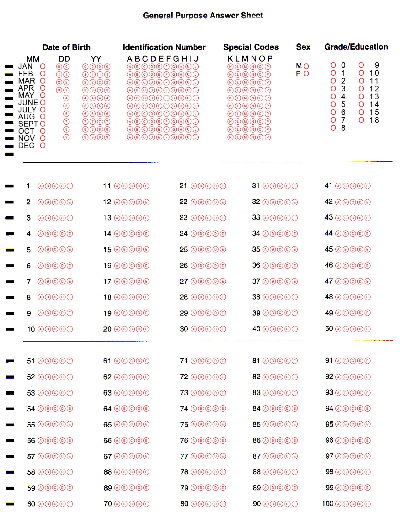
Optical Mark Recognition
Optical mark recognition (also called optical mark reading and OMR) is the process of reading information that people mark on surveys, tests and other paper documents. OMR is used to read questionnaires, multiple choice examination papers in the form of shaded areas. OMR background Many OMR devices have a scanner that shines a light onto a form. The device then looks at the contrasting reflectivity of the light at certain positions on the form. It will detect the black marks because they reflect less light than the blank areas on the form. Some OMR devices use forms that are printed on transoptic paper. The device can then measure the amount of light that passes through the paper. It will pick up any black marks on either side of the paper because they reduce the amount of light passing through. In contrast to the dedicated OMR device, desktop OMR software allows a user to create their own forms in a word processor or computer and print them on a laser laser printer. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Character Recognition
Optical character recognition or optical character reader (OCR) is the electronic or mechanical conversion of images of typed, handwritten or printed text into machine-encoded text, whether from a scanned document, a photo of a document, a scene-photo (for example the text on signs and billboards in a landscape photo) or from subtitle text superimposed on an image (for example: from a television broadcast). Widely used as a form of data entry from printed paper data records – whether passport documents, invoices, bank statements, computerized receipts, business cards, mail, printouts of static-data, or any suitable documentation – it is a common method of digitizing printed texts so that they can be electronically edited, searched, stored more compactly, displayed on-line, and used in machine processes such as cognitive computing, machine translation, (extracted) text-to-speech, key data and text mining. OCR is a field of research in pattern recognition, artificial intellig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)