|
Forced Labour Of Germans After World War II
In the years following World War II, large numbers of German civilians and captured soldiers were forced into labor by the Allied forces. The topic of using Germans as forced labor for reparations was first broached at the Tehran conference in 1943, where Soviet premier Joseph Stalin demanded 4,000,000 German workers. Forced labor was also included in the final protocol of the Yalta conference in January 1945, where it was assented to by UK Prime Minister Winston Churchill and US President Franklin D. Roosevelt. Eastern Europe Soviet Union The largest group of forced laborers in the Soviet Union consisted of several million German prisoners of war. Most German POW survivors of the forced labor camps in the Soviet Union were released in 1953. Estimates of German POW casualties (in both East and West and cumulative for both the war and peacetime period) range from 600,000 to 1,000,000. According to the section of the German Red Cross dealing with tracing the captives, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Eastern Territories Of Germany
The former eastern territories of Germany (german: Ehemalige deutsche Ostgebiete) refer in present-day Germany to those territories east of the current eastern border of Germany i.e. Oder–Neisse line which historically had been considered German and which were annexed by Poland and Soviet Union after World War II, these territories were also the lands where Germans used to be only or main ethnicity. So in contrast to the lands awarded to the restored Polish state by the Treaty of Versailles after World War I, the German territories lost with the Potsdam Agreement after World War II on 1 August 1945 were either almost exclusively inhabited by Germans before 1945 (bulk of East Prussia, bulk of Lower Silesia, Farther Pomerania, and parts of Western Pomerania, Lusatia, and Neumark awarded to Poland), mixed German-Polish with a German majority ( Danzig, Posen-West Prussia Border March, Lauenburg and Bütow Land, the southern and western rim of East Prussia, Ermland, West Upper S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life (magazine)
''Life'' was an American magazine published weekly from 1883 to 1972, as an intermittent "special" until 1978, and as a monthly from 1978 until 2000. During its golden age from 1936 to 1972, ''Life'' was a wide-ranging weekly general-interest magazine known for the quality of its photography, and was one of the most popular magazines in the nation, regularly reaching one-quarter of the population. ''Life'' was independently published for its first 53 years until 1936 as a general-interest and light entertainment magazine, heavy on illustrations, jokes, and social commentary. It featured some of the most notable writers, editors, illustrators and cartoonists of its time: Charles Dana Gibson, Norman Rockwell and Jacob Hartman Jr. Gibson became the editor and owner of the magazine after John Ames Mitchell died in 1918. During its later years, the magazine offered brief capsule reviews (similar to those in ''The New Yorker'') of plays and movies currently running in New York City, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Atomic Bomb Project
The Soviet atomic bomb project was the classified research and development program that was authorized by Joseph Stalin in the Soviet Union to develop nuclear weapons during and after World War II. Although the Soviet scientific community discussed the possibility of an atomic bomb throughout the 1930s, going as far as making a concrete proposal to develop such a weapon in 1940, the full-scale program was not initiated and prioritized until Operation Barbarossa. Because of the conspicuous silence of the scientific publications on the subject of nuclear fission by German, American, and British scientists, Russian physicist Georgy Flyorov suspected that the Allied powers had secretly been developing a "superweapon" since 1939. Flyorov wrote a letter to Stalin urging him to start this program in 1942. Initial efforts were slowed due to the German invasion of the Soviet Union and remained largely composed of the intelligence gathering from the Soviet spy rings working in the U. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
