|
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is usually a bacterial infection involving the inner layers of the skin. It specifically affects the dermis and subcutaneous fat. Signs and symptoms include an area of redness which increases in size over a few days. The borders of the area of redness are generally not sharp and the skin may be swollen. While the redness often turns white when pressure is applied, this is not always the case. The area of infection is usually painful. Lymphatic vessels may occasionally be involved, and the person may have a fever and feel tired. The legs and face are the most common sites involved, although cellulitis can occur on any part of the body. The leg is typically affected following a break in the skin. Other risk factors include obesity, leg swelling, and old age. For facial infections, a break in the skin beforehand is not usually the case. The bacteria most commonly involved are streptococci and ''Staphylococcus aureus''. In contrast to cellulitis, erysipelas is a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erysipelas
Erysipelas () is a relatively common bacterial infection of the superficial layer of the skin ( upper dermis), extending to the superficial lymphatic vessels within the skin, characterized by a raised, well-defined, tender, bright red rash, typically on the face or legs, but which can occur anywhere on the skin. It is a form of cellulitis and is potentially serious. Erysipelas is usually caused by the bacteria ''Streptococcus pyogenes'', also known as ''group A β-hemolytic streptococci'', which enters the body through a break in the skin, such as a scratch or an insect bite. It is more superficial than cellulitis, and is typically more raised and demarcated. The term comes from the Greek ἐρυσίπελας (''erysípelas''), meaning "red skin". In animals, erysipelas is a disease caused by infection with the bacterium '' Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae''. The disease caused in animals is called Diamond Skin Disease, which occurs especially in pigs. Heart valves and skin are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrotizing Fasciitis
Necrotizing fasciitis (NF), also known as flesh-eating disease, is a bacterial infection that results in the death of parts of the body's soft tissue. It is a severe disease of sudden onset that spreads rapidly. Symptoms usually include red or purple skin in the affected area, severe pain, fever, and vomiting. The most commonly affected areas are the limbs and perineum. Typically, the infection enters the body through a break in the skin such as a cut or burn. Risk factors include poor immune function such as from diabetes or cancer, obesity, alcoholism, intravenous drug use, and peripheral artery disease. It does not typically spread between people. The disease is classified into four types, depending on the infecting organism. Between 55 and 80% of cases involve more than one type of bacteria. Methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) is involved in up to a third of cases. Medical imaging is often helpful to confirm the diagnosis. Necrotizing fasciitis may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
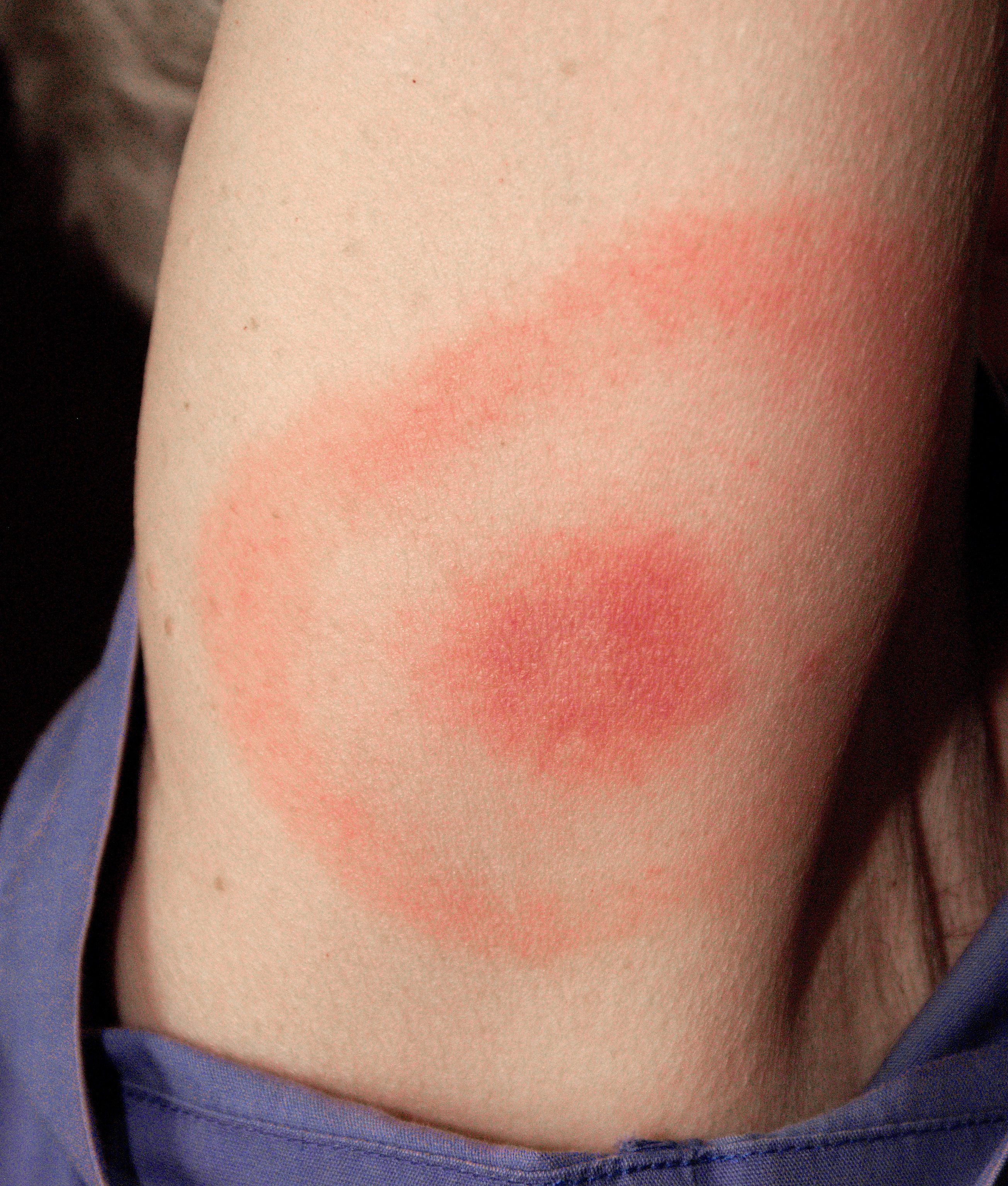
Lyme Disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a vector-borne disease caused by the '' Borrelia'' bacterium, which is spread by ticks in the genus '' Ixodes''. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migrans (EM), which appears at the site of the tick bite about a week afterwards. The rash is typically neither itchy nor painful. Approximately 70–80% of infected people develop a rash. Early diagnosis can be difficult. Other early symptoms may include fever, headaches and tiredness. If untreated, symptoms may include loss of the ability to move one or both sides of the face, joint pains, severe headaches with neck stiffness or heart palpitations. Months to years later repeated episodes of joint pain and swelling may occur. Occasionally shooting pains or tingling in the arms and legs may develop. Despite appropriate treatment about 10 to 20% of those affected develop joint pains, memory problems and tiredness for at least six months. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the feet, spine, and hips are most commonly involved in adults. The cause is usually a bacterial infection, but rarely can be a fungal infection. It may occur by spread from the blood or from surrounding tissue. Risks for developing osteomyelitis include diabetes, intravenous drug use, prior removal of the spleen, and trauma to the area. Diagnosis is typically suspected based on symptoms and basic laboratory tests as C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).This is because plain radiographs are unremarkable in the first few days following acute infection. Diagnosis is further confirmed by blood tests, medical imaging, or bone biopsy. Treatment of bacterial osteomyelitis often involves both antimicrobials and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends beyond the swelling. Carbuncles and boils are types of abscess that often involve hair follicles, with carbuncles being larger. They are usually caused by a bacterial infection. Often many different types of bacteria are involved in a single infection. In many areas of the world, the most common bacteria present is '' methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus''. Rarely, parasites can cause abscesses; this is more common in the developing world. Diagnosis of a skin abscess is usually made based on what it looks like and is confirmed by cutting it open. Ultrasound imaging may be useful in cases in which the diagnosis is not clear. In abscesses around the anus, computer tomography (CT) may be important to look for deeper infection. St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stasis Dermatitis
Stasis dermatitis refers to the skin changes that occur in the leg as a result of "stasis" or blood pooling from insufficient venous return; the alternative name of varicose eczema comes from a common cause of this being varicose veins. Insufficient venous return results in increased pressure in the capillaries with the result that both fluid and cells may "leak" out of the capillaries. This results in red cells breaking down, with iron containing hemosiderin possibly contributing to the pathology of this entity. Symptoms Stasis dermatitis may be characterized by: * Skin that appears thin, brown and tissue-like, with possible skin lesions (macule or patches), red spots, superficial skin irritation and/or darkening and/or thickening of the skin at the ankles or legs * Weak skin may ulcerate in some areas and legs, ankles, or other areas may become swollen * Open sores, ulcers * Itching and/or leg pains * Sometimes pain may persist from swollen tissues and may feel like "stabbin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. ''S. aureus'' is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant ''S. aureu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus
Methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) is a group of Gram-positive bacteria that are genetically distinct from other strains of ''Staphylococcus aureus''. MRSA is responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. It caused more than 100,000 deaths attributable to antimicrobial resistance in 2019. MRSA is any strain of ''S. aureus'' that has developed (through natural selection) or acquired (through horizontal gene transfer) a multiple drug resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. Beta-lactam (β-lactam) antibiotics are a broad-spectrum group that include some penams (penicillin derivatives such as methicillin and oxacillin) and cephems such as the cephalosporins. Strains unable to resist these antibiotics are classified as methicillin-susceptible ''S. aureus'', or MSSA. MRSA is common in hospitals, prisons, and nursing homes, where people with open wounds, invasive devices such as catheters, and weakened immune systems are at greater risk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enlarged veins in the affected area, but some DVTs have no symptoms. The most common life-threatening concern with DVT is the potential for a clot to embolize (detach from the veins), travel as an embolus through the right side of the heart, and become lodged in a pulmonary artery that supplies blood to the lungs. This is called a pulmonary embolism (PE). DVT and PE comprise the cardiovascular disease of venous thromboembolism (VTE). About two-thirds of VTE manifests as DVT only, with one-third manifesting as PE with or without DVT. The most frequent long-term DVT complication is post-thrombotic syndrome, which can cause pain, swelling, a sensation of heaviness, itching, and in severe cases, ulcers. Recurrent VTE occurs in about 30% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalexin
Cefalexin, also spelled cephalexin, is an antibiotic that can treat a number of bacterial infections. It kills gram-positive and some gram-negative bacteria by disrupting the growth of the bacterial cell wall. Cefalexin is a beta-lactam antibiotic within the class of first-generation cephalosporins. It works similarly to other agents within this class, including intravenous cefazolin, but can be taken by mouth. Cefalexin can treat certain bacterial infections, including those of the middle ear, bone and joint, skin, and urinary tract. It may also be used for certain types of pneumonia and strep throat and to prevent bacterial endocarditis. Cefalexin is not effective against infections caused by methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA), most ''Enterococcus'', or ''Pseudomonas''. Like other antibiotics, cefalexin cannot treat viral infections, such as the flu, common cold or acute bronchitis. Cefalexin can be used in those who have mild or moderate allergies to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloxacillin
Cloxacillin is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes impetigo, cellulitis, pneumonia, septic arthritis, and otitis externa. It is not effective for methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA). It is used by mouth and by injection. Side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and allergic reactions including anaphylaxis. ''Clostridium difficile'' diarrhea may also occur. It is not recommended in people who have previously had a penicillin allergy. Use during pregnancy appears to be relatively safe. Cloxacillin is in the penicillin family of medications. Cloxacillin was patented in 1960 and approved for medical use in 1965. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is not commercially available in the United States. Mechanism of action It is semisynthetic and in the same class as penicillin. Cloxacillin is used against staphylococci that produce beta-lactamase, due to its large R chain, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is an antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections. These include middle ear infection, strep throat, pneumonia, skin infections, and urinary tract infections among others. It is taken by mouth, or less commonly by injection. Common adverse effects include nausea and rash. It may also increase the risk of yeast infections and, when used in combination with clavulanic acid, diarrhea. It should not be used in those who are allergic to penicillin. While usable in those with kidney problems, the dose may need to be decreased. Its use in pregnancy and breastfeeding does not appear to be harmful. Amoxicillin is in the beta-lactam family of antibiotics. Amoxicillin was discovered in 1958 and came into medical use in 1972. Amoxil was approved for medical use in the United States in 1974, and in the United Kingdom in 1977. It is on the (WHO) World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is one of the most commonly prescribed antibi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |