|
Food Grading
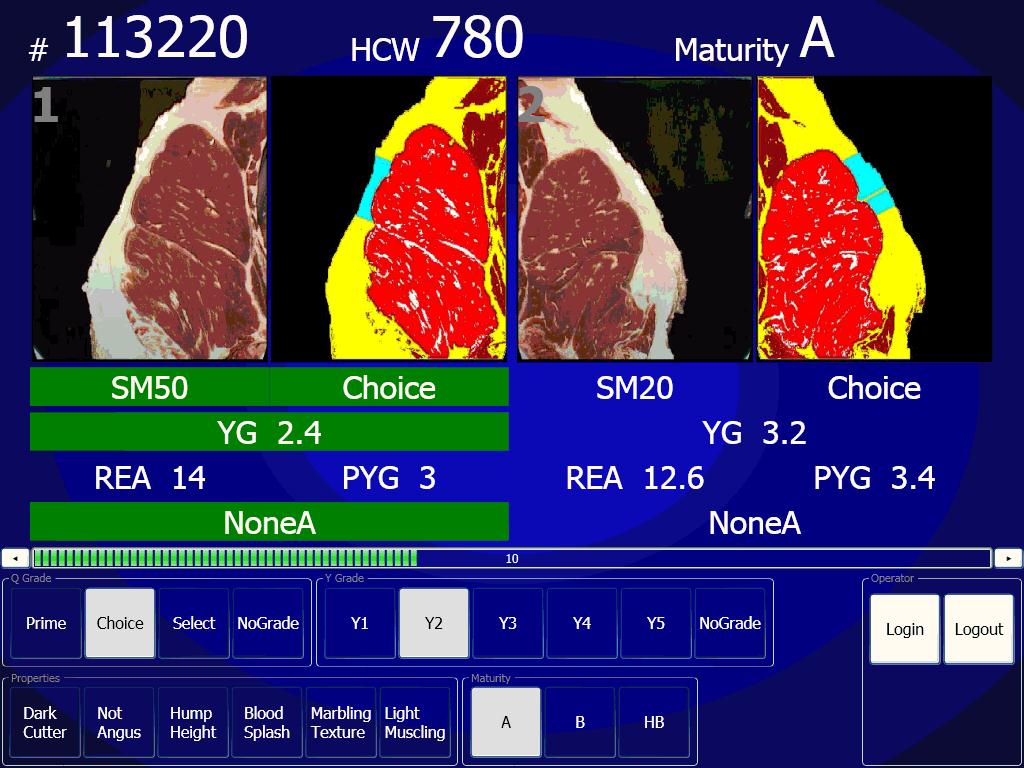
Food grading involves the inspection, assessment and sorting of various foods regarding quality, freshness, legal conformity and market value.Saravacos, George D.; Maroulis, Zacharias B. (2011''Food Process Engineering Operations'' CRC Press. pp. 198-199. Sivasankar, B. (2002)Processing and Preservation'' PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd. pp. 175-177. Food grading is often done by hand, in which foods are assessed and sorted. Machinery is also used to grade foods, and may involve sorting products by size, shape and quality. For example, machinery can be used to remove spoiled food from fresh product. By food type Beef Beef grading in the United States is performed by the United States Department of Agriculture's (USDA) Agricultural and Marketing Service. There are eight beef quality grades, with U.S. Prime being the highest grade and U.S. Canner being the lowest grade. Beef grading is a complex process. Beer In beer grading, the letter "X" is used on some beers, and was traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Commonwealth Secretariat, which focuses on intergovernmental aspects, and the Commonwealth Foundation, which focuses on non-governmental relations amongst member states. Numerous organisations are associated with and operate within the Commonwealth. The Commonwealth dates back to the first half of the 20th century with the decolonisation of the British Empire through increased self-governance of its territories. It was originally created as the British Commonwealth of Nations through the Balfour Declaration at the 1926 Imperial Conference, and formalised by the United Kingdom through the Statute of Westminster in 1931. The current Commonwealth of Nations was formally constituted by the London Declaration in 1949, which modernised the comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter waves and acoustic waves can also be considered forms of radiative energy, and recently gravitational waves have been associated with a spectral signature in the context of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) In simpler terms, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. Historically, spectroscopy originated as the study of the wavelength dependence of the absorption by gas phase matter of visible light dispersed by a prism. Spectroscopy, primarily in the electromagnetic spectrum, is a fundamental exploratory tool in the fields of astronomy, chemistry, materials science, and physics, allowing the composition, physical structure and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300 GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (430 THz). Longer IR wavelengths (30 μm-100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation range. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires emit invisible heat; in 1681 the pioneering experimenter Edme Mariotte showed that glass, though transparent to sunlight, obstructed radiant heat. In 1800 the astronomer Sir William Herschel discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
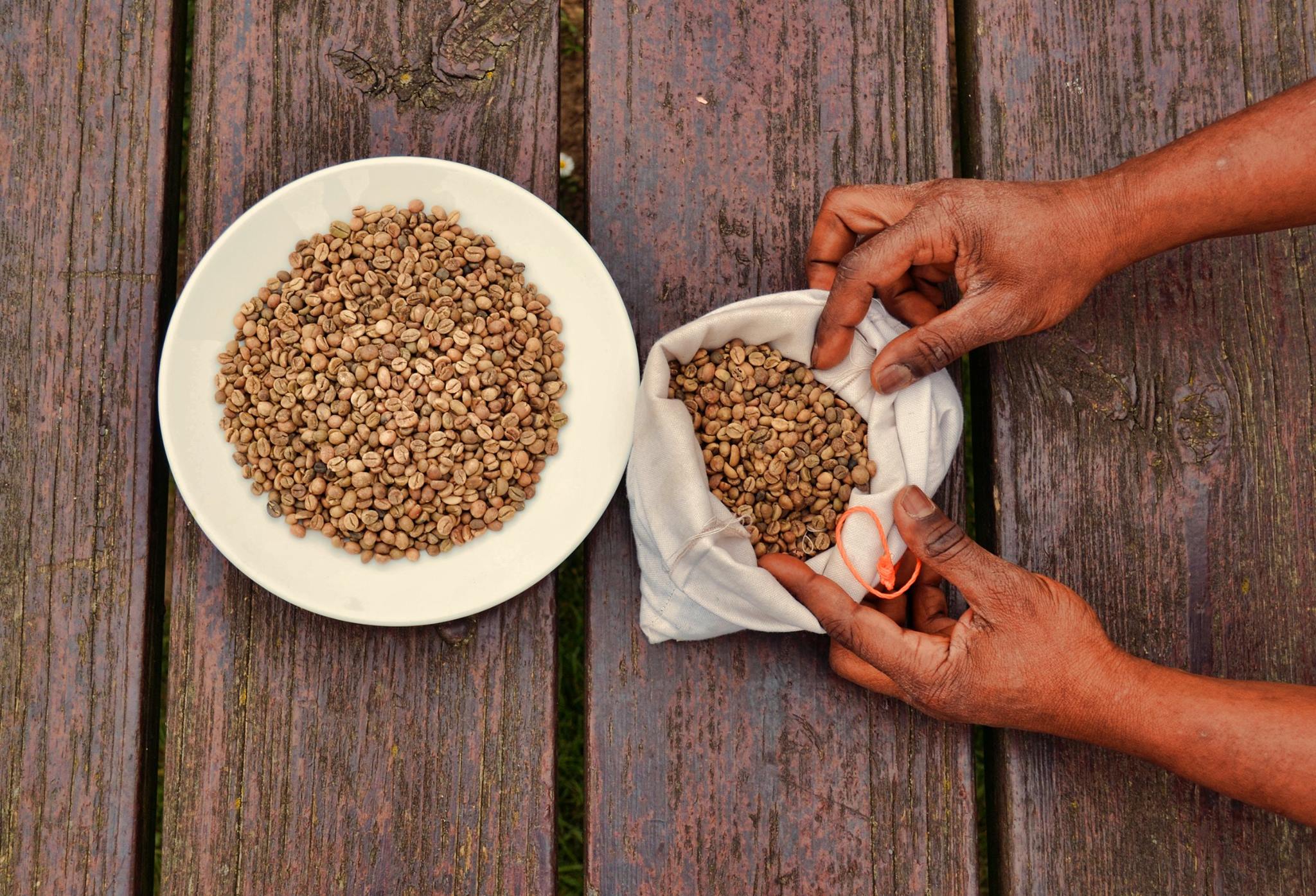
Coffee Roasting
Roasting coffee transforms the chemical and physical properties of green coffee beans into roasted coffee products. The roasting process is what produces the characteristic flavor of coffee by causing the green coffee beans to change in taste. Unroasted beans contain similar if not higher levels of acids, protein, sugars, and caffeine as those that have been roasted, but lack the taste of roasted coffee beans due to the Maillard and other chemical reactions that occur during roasting. Coffee tends to be roasted close to where it will be consumed, as green coffee is more stable than roasted beans. The vast majority of coffee is roasted commercially on a large scale, but small-scale commercial roasting has grown significantly with the trend toward "single-origin" coffees served at specialty shops. Some coffee drinkers even roast coffee at home as a hobby in order to both experiment with the flavor profile of the beans and ensure the freshest possible roasted coffee. The first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coffee
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulant, stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world. Seeds of the ''Coffea'' plant's fruits are separated to produce unroasted green coffee beans. The beans are Coffee roasting, roasted and then ground into fine particles that are typically steeped in hot water before being filtered out, producing a cup of coffee. It is usually served hot, although chilled or iced coffee is common. Coffee can be prepared and presented in a variety of ways (e.g., espresso, French press, caffè latte, or already-brewed canned coffee). Sugar, sugar substitutes, milk, and cream are often used to mask the bitter taste or enhance the flavor. Though coffee is now a global commodity, it has a History of coffee, long history tied closely to food traditions around the Red Sea. The earliest credible evidence of coffee d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coffee Beans Closeup
Coffee is a drink prepared from roasted coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content. It is the most popular hot drink in the world. Seeds of the ''Coffea'' plant's fruits are separated to produce unroasted green coffee beans. The beans are roasted and then ground into fine particles that are typically steeped in hot water before being filtered out, producing a cup of coffee. It is usually served hot, although chilled or iced coffee is common. Coffee can be prepared and presented in a variety of ways (e.g., espresso, French press, caffè latte, or already-brewed canned coffee). Sugar, sugar substitutes, milk, and cream are often used to mask the bitter taste or enhance the flavor. Though coffee is now a global commodity, it has a long history tied closely to food traditions around the Red Sea. The earliest credible evidence of coffee drinking in the form of the modern beverage ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coconut Milk
Coconut milk is an opaque, milky-white liquid extracted from the grated pulp of mature coconuts. The opacity and rich taste of coconut milk are due to its high oil content, most of which is saturated fat. Coconut milk is a traditional food ingredient used in Southeast Asia, Oceania, South Asia, and East Africa. It is also used for cooking in the Caribbean, tropical Latin America, and West Africa, where coconuts were introduced during the colonial era. Coconut milk is differentiated into subtypes based on fat content. They can be generalized into coconut cream (or thick coconut milk) with the highest amount of fat; coconut milk (or thin coconut milk) with a maximum of around 20% fat; and coconut skim milk with negligible amounts of fat. This terminology is not always followed in commercial coconut milk sold in western countries. Coconut milk can also be used to produce milk substitutes (differentiated as "coconut milk beverages"). These products are not the same as regular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hops
Hops are the flowers (also called seed cones or strobiles) of the hop plant ''Humulus lupulus'', a member of the Cannabaceae family of flowering plants. They are used primarily as a bittering, flavouring, and stability agent in beer, to which, in addition to bitterness, they impart floral, fruity, or citrus flavours and aromas. Hops are also used for various purposes in other beverages and herbal medicine. The hops plants have separate female and male plants, and only female plants are used for commercial production. The hop plant is a vigorous, climbing, herbaceous perennial, usually trained to grow up strings in a field called a hopfield, hop garden (in the South of England), or hop yard (in the West Country and United States) when grown commercially. Many different varieties of hops are grown by farmers around the world, with different types used for particular styles of beer. The first documented use of hops in beer is from the 9th century, though Hildegard of Bingen, 30 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Society Of Brewing Chemists
The American Society of Brewing Chemists (ASBC) is a professional organization of scientists and technical professionals in the brewing, malting, and allied industries. It publishes an journal A journal, from the Old French ''journal'' (meaning "daily"), may refer to: *Bullet journal, a method of personal organization *Diary, a record of what happened over the course of a day or other period *Daybook, also known as a general journal, a ..., the Journal of the American Society of Brewing Chemists'. External linksASBC Website Beer organizations Chemistry societies {{sci-org-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Brewery Convention
The European Brewery Convention (EBC) is an organisation representing the technical and scientific interests of the brewing sector in Europe. The EBC defines itself as the scientific and technological arm of The Brewers of Europe. Among brewers, EBC is perhaps best known for the EBC units measuring beer and wort colour, as well as EBC units for quantifying turbidity (also known as haze) in beer. Equally, the EBC congress is recognised globally as a significant meeting event for the world's brewing, malting and beer fermentation scientists and technologists, taking place every two years. History The European Brewery Convention was founded in 1946 as a direct result of the critical situation concerning raw material supply (specifically malted barley and hops) which had arisen due to World War II. The founding members included the first president of the organisation, Prof. Philippe Kreiss. The name European Brewery Convention was adopted at the first EBC congress held in 1947 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


.jpg)