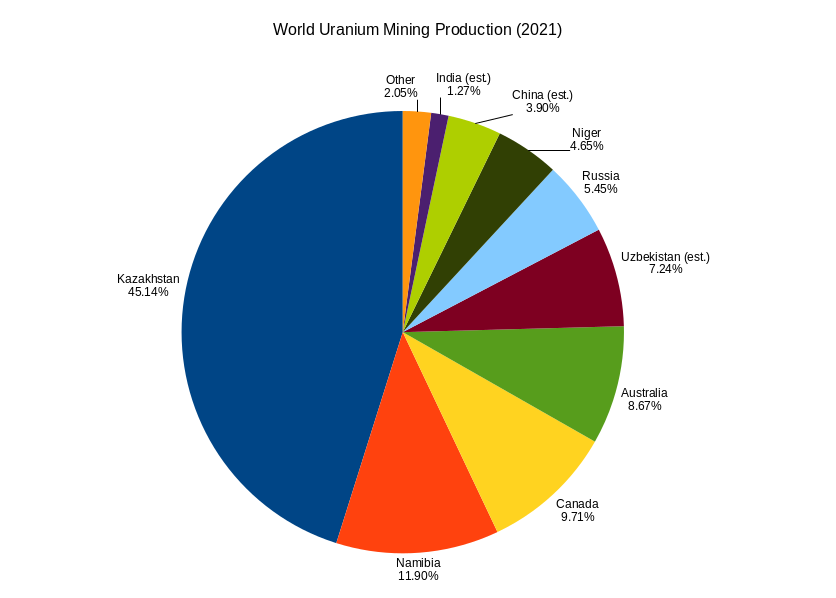
Uranium Mining
Uranium mining is the process of extraction of uranium ore from the ground. Over 50 thousand tons of uranium were produced in 2019. Kazakhstan, Canada, and Australia were the top three uranium producers, respectively, and together account for 68% of world production. Other countries producing more than 1,000 tons per year included Namibia, Niger, Russia, Uzbekistan, the United States, and China. Nearly all of the world's mined uranium is used to power nuclear power plants. Historically uranium was also used in applications such as uranium glass or ferrouranium but those applications have declined due to the radioactivity of uranium and are nowadays mostly supplied with a plentiful cheap supply of depleted uranium which is also used in uranium ammunition. In addition to being cheaper, depleted uranium is also less radioactive due to a lower content of short-lived and than natural uranium. Uranium is mined by in-situ leaching (57% of world production) or by conventional und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state was a part of the Eastern Bloc in the Cold War. Commonly described as a communist state, it described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state".Patrick Major, Jonathan Osmond, ''The Workers' and Peasants' State: Communism and Society in East Germany Under Ulbricht 1945–71'', Manchester University Press, 2002, Its territory was administered and occupied by Soviet forces following the end of World War II—the Soviet occupation zone of the Potsdam Agreement, bounded on the east by the Oder–Neisse line. The Soviet zone surrounded West Berlin but did not include it and West Berlin remained outside the jurisdiction of the GDR. Most scholars and academics describe the GDR as a totalitarian dictatorship. The GDR was establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert Hoover
Herbert Clark Hoover (August 10, 1874 – October 20, 1964) was an American politician who served as the 31st president of the United States from 1929 to 1933 and a member of the Republican Party, holding office during the onset of the Great Depression in the United States. A self-made man who became rich as a mining engineer, Hoover led the Commission for Relief in Belgium, served as the director of the U.S. Food Administration, and served as the U.S. Secretary of Commerce. Hoover was born to a Quaker family in West Branch, Iowa, but he grew up in Oregon. He was one of the first graduates of the new Stanford University in 1895. He took a position with a London-based mining company working in Australia and China. He rapidly became a wealthy mining engineer. In 1914 at the outbreak of World War I, he organized and headed the Commission for Relief in Belgium, an international relief organization that provided food to occupied Belgium. When the U.S. entered the war in 191 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudetenland
The Sudetenland ( , ; Czech and sk, Sudety) is the historical German name for the northern, southern, and western areas of former Czechoslovakia which were inhabited primarily by Sudeten Germans. These German speakers had predominated in the border districts of Bohemia, Moravia, and Czech Silesia since the Middle Ages. Sudetenland had been since the 9th century an integral part of the Czech state (first within the Duchy of Bohemia and later the Kingdom of Bohemia) both geographically and politically. The word "Sudetenland" did not come into being until the early part of the 20th century and did not come to prominence until almost two decades into the century, after World War I, when Austria-Hungary was dismembered and the Sudeten Germans found themselves living in the new country of Czechoslovakia. The ''Sudeten crisis'' of 1938 was provoked by the Pan-Germanist demands of Nazi Germany that the Sudetenland be annexed to Germany, which happened after the later Munich Agreeme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of National Remembrance
The Institute of National Remembrance – Commission for the Prosecution of Crimes against the Polish Nation ( pl, Instytut Pamięci Narodowej – Komisja Ścigania Zbrodni przeciwko Narodowi Polskiemu, abbreviated IPN) is a Polish state research institute in charge of education and archives with investigative and lustration powers. The IPN was established by the Polish parliament by the Act on the Institute of National Remembrance of 18 December 1998, which incorporated the earlier Main Commission for the Prosecution of Crimes against the Polish Nation of 1991. IPN itself had replaced a body on Nazi crimes established in 1945. In 2018, IPN's mission statement was amended by the controversial Amendment to the Act on the Institute of National Remembrance to include "protecting the reputation of the Republic of Poland and the Polish Nation". The IPN investigates Nazi and Communist crimes committed between 1917 and 1990, documents its findings, and disseminates them to the public ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zgoda Labour Camp
Zgoda () was a labour camp (sometimes also described as a concentration camp), set up in February 1945 in Zgoda district of Świętochłowice, Silesia. It was controlled by the communist secret police until its closure in November of the same year.The Polish Institute of National Remembrance Bulletin"Salomon Morel and the camp at Świętochłowice-Zgoda" including Index of articles, copies of IPN documents and notes. Publication date: 21 July 2005. Between 1943 and January 1945 during World War II, the camp in Świętochłowice operated by Nazi Germany as Arbeitslager. It was a labour subcamp (''Arbeitslager Eintrachtshütte'') or the Eintrachthütte concentration camp of the Nazi concentration camp Auschwitz. After the NKVD transfer of the facility to MBP, Colonel Salomon Morel became the commander of the renamed Zgoda camp on 15 March 1945.Dr. Adam Dziurok Obóz Pracy Świętochłowice-Zgoda. Instytut Pamięci Narodowej, 2010 Zgoda Labour Camp operation The Nazi German cam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Łambinowice
Łambinowice (german: Lamsdorf) is a village in Nysa County, Opole Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Łambinowice. It lies approximately north-east of Nysa and south-west of the regional capital Opole. Łambinowice was the location of ''Camp Lamsdorf'' which served as a prisoner of war camp during the Franco-Prussian war of 1870, and First as well as Second World Wars. When the area became Polish, the camp was maintained as ''Camp Łambinowice'' and served as a forced labour and resettlement camp for Germans. Village First mentioned under the name of Lambinowicz in 1273, the town shared the fate of the Upper Silesia and the land of Opole throughout the ages. Much damaged by the wars of the 17th century, most notably the Thirty Years' War, it lost much of its meaning as a centre of commerce and was reduced to but a small village. Camp German Empire In 1864 a large military training ground was establis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Labour Camp Potulice
After the end of World War II, the Central Labour Camp in Potulice ( pl, Centralny Obóz Pracy w Potulicach) became a detention centre for Germans and anti-communist Poles. It was set up by the Soviet and Polish Communist authorities in Potulice in place of the former Nazi German Potulice concentration camp (known as the ''Ostjugendbewahrlager Potulitz'' or ''Lebrechtsdorf'' camp), the subcamp of Stutthof built in 1941. Following liberation by the Red Army, the camp was controlled by the Soviet NKVD Department of Prisoners and Internees until June 1945. Repopulated, it remained in operation until 1949 under the management of the Stalinist Ministry of Public Security of Poland. Camp operation A total of 34,932 people were imprisoned in the camp between 1945 and 1949. At first, the inmates were mainly "ethnic Germans" from the ''Volksliste'' (DVL) including some prisoners-of-war, but also women, and 1,285 children – most of them orphaned. The prisoners worked in several workshops ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |