readout integrated circuits on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A Readout integrated circuit (ROIC) is an
A Readout integrated circuit (ROIC) is an  A Digital readout integrated circuit (DROIC) is a class of ROIC that uses on-chip
A Digital readout integrated circuit (DROIC) is a class of ROIC that uses on-chip 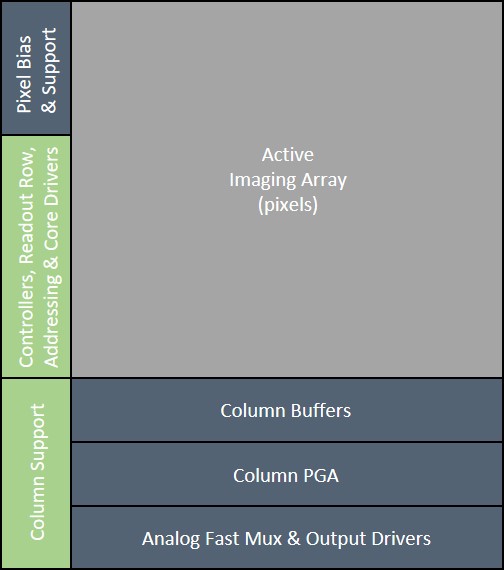
integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
(IC) specifically used for reading detector
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends ...
s of a particular type. They are compatible with different types of detectors such as infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
and ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nanometer, nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 Hertz, PHz) to 400 nm (750 Hertz, THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than ...
. The primary purpose for ROICs is to accumulate the photocurrent from each pixel and then transfer the resultant signal onto output taps for readout. Conventional ROIC technology stores the signal charge at each pixel and then routes the signal onto output taps for readout. This requires storing large signal charge at each pixel site and maintaining signal-to-noise ratio (or dynamic range) as the signal is read out and digitized.
A ROIC has high-speed analog outputs to transmit pixel data outside of the integrated circuit. If digital outputs are implemented, the IC is referred to as a Digital Readout Integrated Circuit (DROIC).
 A Digital readout integrated circuit (DROIC) is a class of ROIC that uses on-chip
A Digital readout integrated circuit (DROIC) is a class of ROIC that uses on-chip analog-to-digital conversion
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a digital signal. An ADC may also provi ...
(ADC) to digitize the accumulated photocurrent in each pixel of the imaging array. DROICs are easier to integrate into a system compared to ROICs as the package size and complexity are reduced, they are less sensitive to noise and have higher bandwidth compared to analog outputs.
A Digital pixel readout integrated circuit (DPROIC) is a ROIC that uses on-chip analog-to-digital conversion
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a digital signal. An ADC may also provi ...
(ADC) within each pixel (or small group of pixels) to digitize the accumulated photocurrent within the imaging array. DPROICs have an even higher bandwidth than DROICs and can significantly increase the well capacity and dynamic range of the device.

References
* ''Digital Converters for Image Sensors'', Kenton T. Veeder, SPIE Press, 2015. * ''A 25μm pitch LWIR focal plane array with pixel-level 15-bit ADC providing high well capacity and targeting 2mK NETD'', Fabrice Guellec et al, Proceedings Volume 7660, Infrared Technology and Applications XXXVI, 2010. * ''A high-resolution, compact and low-power ADC suitable for array implementation in standard CMOS'', Christer Jansson, IEEE Transactions on circuits and systems - I: Fundamental theory and applications, Vol. 42, No. 11, November 1995. * ''Digital Pixel Readout Integrated Circuit for High Dynamic Range Infrared Imaging Applications'', Phase I SBIR, Technology report, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, July 2018. * ''Digital pixel readout integrated circuit architectures for LWIR'', Shafique, A., Yaziki, M., Kayahan, H., Ceylan, O., Gurbuz, Y., Proceedings Volume 9451, Infrared Technology and Applications XLI; 94510V, 2015. Integrated circuits Detectors * ''Digital-Pixel Focal Plane Array Technology'', Schultz, K., et al, Lincoln Laboratory Journal, Vol. 20, No. 2, 2014. *''Sensors, Space Probes and Wi-Fi Cybersecurity, Oh My!'', Maxfield, Max., Electronic Engineering Journal, February, 2020. *''Digital Pixel Infrared Imaging Boosts Camera Speed and Performance'', Bannatyne, R., Vision Systems Design, June 2020. {{electronics-stub