|
Focal-plane Array
A staring array, also known as staring-plane array or focal-plane array (FPA), is an image sensor consisting of an array (typically rectangular) of light-sensing pixels at the focal plane of a lens. FPAs are used most commonly for imaging purposes (e.g. taking pictures or video imagery), but can also be used for non-imaging purposes such as spectrometry, LIDAR, and wave-front sensing. In radio astronomy, the FPA is at the focus of a radio telescope. At optical and infrared wavelengths, it can refer to a variety of imaging device types, but in common usage it refers to two-dimensional devices that are sensitive in the infrared spectrum. Devices sensitive in other spectra are usually referred to by other terms, such as CCD (charge-coupled device) and CMOS image sensor in the visible spectrum. FPAs operate by detecting photons at particular wavelengths and then generating an electrical charge, voltage, or resistance in relation to the number of photons detected at each pixel. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Sensor
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to make an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they pass through or reflect off objects) into signals, small bursts of current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronic imaging devices of both analog and digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, camera phones, optical mouse devices, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging. The two main types of electronic image sensors are the charge-coupled device (CCD) and the active-pixel sensor (CMOS sensor). Both CCD and CMOS sensors are based on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) technology, with CCDs based on MOS capacitors and CMOS sensors based on M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indium Antimonide
Indium antimonide (InSb) is a crystalline compound made from the elements indium (In) and antimony (Sb). It is a narrow- gap semiconductor material from the III- V group used in infrared detectors, including thermal imaging cameras, FLIR systems, infrared homing missile guidance systems, and in infrared astronomy. The indium antimonide detectors are sensitive between 1–5 μm wavelengths. Indium antimonide was a very common detector in the old, single-detector mechanically scanned thermal imaging systems. Another application is as a terahertz radiation source as it is a strong photo-Dember emitter. History The intermetallic compound was first reported by Liu and Peretti in 1951, who gave its homogeneity range, structure type, and lattice constant. Polycrystalline ingots of InSb were prepared by Heinrich Welker in 1952, although they were not very pure by today's semiconductor standards. Welker was interested in systematically studying the semiconducting properties of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air-to-air Missile
The newest and the oldest member of Rafael's Python family of AAM for comparisons, Python-5 (displayed lower-front) and Shafrir-1 (upper-back) An air-to-air missile (AAM) is a missile fired from an aircraft for the purpose of destroying another aircraft. AAMs are typically powered by one or more rocket motors, usually solid fueled but sometimes liquid fueled. Ramjet engines, as used on the Meteor, are emerging as propulsion that will enable future medium-range missiles to maintain higher average speed across their engagement envelope. Air-to-air missiles are broadly put in two groups. Those designed to engage opposing aircraft at ranges of less than 16 km are known as short-range or "within visual range" missiles (SRAAMs or WVRAAMs) and are sometimes called "dogfight" missiles because they are designed to optimize their agility rather than range. Most use infrared guidance and are called heat-seeking missiles. In contrast, medium- or long-range missiles (MRAAMs or L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field-programmable Gate Array
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturinghence the term '' field-programmable''. The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a hardware description language (HDL), similar to that used for an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC). Circuit diagrams were previously used to specify the configuration, but this is increasingly rare due to the advent of electronic design automation tools. FPGAs contain an array of programmable logic blocks, and a hierarchy of reconfigurable interconnects allowing blocks to be wired together. Logic blocks can be configured to perform complex combinational functions, or act as simple logic gates like AND and XOR. In most FPGAs, logic blocks also include memory elements, which may be simple flip-flops or more complete blocks of memory. Many FPGAs can be reprogrammed to implement different logic functions, allowing flexible reconfigur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
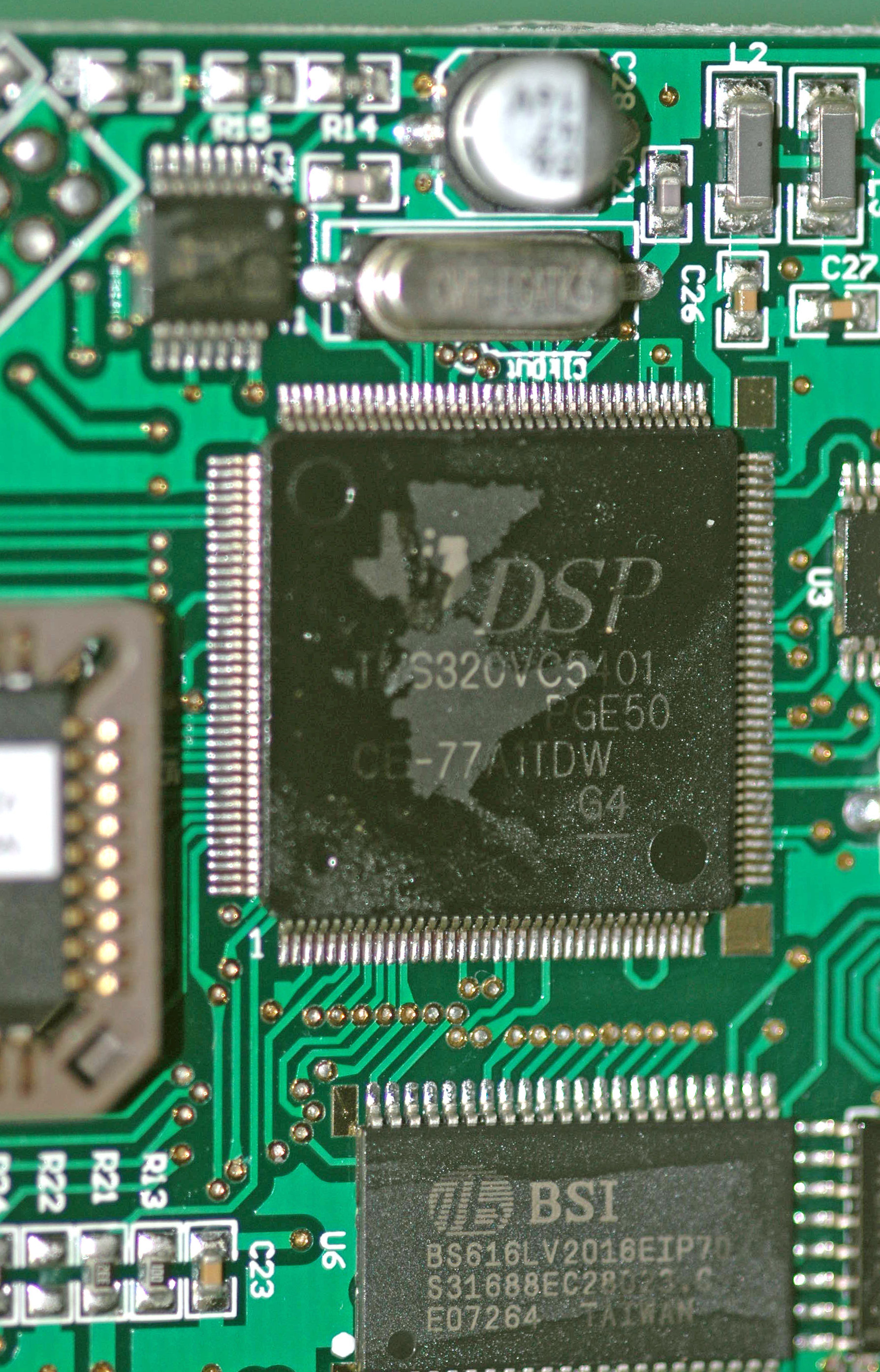
Digital Signal Processor
A digital signal processor (DSP) is a specialized microprocessor chip, with its architecture optimized for the operational needs of digital signal processing. DSPs are fabricated on MOS integrated circuit chips. They are widely used in audio signal processing, telecommunications, digital image processing, radar, sonar and speech recognition systems, and in common consumer electronic devices such as mobile phones, disk drives and high-definition television (HDTV) products. The goal of a DSP is usually to measure, filter or compress continuous real-world analog signals. Most general-purpose microprocessors can also execute digital signal processing algorithms successfully, but may not be able to keep up with such processing continuously in real-time. Also, dedicated DSPs usually have better power efficiency, thus they are more suitable in portable devices such as mobile phones because of power consumption constraints. DSPs often use special memory architectures that are able t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photo Response Non-uniformity
Photo response non-uniformity, pixel response non-uniformity, or PRNU, is a form of fixed-pattern noise related to digital image sensors, as used in cameras and optical instruments. Both CCD and CMOS sensors are two-dimensional arrays of photosensitive cells, each broadly corresponding to an image pixel. Due to the non-uniformity of image sensors, each cell responds with a different voltage level when illuminated with a uniform light source, and this leads to luminance inaccuracy at the pixel level. High-end and metrology camera vendors tend to characterise this non-uniformity during instrument manufacture. The sensor is illuminated with a standardized light source and a two-dimensional table of correction factors is generated. This table is either carried in camera non-volatile memory and dynamically applied to the image on each capture, or ships with the camera to be applied by an external image processing and correcting pipeline. See also * Color balance * Color correction * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermo-electric Cooler
Thermoelectric cooling uses the Peltier effect to create a heat flux at the junction of two different types of materials. A Peltier cooler, heater, or thermoelectric heat pump is a solid-state active heat pump which transfers heat from one side of the device to the other, with consumption of electrical energy, depending on the direction of the current. Such an instrument is also called a Peltier device, Peltier heat pump, solid state refrigerator, or thermoelectric cooler (TEC) and occasionally a thermoelectric battery. It can be used either for heating or for cooling, although in practice the main application is cooling. It can also be used as a temperature controller that either heats or cools. This technology is far less commonly applied to refrigeration than vapor-compression refrigeration is. The primary advantages of a Peltier cooler compared to a vapor-compression refrigerator are its lack of moving parts or circulating liquid, very long life, invulnerability to leaks, smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen—LN2—is nitrogen in a liquid state at low temperature. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of about . It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is a colorless, low viscosity liquid that is widely used as a coolant. Physical properties The diatomic character of the N2 molecule is retained after liquefaction. The weak van der Waals interaction between the N2 molecules results in little interatomic interaction, manifested in its very low boiling point. The temperature of liquid nitrogen can readily be reduced to its freezing point by placing it in a vacuum chamber pumped by a vacuum pump. Liquid nitrogen's efficiency as a coolant is limited by the fact that it boils immediately on contact with a warmer object, enveloping the object in an insulating layer of nitrogen gas bubbles. This effect, known as the Leidenfrost effect, occurs when any liquid comes in contact with a surface which is significantly hotter than its boiling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnson–Nyquist Noise
Johnson–Nyquist noise (thermal noise, Johnson noise, or Nyquist noise) is the electronic noise generated by the thermal agitation of the charge carriers (usually the electrons) inside an electrical conductor at equilibrium, which happens regardless of any applied voltage. Thermal noise is present in all electrical circuits, and in sensitive electronic equipment (such as radio receivers) can drown out weak signals, and can be the limiting factor on sensitivity of electrical measuring instruments. Thermal noise increases with temperature. Some sensitive electronic equipment such as radio telescope receivers are cooled to cryogenic temperatures to reduce thermal noise in their circuits. The generic, statistical physical derivation of this noise is called the fluctuation-dissipation theorem, where generalized impedance or generalized susceptibility is used to characterize the medium. Thermal noise in an ideal resistor is approximately white, meaning that the power spectral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbolometer
A microbolometer is a specific type of bolometer used as a detector in a thermal camera. Infrared radiation with wavelengths between 7.5–14 μm strikes the detector material, heating it, and thus changing its electrical resistance. This resistance change is measured and processed into temperatures which can be used to create an image. Unlike other types of infrared detecting equipment, microbolometers do not require cooling. Theory of construction A microbolometer is an uncooled thermal sensor. Previous high resolution thermal sensors required exotic and expensive cooling methods including stirling cycle coolers and liquid nitrogen coolers. These methods of cooling made early thermal imagers expensive to operate and unwieldy to move. Also, older thermal imagers required a cool down time in excess of 10 minutes before being usable. A microbolometer consists of an array of pixels, each pixel being made up of several layers. The cross-sectional diagram shown in Figure 1 provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryogenic
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures. The 13th IIR International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington DC in 1971) endorsed a universal definition of “cryogenics” and “cryogenic” by accepting a threshold of 120 K (or –153 °C) to distinguish these terms from the conventional refrigeration. This is a logical dividing line, since the normal boiling points of the so-called permanent gases (such as helium, hydrogen, neon, nitrogen, oxygen, and normal air) lie below 120K while the Freon refrigerants, hydrocarbons, and other common refrigerants have boiling points above 120K. The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology considers the field of cryogenics as that involving temperatures below -153 Celsius (120K; -243.4 Fahrenheit) Discovery of superconducting materials with critical temperatures significantly above the boiling point of nitrogen has provided new interest in reliable, low cost methods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Readout Integrated Circuits
A Readout integrated circuit (ROIC) is an integrated circuit (IC) specifically used for reading detectors of a particular type. They are compatible with different types of detectors such as infrared and ultraviolet. The primary purpose for ROICs is to accumulate the photocurrent from each pixel and then transfer the resultant signal onto output taps for readout. Conventional ROIC technology stores the signal charge at each pixel and then routes the signal onto output taps for readout. This requires storing large signal charge at each pixel site and maintaining signal-to-noise ratio (or dynamic range) as the signal is read out and digitized. A ROIC has high-speed analog outputs to transmit pixel data outside of the integrated circuit. If digital outputs are implemented, the IC is referred to as a Digital Readout Integrated Circuit (DROIC). A Digital readout integrated circuit (DROIC) is a class of ROIC that uses on-chip analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) to digitize the accumulated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




