|
Flucloxacillin
Flucloxacillin, also known as floxacillin, is an antibiotic used to treat skin infections, external ear infections, infections of leg ulcers, diabetic foot infections, and infection of bone. It may be used together with other medications to treat pneumonia, and endocarditis. It may also be used prior to surgery to prevent ''Staphylococcus'' infections. It is not effective against methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA). It is taken by mouth or given by injection into a vein or muscle. Common side effects include an upset stomach. Other side effects may include muscle or joint pains, shortness of breath, and liver problems. It appears to be safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It should not be used in those who are allergic to penicillin. It is a narrow-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class. It is similar in effect to cloxacillin and dicloxacillin, being active against penicillinase forming bacteria. Flucloxacillin was patented in 196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicloxacillin
Dicloxacillin is a narrow-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class. It is used to treat infections caused by susceptible (non-resistant) Gram-positive bacteria.Product Information: DICLOXACILLIN SODIUM-dicloxacillin sodium capsule. Teva Pharmaceuticals USA Inc, Revised 8/2015 It is active against beta-lactamase-producing organisms such as ''Staphylococcus aureus'', which would otherwise be resistant to most penicillins. Dicloxacillin is available under a variety of trade names including Diclocil ( BMS). It was patented in 1961 and approved for medical use in 1968. Medical uses Dicloxacillin is used to treat mild-to-moderate staphylococcal infections. To decrease the development of resistance, dicloxacillin is recommended to treat infections that are suspected or proven to be caused by beta-lactamase-producing bacteria. Dicloxacillin is similar in pharmacokinetics, antibacterial activity, and indications to flucloxacillin, and the two agents are considered interc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using deep tank fermentation and then purified. A number of natural penicillins have been discovered, but only two purified compounds are in clinical use: penicillin G ( intramuscular or intravenous use) and penicillin V (given by mouth). Penicillins were among the first medications to be effective against many bacterial infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci. They are still widely used today for different bacterial infections, though many types of bacteria have developed resistance following extensive use. 10% of the population claims penicillin allergies but because the frequency of positive skin test results decreases by 10% with each year of avoidance, 90% of these patients can tolerate penicillin. Additionally, those w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
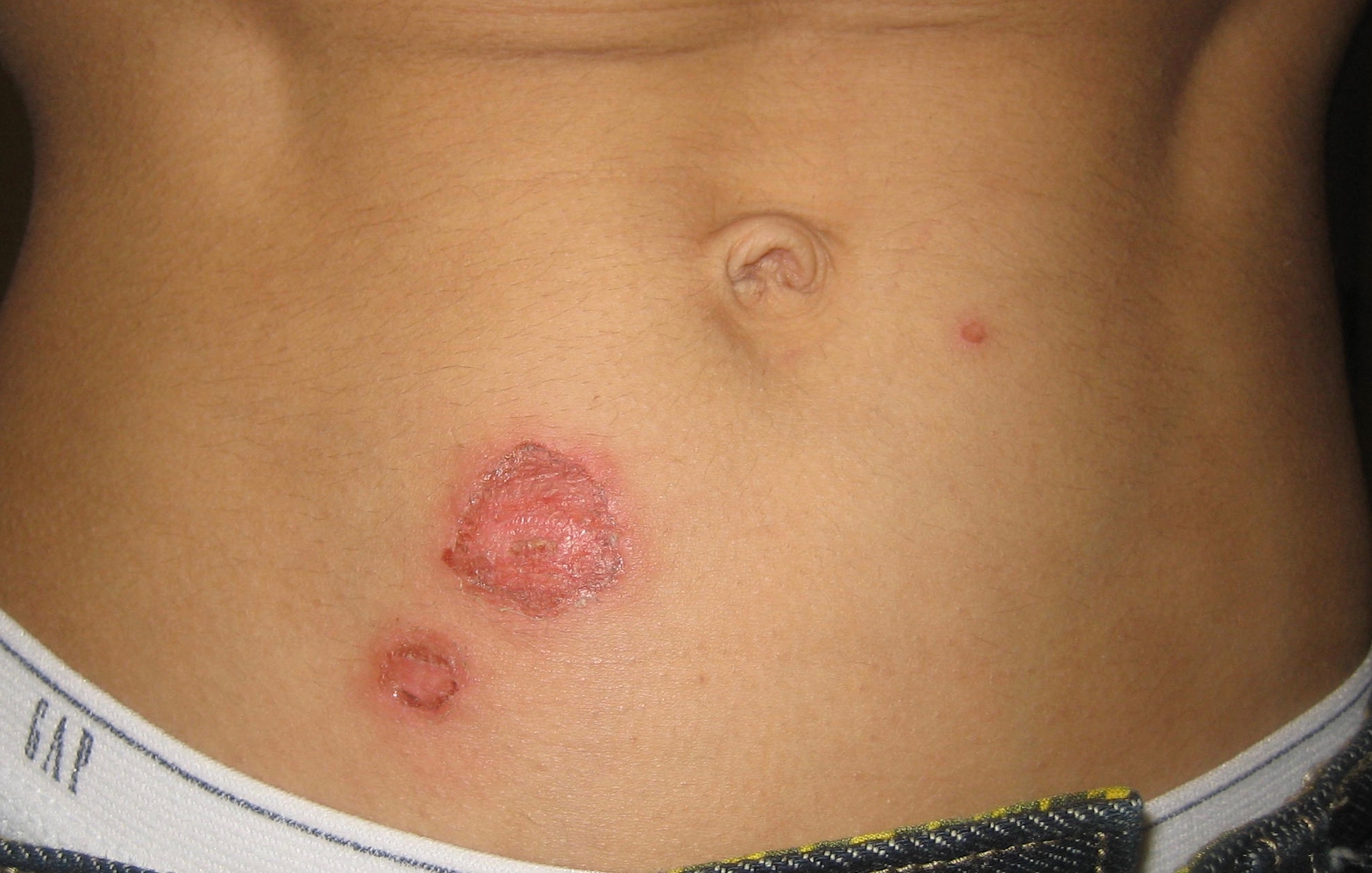
Impetigo
Impetigo is a bacterial infection that involves the superficial skin. The most common presentation is yellowish crusts on the face, arms, or legs. Less commonly there may be large blisters which affect the groin or armpits. The lesions may be painful or itchy. Fever is uncommon. It is typically due to either ''Staphylococcus aureus'' or ''Streptococcus pyogenes''. Risk factors include attending day care, crowding, poor nutrition, diabetes mellitus, contact sports, and breaks in the skin such as from mosquito bites, eczema, scabies, or herpes. With contact it can spread around or between people. Diagnosis is typically based on the symptoms and appearance. Prevention is by hand washing, avoiding people who are infected, and cleaning injuries. Treatment is typically with antibiotic creams such as mupirocin or fusidic acid. Antibiotics by mouth, such as cefalexin, may be used if large areas are affected. Antibiotic-resistant forms have been found. Impetigo affected ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folliculitis
Folliculitis is the infection and inflammation of one or more hair follicles. The condition may occur anywhere on hair-covered skin. The rash may appear as pimples that come to white tips on the face, chest, back, arms, legs, buttocks, or head. Although acne can often involve superficial infection and inflammation of some hair follicles, the condition of those follicles is usually not called folliculitis, as that term is usually reserved for the separate set of disease entities comprising infected and inflamed hair follicles with causes other than acne. Signs and symptoms * Rash (reddened skin area) * Itching skin * Pimples or pustules located around a hair or follicle; may be confused with chicken pox ** May crust over ** Typically occur on neck, armpit, or groin ** May present as genital lesions * Spreading from leg to arm to body through improper treatment with antibiotics File:Sebaceaous Hyperplasia Chronic folliculits Right Mid Chest.jpg, Chronic folliculitis surroundi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narrow-spectrum Antibiotic
A narrow- spectrum antibiotic is an antibiotic that is only able to kill or inhibit limited species of bacteria. Examples of narrow-spectrum antibiotics include fidaxomicin and sarecycline. Advantages * Narrow-spectrum antibiotic allow to kill or inhibit only those bacteria species that are unwanted (i.e. causing disease). As such, it leaves most of the beneficial bacteria unaffected, hence minimizing the collateral damage on the microbiota. *Low propensity for bacterial resistance Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. P ... development. Disadvantages Often, the exact species of bacteria causing the illness is unknown, in which case narrow-spectrum antibiotics can't be used, and broad-spectrum antibiotics are used instead. To know the exact species of bacteria causing the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrotising Fasciitis
Necrotizing fasciitis (NF), also known as flesh-eating disease, is a bacterial infection that results in the death of parts of the body's soft tissue. It is a severe disease of sudden onset that spreads rapidly. Symptoms usually include red or purple skin in the affected area, severe pain, fever, and vomiting. The most commonly affected areas are the limbs and perineum. Typically, the infection enters the body through a break in the skin such as a cut or burn. Risk factors include poor immune function such as from diabetes or cancer, obesity, alcoholism, intravenous drug use, and peripheral artery disease. It does not typically spread between people. The disease is classified into four types, depending on the infecting organism. Between 55 and 80% of cases involve more than one type of bacteria. Methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) is involved in up to a third of cases. Medical imaging is often helpful to confirm the diagnosis. Necrotizing fasciitis may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erysipelas
Erysipelas () is a relatively common bacterial infection of the superficial layer of the skin ( upper dermis), extending to the superficial lymphatic vessels within the skin, characterized by a raised, well-defined, tender, bright red rash, typically on the face or legs, but which can occur anywhere on the skin. It is a form of cellulitis and is potentially serious. Erysipelas is usually caused by the bacteria ''Streptococcus pyogenes'', also known as ''group A β-hemolytic streptococci'', which enters the body through a break in the skin, such as a scratch or an insect bite. It is more superficial than cellulitis, and is typically more raised and demarcated. The term comes from the Greek ἐρυσίπελας (''erysípelas''), meaning "red skin". In animals, erysipelas is a disease caused by infection with the bacterium '' Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae''. The disease caused in animals is called Diamond Skin Disease, which occurs especially in pigs. Heart valves and skin are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is usually a bacterial infection involving the inner layers of the skin. It specifically affects the dermis and subcutaneous fat. Signs and symptoms include an area of redness which increases in size over a few days. The borders of the area of redness are generally not sharp and the skin may be swollen. While the redness often turns white when pressure is applied, this is not always the case. The area of infection is usually painful. Lymphatic vessels may occasionally be involved, and the person may have a fever and feel tired. The legs and face are the most common sites involved, although cellulitis can occur on any part of the body. The leg is typically affected following a break in the skin. Other risk factors include obesity, leg swelling, and old age. For facial infections, a break in the skin beforehand is not usually the case. The bacteria most commonly involved are streptococci and ''Staphylococcus aureus''. In contrast to cellulitis, erysipelas is a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecthyma
Ecthyma( ec·thy·ma , \ ek-ˈthī-mə )is a variation of impetigo Impetigo is a bacterial infection that involves the superficial skin. The most common presentation is yellowish crusts on the face, arms, or legs. Less commonly there may be large blisters which affect the groin or armpits. The lesions may be ..., presenting at a deeper level of tissue. It is usually associated with Group A (beta-hemolytic) Streptococcus (abbreviated GAS). See also * Ecthyma gangrenosum References External links {{Bacterial cutaneous infections Bacterium-related cutaneous conditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbuncles
A carbuncle is a cluster of boils caused by bacterial infection, most commonly with ''Staphylococcus aureus'' or ''Streptococcus pyogenes''. The presence of a carbuncle is a sign that the immune system is active and fighting the infection. The infection is contagious and may spread to other areas of the body, or other people; those living in the same residence may develop carbuncles at the same time. In the early 21st century, infection involving methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) has become more common. Signs and symptoms A carbuncle is a cluster of several boils, which is typically filled with purulent exudate (dead neutrophils, phagocytized bacteria, and other cellular components). Fluid may drain freely from the carbuncle, or intervention involving an incision and drainage procedure may be needed. Carbuncles may develop anywhere, but they are most common on the back and the nape of the neck. A carbuncle is palpable and can range in size to be as sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcus Pyogenes
''Streptococcus pyogenes'' is a species of Gram-positive, aerotolerant bacteria in the genus '' Streptococcus''. These bacteria are extracellular, and made up of non-motile and non-sporing cocci (round cells) that tend to link in chains. They are clinically important for humans, as they are an infrequent, but usually pathogenic, part of the skin microbiota that can cause Group A streptococcal infection. ''S. pyogenes'' is the predominant species harboring the Lancefield group A antigen, and is often called group A ''Streptococcus'' (GAS). However, both '' Streptococcus dysgalactiae'' and the '' Streptococcus anginosus'' group can possess group A antigen as well. Group A streptococci, when grown on blood agar, typically produce small (2–3 mm) zones of beta-hemolysis, a complete destruction of red blood cells. The name group A (beta-hemolytic) ''Streptococcus'' (GABHS) is thus also used. The species name is derived from Greek words meaning 'a chain' () of berri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetic Foot Infection
Diabetic foot infection is any infection of the foot in a diabetic person. The most frequent cause of hospitalization for diabetic patients is due to foot infections. Symptoms may include pus from a wound, redness, swelling, pain, warmth, tachycardia, or tachypnea. Complications can include infection of the bone, tissue death, amputation, or sepsis. They are common and occur equally frequently in males and females. Older people are more commonly affected. They most often form following a diabetic foot ulcer, though not all foot ulcers become infected. Diabetic foot ulcers can be caused by vascular disease or neuropathy and its prevalence occurs in approximately 25% of diabetics throughout their lifetime. Some risk factors for developing diabetic foot infections include history of repeated foot ulcers, foot ulcers lasting for longer than 30 days, poor control over blood glucose levels, peripheral neuropathy, renal impairment, peripheral artery disease, injury or trauma to foot, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |