|
Flutter Valve
A flutter valve (also known as the Heimlich valve after its inventor, Henry Heimlich) is a Check_valve, one-way valve used in respiratory medicine to prevent air from travelling back along a chest tube. One can also use a Chest_drainage_management, chest drainage management system, which typically enables vacuum to be applied along with quantifying the effluent. However, it is much larger with more tubing, which may encumber the patient. It is most commonly used to help remove air from a pneumothorax. The valve is usually designed as a rubber sleeve within a plastic case where the rubber sleeve is arranged so that when air passes through the valve one way the sleeve opens and lets the air through. However, when air is sucked back the other way, the sleeve closes off and no air is allowed backwards. This construction enables it to act as a one-way valve allowing air (or fluid) to flow only one way along the drainage tube. The end of the drainage tube is placed inside the patient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heimlich Valve
A flutter valve (also known as the Heimlich valve after its inventor, Henry Heimlich) is a one-way valve used in respiratory medicine to prevent air from travelling back along a chest tube. One can also use a chest drainage management system, which typically enables vacuum to be applied along with quantifying the effluent. However, it is much larger with more tubing, which may encumber the patient. It is most commonly used to help remove air from a pneumothorax. The valve is usually designed as a rubber sleeve within a plastic case where the rubber sleeve is arranged so that when air passes through the valve one way the sleeve opens and lets the air through. However, when air is sucked back the other way, the sleeve closes off and no air is allowed backwards. This construction enables it to act as a one-way valve allowing air (or fluid) to flow only one way along the drainage tube. The end of the drainage tube is placed inside the patient's chest cavity, within the air or f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Heimlich
Henry Judah Heimlich (February 3, 1920 – December 17, 2016) was an American thoracic surgeon and medical researcher. He is widely credited as the inventor of the Heimlich maneuver, a technique of abdominal thrusts for stopping choking, first described in 1974. He also invented the Micro Trach portable oxygen system for ambulatory patients and the Heimlich Chest Drain Valve, or "flutter valve", which drains blood and air out of the chest cavity. Early life and education Heimlich was born in Wilmington, Delaware, the son of Mary (Epstein) and Philip Heimlich. His paternal grandparents were Hungarian-Jewish immigrants, and his maternal grandparents were Russian Jews. He graduated from New Rochelle High School (NY) in 1937 and from Cornell University (where he also served as drum major of the Cornell Big Red Marching Band) with a BA in 1941. At the age of 23, he received his MD from the Weill Cornell Medical College in 1943.Heimlich's ManeuversHenry J Heimlich, Prometheus Books ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
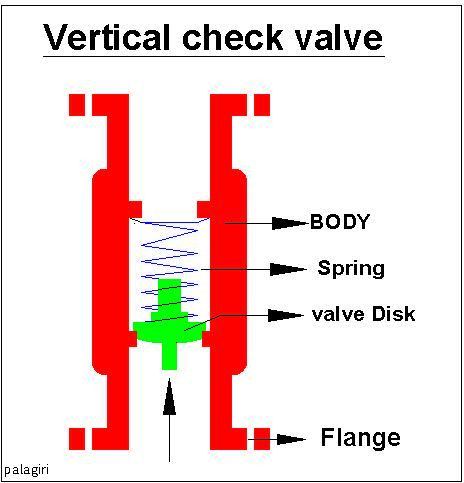
Check Valve
A check valve, non-return valve, reflux valve, retention valve, foot valve, or one-way valve is a valve that normally allows fluid (liquid or gas) to flow through it in only one direction. Check valves are two-port valves, meaning they have two openings in the body, one for fluid to enter and the other for fluid to leave. There are various types of check valves used in a wide variety of applications. Check valves are often part of common household items. Although they are available in a wide range of sizes and costs, check valves generally are very small, simple, and inexpensive. Check valves work automatically and most are not controlled by a person or any external control; accordingly, most do not have any valve handle or stem. The bodies (external shells) of most check valves are made of plastic or metal. An important concept in check valves is the cracking pressure which is the minimum differential upstream pressure between inlet and outlet at which the valve will operate. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chest Tube
A chest tube (also chest drain, thoracic catheter, tube thoracostomy or intercostal drain) is a surgical drain that is inserted through the chest wall and into the pleural space or the mediastinum in order to remove clinically undesired substances such as air (pneumothorax), excess fluid (pleural effusion or hydrothorax), blood (hemothorax), chyle ( chylothorax) or pus (empyema) from the intrathoracic space. An intrapleural chest tube is also known as a Bülau drain or an intercostal catheter (ICC), and can either be a thin, flexible silicone tube (known as a "pigtail" drain), or a larger, semi-rigid, fenestrated plastic tube, which often involves a flutter valve or underwater seal. The concept of chest drainage was first advocated by Hippocrates when he described the treatment of empyema by means of incision, cautery and insertion of metal tubes. However, the technique was not widely used until the influenza epidemic of 1918 to evacuate post-pneumonic empyema, which was first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chest Drainage Management
Chest drains are surgical drains placed within the pleural space to facilitate removal of unwanted substances (pneumothorax, air, hemothorax, blood, pleural effusion, fluid, etc.) in order to preserve respiratory system, respiratory functions and hemodynamic stability. Some chest drains may utilize a flutter valve to prevent retrograde flow, but those that do not have physical valves employ a trap (plumbing), water trap seal design, often aided by continuous suction from a suction (medicine), wall suction or a aspirator (medical device), portable vacuum pump. The active maintenance of an intrapleural negative pressure via chest drains builds the basis of chest drain management, as an intrapleural pressure lower than the surrounding atmosphere allows easier lung expansion and thus better pulmonary alveolus, alveolar ventilation (physiology), ventilation and gas exchange. History The so-called “central vacuum” was the first sub-atmospheric pressure device available. Sub-atmos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve is formed by an area of damaged tissue, and the amount of air in the space between chest wall and lungs increases; this is called a tension pneumothorax. This can cause a steadily worsening oxygen shortage and low blood pressure. This leads to a type of shock called obstructive shock, which can be fatal unless reversed. Very rarely, both lungs may be affected by a pneumothorax. It is often called a "collapsed lung", although that term may also refer to atelectasis. A primary spontaneous pneumothorax is one that occurs without an apparent cause and in the absence of significant lung disease. A secondary spontaneous pneumothorax occurs in the presence of existing lung disease. Smoking increases the risk of primary spontaneous pneumothora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous Emphysema
Subcutaneous emphysema (SCE, SE) occurs when gas or air accumulates and seeps under the skin, where normally no gas should be present. ''Subcutaneous'' refers to the subcutaneous tissue, and ''emphysema'' refers to trapped air pockets resembling the pneumatosis seen in pulmonary emphysema. Since the air generally comes from the chest cavity, subcutaneous emphysema usually occurs around the upper torso, such as on the chest, neck, face, axillae and arms, where it is able to travel with little resistance along the loose connective tissue within the superficial fascia. Subcutaneous emphysema has a characteristic crackling-feel to the touch, a sensation that has been described as similar to touching warm Rice Krispies. This sensation of air under the skin is known as ''subcutaneous crepitation,'' a form of Crepitus. Numerous etiologies of subcutaneous emphysema have been described. Pneumomediastinum was first recognized as a medical entity by Laennec, who reported it as a conseq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empyema
An empyema () is a collection or gathering of pus within a naturally existing anatomical cavity. For example, pleural empyema is empyema of the pleural cavity. It must be differentiated from an abscess, which is a collection of pus in a newly formed cavity. The term is from Ancient Greek, Greek ἐμπύημα, "abscess". Classification Empyema occurs in: * the pleural cavity (pleural empyema also known as pyothorax) * the thoracic cavity * the uterus (pyometra) * the Vermiform appendix, appendix (appendicitis) * the meninges (subdural empyema) * the joints (septic arthritis) * the gallbladder External links * {{Authority control Immune system Medical terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |