|
Fodderty
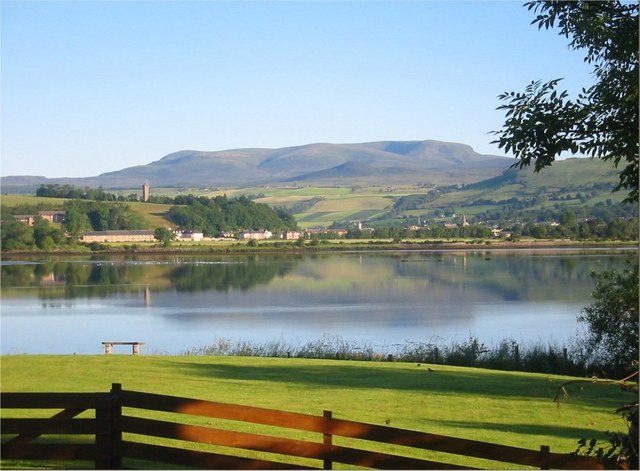
Fodderty ( gd, Fodhraitidh) is a small hamlet, close to Dingwall, Ross-shire in the Scottish Highlands and is in the Scotland, Scottish council area of Highland Council area, Highland. The small hamlet of Bottacks is located 1 mile to the west, and just to the east is Brae or Brea, formed in 1777 from the lands (long held by a branch of the Clan Mackenzie, Mackenzies) of Davochcarn, Davochmaluag and Davochpollo.William John Watson, ''Place names of Ross and Cromarty'' (Inverness Northern Counties Pub. 1904), apage 100/ref> "Davochmaluag" is named after the famous missionary saint - St Moluag of Lismore (died AD592) - to whom the church at Fodderty was dedicated. Only a mound remains in the burial-ground to mark where this church stood. Fodderty Cemetery also contains the burial place''Bridgescapes'' by Bruce Keith (pub.2017) of Willie Logan (Loganair), Willie Logan (1913-1966) that is marked by a memorial in the shape of a pier of the Tay Road Bridge which, through his father's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John M'Gilligen
John M'Gilligen was a 17th-century Presbyterian minister. He resisted the demands of the Episcopalian authorities and was imprisoned on the Bass Rock. His name is sometimes also spelled as John MacKilligen or John M'Killican or John MacKillican or even John M'Gilligine. Early life and ordination John M'Gilligen was minister of Fodderty which Anderson describes as "a parish lying partly in Ross-shire and partly in the shire of Cromarty, chiefly in the beautiful and arable vale of Strathpeffer, west from Dingwall." He was licensed by the Presbytery of Aberdeen and received by the Presbytery of Forres 28 March 1655. He was called to North of Ireland and to Islay but did not go. He was admitted to Fodderty 26 February 1656. Having been admitted to that charge, subsequent to 1649, M'Gilligen came under the Act of 1662 which required that he should anew seek presentation from his patron and collation from the Bishop of the diocese, or be ejected. With the terms of this Act he refu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willie Logan (Loganair)
William Logan (1913–1966) was a Scottish construction engineer who founded Loganair. He contributed to many important infrastructure projects in Scotland during the 1950s and 1960s, primarily road networks bridges and hydroelectric schemes. He was managing director of Duncan Logan Ltd, an engineering company started by his father, Duncan Logan, and based in Muir of Ord. Early life Logan was educated at Dingwall Academy, and lived in Dingwall in a house built to his own designs called Parklea, which was also the name of his wife Helen Dunbar's previous family home in Dingwall town centre. Selected construction projects * Orrin Reservoir *Tay Road Bridge Parklea House A highly advanced house for its time, especially for the North of Scotland, Parklea was built during the early 1950s and was full of luxurious touches, including an automatic garage door opening system—Willie's chauffeur would drop off the Logans at the north-facing front door, then swing down the steep curved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bottacks
Bottacks (''Na Botagan'' in Scottish Gaelic) is a small scattered township, located 1.5 miles north north east of Strathpeffer, in Ross-shire, Scottish Highlands and is in the Scottish council area of Highland. The village of Fodderty Fodderty ( gd, Fodhraitidh) is a small hamlet, close to Dingwall, Ross-shire in the Scottish Highlands and is in the Scotland, Scottish council area of Highland Council area, Highland. The small hamlet of Bottacks is located 1 mile to the west, ... lies 1 mile to the east. References * http://www.oldscottish.com/fodderty.html - 1843 census that lists a (single) head of household in Bottacks Populated places in Ross and Cromarty {{Highland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dingwall
Dingwall ( sco, Dingwal, gd, Inbhir Pheofharain ) is a town and a royal burgh in the Highland council area of Scotland. It has a population of 5,491. It was an east-coast harbour that now lies inland. Dingwall Castle was once the biggest castle north of Stirling. On the town's present-day outskirts lies Tulloch Castle, parts of which may date back to the 12th century. In 1411 the Battle of Dingwall is said to have taken place between the Clan Mackay and the Clan Donald. History Its name, derived from the Scandinavian (field or meeting-place of the ''thing'', or local assembly; compare Tynwald, Tingwall, Thingwall in the British Isles alone, plus many others across northern Europe), preserves the Viking connections of the town; Gaels call it (), meaning "the mouth of the Peffery" or meaning "cabbage town". The site of the , and of the medieval Moothill, thought to have been established by the Vikings after they invaded in the 8th century, lies beneath the Cromartie memor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highland (council Area)
Highland ( gd, A' Ghàidhealtachd, ; sco, Hieland) is a council area in the Scottish Highlands and is the largest local government area in the United Kingdom. It was the 7th most populous council area in Scotland at the 2011 census. It shares borders with the council areas of Aberdeenshire, Argyll and Bute, Moray and Perth and Kinross. Their councils, and those of Angus and Stirling, also have areas of the Scottish Highlands within their administrative boundaries. The Highland area covers most of the mainland and inner-Hebridean parts of the historic counties of Inverness-shire and Ross and Cromarty, all of Caithness, Nairnshire and Sutherland and small parts of Argyll and Moray. Despite its name, the area does not cover the entire Scottish Highlands. Name Unlike the other council areas of Scotland, the name ''Highland'' is often not used as a proper noun. The council's website only sometimes refers to the area as being ''Highland'', and other times as being ''the Hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ross-shire
Ross-shire (; gd, Siorrachd Rois) is a historic county in the Scottish Highlands. The county borders Sutherland to the north and Inverness-shire to the south, as well as having a complex border with Cromartyshire – a county consisting of numerous enclaves or exclaves scattered throughout Ross-shire's territory. Ross-shire includes most of Ross along with Lewis in the Outer Hebrides. Dingwall is the traditional county town. The area of Ross-shire is based on that of the historic province of Ross, but with the exclusion of the many enclaves that form Cromartyshire. For shreival purposes the area was first separated from the authority of the sheriff of Inverness by Act of Parliament during the reign of King James IV, the sheriff to sit at Tain or Dingwall. Sheriffs were seldom appointed, and further acts of 1649 and 1661 restated its separation from Inverness. The 1661 act also clarified the area encompassed, based on the pre-Reformation Diocese of Ross. Sir George ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Highlands
The Highlands ( sco, the Hielands; gd, a’ Ghàidhealtachd , 'the place of the Gaels') is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowland Scots replaced Scottish Gaelic throughout most of the Lowlands. The term is also used for the area north and west of the Highland Boundary Fault, although the exact boundaries are not clearly defined, particularly to the east. The Great Glen divides the Grampian Mountains to the southeast from the Northwest Highlands. The Scottish Gaelic name of ' literally means "the place of the Gaels" and traditionally, from a Gaelic-speaking point of view, includes both the Western Isles and the Highlands. The area is very sparsely populated, with many mountain ranges dominating the region, and includes the highest mountain in the British Isles, Ben Nevis. During the 18th and early 19th centuries the population of the Highlands rose to around 300,000, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the Scott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highland Council Area
Highland ( gd, A' Ghàidhealtachd, ; sco, Hieland) is a council area in the Scottish Highlands and is the largest local government area in the United Kingdom. It was the 7th most populous council area in Scotland at the 2011 census. It shares borders with the council areas of Aberdeenshire, Argyll and Bute, Moray and Perth and Kinross. Their councils, and those of Angus and Stirling, also have areas of the Scottish Highlands within their administrative boundaries. The Highland area covers most of the mainland and inner-Hebridean parts of the historic counties of Inverness-shire and Ross and Cromarty, all of Caithness, Nairnshire and Sutherland and small parts of Argyll and Moray. Despite its name, the area does not cover the entire Scottish Highlands. Name Unlike the other council areas of Scotland, the name ''Highland'' is often not used as a proper noun. The council's website only sometimes refers to the area as being ''Highland'', and other times as being ''the Highl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clan Mackenzie
Clan Mackenzie ( gd, Clann Choinnich ) is a Scottish clan, traditionally associated with Kintail and lands in Ross-shire in the Scottish Highlands. Traditional genealogies trace the ancestors of the Mackenzie chiefs to the 12th century. However, the earliest Mackenzie chief recorded by contemporary evidence is Alexander Mackenzie of Kintail who died some time after 1471. Traditionally, during the Wars of Scottish Independence, the Mackenzies supported Robert the Bruce, but feuded with the Earls of Ross in the latter part of the 14th century. During the 15th and 16th-centuries the Mackenzies feuded with the neighboring clans of Munro and MacDonald. In the 17th century the Mackenzie chief was made Earl of Seaforth in the peerage of Scotland. During the Scottish Civil War of the 17th century the Mackenzies largely supported the Royalists. During the Jacobite rising of 1715 the chief and clan of Mackenzie supported the Jacobite cause. However, during the Jacobite rising of 1745 the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Moluag
Saint Moluag (c. 510 – 592; also known as ''Lua'', ''Luan'', ''Luanus'', ''Lugaidh'', ''Moloag'', ''Molluog'', ''Molua'', ''Murlach'', ''Malew''Saint of the Day, 25 June: ''Moloc of Mortlach'' ''SaintPatrickDC.org''. Retrieved on 6 March 2012''Irish Saints in Great Britain'', pp. 76–77) was a Scottish missionary, and a contemporary of , who evangelized the of in the sixth century. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tay Road Bridge
The Tay Road Bridge ( gd, Drochaid-rathaid na Tatha) carries the A92 road across the Firth of Tay from Newport-on-Tay in Fife to Dundee in Scotland, just downstream of the Tay Rail Bridge. At around , it is one of the longest road bridges in Europe, and was opened in 1966, replacing the old Tay ferry. Construction As part of the modernisation projects of the 1950s, a road bridge across the Tay had been considered for several years. In August 1958 a traffic census was undertaken and test bores were taken in order to establish the most suitable location for a bridge crossing. Despite government opposition to the project, local lobbying, led by Dundee businessman Sir Douglas Hardie, brought a final agreement to the cost of the project. The bridge was designed by consulting engineers WA Fairhurst & Partners of Glasgow and Dundee, under the direct supervision of the firm's founding partner, civil engineer William Fairhurst. Construction began in March 1963 with the infilling of W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |