|
Footrot
Foot rot, or infectious pododermatitis, is a hoof infection commonly found in sheep, goats, and cattle. As the name suggests, it rots away the foot of the animal, more specifically the area between the two toes of the affected animal. It is extremely painful and contagious. It can be treated with a series of medications, but if not treated, the whole herd can become infected. The cause of the infection in cattle is two species of anaerobic bacteria, ''Fusobacterium necrophorum'' and ''Bacteroides melaninogenicus''. Both bacteria are common to the environment in which cattle live, and ''Fusobacterium'' is present in the rumen and fecal matter of the cattle. In sheep, ''F. necrophorum'' first invades the interdigital skin following damage to the skin, and causes interdigital lesions and slight inflammation. The second stage of the disease is marked by the invasion of the foot by the foot rot bacterium ''Dichelobacter nodosus'', a Gram-negative anaerobe. Usually, an injury to the skin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichelobacter Nodosus
''Dichelobacter nodosus'', formerly ''Bacteroides nodosus'', is a Gram-negative, obligate anaerobe of the family Cardiobacteriaceae. It has polar fimbriae and is the causative agent of ovine foot rot as well as interdigital dermatitis. It is the lone species in the genus ''Dichelobacter''. ''Dichelobacter nodosus'', formerly ''Bacteroides nodosus'', is a gram negative, rod shaped, obligate anaerobe of the family Cardiobacteriaceae. It has polar fimbriae epitomes that separate the bacteria into multiple serogroups. ''D. nodosus,'' along with ''Fusobacterium necrophorum,'' co-exist as the causative agents of ovine foot rot and interdigital dermatitis in ungulates globally, especially in temperate zones. Clinical signs can vary into two categories; virulent and benign, with the distinction between the two varying dependent on location. Treatment options include footbaths, parenteral administration of long-acting antimicrobials, concurrent use of vaccines, and removal of affecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
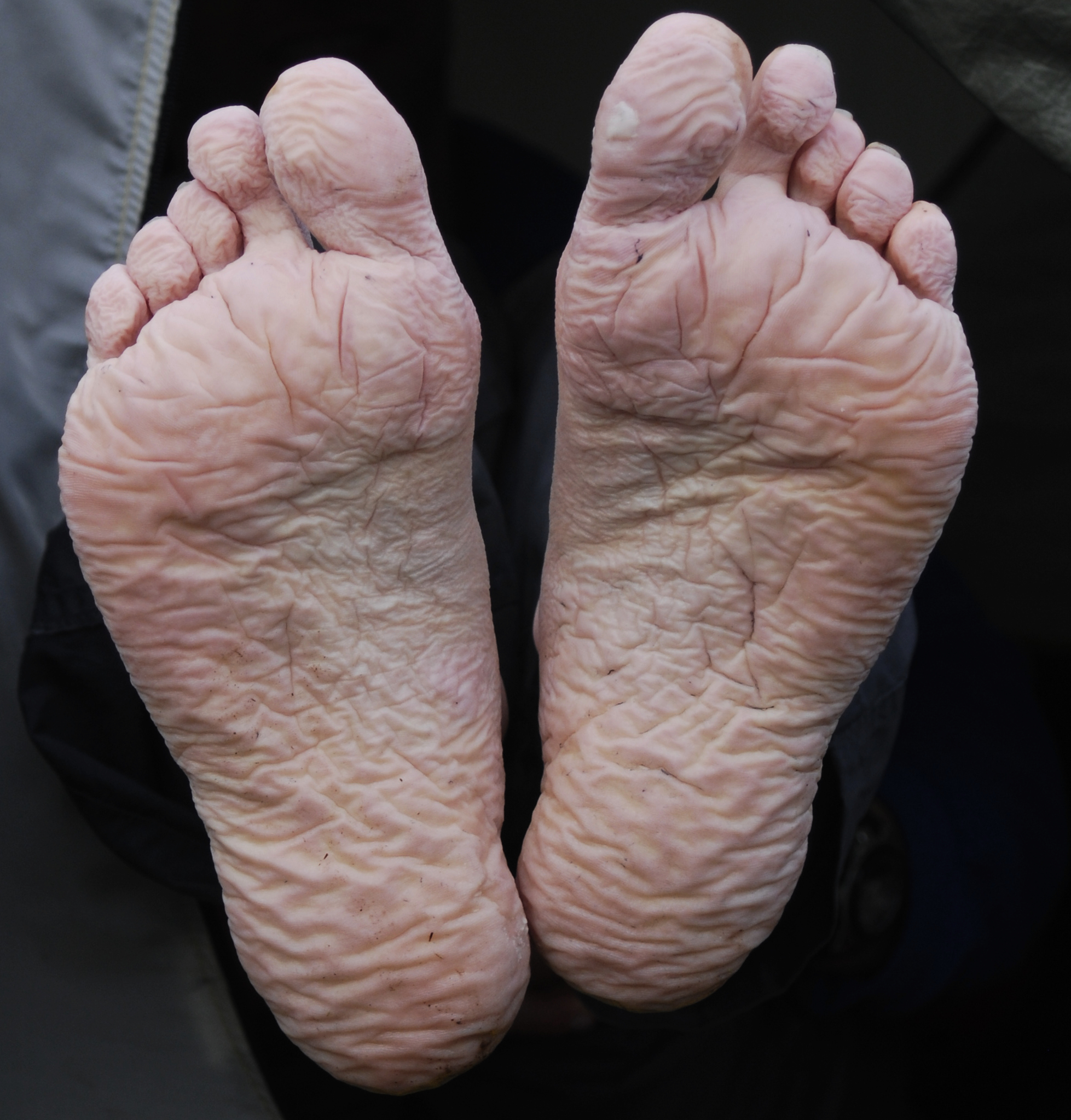
Pododermatitis
Bumblefoot (ulcerative pododermatitis) is a common bacterial infection and inflammatory reaction that occurs on the feet of birds, rodents. It is caused by bacteria, namely species of ''Staphylococcus'', ''Pseudomonas'', and ''Escherichia'', with '' S. aureus'' being the most common cause of the infection. The aforementioned opportunistic bacteria occur naturally in the animal's environment, and infection occurs when one or a combination of these enters the body through a scrape or cut in the skin. Bumblefoot can take various forms, but it usually looks like an abscess-like swelling with a central, dark-colored scab that may or may not ooze. Sometimes, this swollen bump contains pus or cottage cheese-like material. Alternately, the swelling could contain a hard lump when these materials harden, or if the abscess becomes impacted with substrate (e.g. soil, straw, etc.) Bumblefoot may also present as redness, swelling, small red sores, and depending upon severity and length of time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lameness (equine)
Lameness is an abnormal gait or stance of an animal that is the result of dysfunction of the locomotor system. In the horse, it is most commonly caused by pain, but can be due to neurologic or mechanical dysfunction. Lameness is a common veterinary problem in racehorses, sport horses, and pleasure horses. It is one of the most costly health problems for the equine industry, both monetarily for the cost of diagnosis and treatment, and for the cost of time off resulting in loss-of-use. Causes of lameness Lameness is most commonly caused by pain, but may also be the result of neuromuscular disease or mechanical restriction. Lameness itself is a clinical sign, and not a diagnosis. Pain Pain is the most common cause of lameness in the horse. It is usually the result of trauma or orthopedic disease, but other causes such as metabolic dysfunction, circulatory disease, and infection can also cause pain and subsequent lameness. Orthopedic causes of lameness are very common and may be the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bovine Diseases
Bovines (subfamily Bovinae) comprise a diverse group of 10 genera of medium to large-sized ungulates, including cattle, bison, African buffalo, water buffalos, and the four-horned and spiral-horned antelopes. The evolutionary relationship between the members of the group is still debated, and their classification into loose tribes rather than formal subgroups reflects this uncertainty. General characteristics include cloven hooves and usually at least one of the sexes of a species having true horns. The largest extant bovine is the gaur. In many countries, bovid milk and meat is used as food by humans. Cattle are kept as livestock almost everywhere except in parts of India and Nepal, where they are considered sacred by most Hindus. Bovids are used as draft animals and as riding animals. Small breeds of domestic bovid, such as the Miniature Zebu, are kept as pets. Bovid leather is durable and flexible and is used to produce a wide range of goods including clothing and bags. Sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrush (horse)
Thrush is a very common bacterial infection that occurs on the hoof of a horse, specifically in the region of the frog. The bacterium involved is'' Fusobacterium necrophorum'', and occurs naturally in the animal's environment—especially in wet, muddy, or unsanitary conditions, such as an unclean stall—and grows best with low oxygen. Horses with deep clefts, or narrow or contracted heels are more at risk of developing thrush. Symptoms The most obvious sign of thrush is usually the odor that occurs when picking out the feet. Additionally, the infected areas of the hoof will be black in color (even on a dark-horned hoof), and will easily break or crumble when scraped with a hoof pick. When picking the hooves around thrush areas, the differences between healthy and infected areas can be seen when white or gray tissue (healthy frog) is surrounding a dark, smelly (infected) area. Most horses do not become lame if infected with thrush. However, if left untreated, the bacteria may m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trench Foot
Trench foot is a type of foot damage due to moisture. Initial symptoms often include tingling or itching which can progress to numbness. The feet may become red or bluish in color. As the condition worsens the feet can start to swell and smell of decay. Complications may include skin breakdown or infection. Trench foot occurs due to prolonged exposure of the feet to cold, damp, and often unsanitary conditions. Unlike frostbite, trench foot usually occurs at temperatures above freezing, and can be classed as a form of non-freezing cold injury. Onset can be as rapid as 10 hours. Risk factors include overly tight boots and not moving. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve constriction of blood vessels resulting in insufficient blood flow to the feet. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and examination. Prevention involves keeping the feet warm, dry, and clean. After the condition has occurred, pain medications may be required during the gradual rewarming process. Pain m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formalin
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula and structure . The pure compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section Forms below), hence it is stored as an aqueous solution (formalin), which is also used to store animal specimens. It is the simplest of the aldehydes (). The common name of this substance comes from its similarity and relation to formic acid. Formaldehyde is an important precursor to many other materials and chemical compounds. In 1996, the installed capacity for the production of formaldehyde was estimated at 8.7 million tons per year. It is mainly used in the production of industrial resins, e.g., for particle board and coatings. Forms Formaldehyde is more complicated than many simple carbon compounds in that it adopts several diverse forms. These compounds can often be used interchangeably and can be interconverted. *Molecular formaldeh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Sulphate
Copper sulfate may refer to: * Copper(II) sulfate, CuSO4, a common compound used as a fungicide and herbicide * Copper(I) sulfate Copper(I) sulfate, also known as cuprous sulfate, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Cu2 SO4. It is a white solid that has attracted little attention, in contrast to copper(II) sulfate. It is an unusual example of a copper(I) ..., Cu2SO4, which is uncommonly used * Copper(II) sulfate, CuSO4 is greenish blue Copper compounds {{Chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccinate
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The agent stimulates the body's to recognize the agent as a threat, destroy it, and to further recognize and destroy any of the microorganisms associated with that agent that it may encounter in the future. Vaccines can be |
Zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic table. In some respects, zinc is chemically similar to magnesium: both elements exhibit only one normal oxidation state (+2), and the Zn2+ and Mg2+ ions are of similar size.The elements are from different metal groups. See periodic table. Zinc is the 24th most abundant element in Earth's crust and has five stable isotopes. The most common zinc ore is sphalerite (zinc blende), a zinc sulfide mineral. The largest workable lodes are in Australia, Asia, and the United States. Zinc is refined by froth flotation of the ore, roasting, and final extraction using electricity ( electrowinning). Zinc is an essential trace element for humans, animals, plants and for microorganisms and is necessary for prenatal and postnatal development. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an oral antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including Acne vulgaris, acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague (disease), plague, malaria, and syphilis. Common side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, rash, and loss of appetite. Other side effects include poor tooth development if used by children less than eight years of age, kidney problems, and sunburning easily. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby. It works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria. Tetracycline was patented in 1953 and came into commercial use in 1978. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Tetracycline is available as a generic medication. Tetracycline was originally made from bacteria of the genus ''Streptomyces''. Medical uses Spectrum of activity Tetracyclines have a broad spectrum of antibiotic action. Originally, they possessed some level of bacteriostatic acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |