|
Flt3L
Fms-related tyrosine kinase 3 ligand (FLT3LG) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''FLT3LG'' gene. Flt3 ligand (FL) is a haematopoiesis, hematopoietic four helical bundle cytokine. It is structurally homologous to stem cell factor (SCF) and colony stimulating factor 1 (Macrophage colony-stimulating factor, CSF-1). In synergy with other growth factors, Flt3 ligand stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of various blood cell progenitor cell, progenitors. For example, it is a major growth factor stimulating the growth of dendritic cells. FLT3L functions as a cytokine and growth factor that increases the number of immune cells (lymphocytes (B cells and T cells)) by activating the hematopoietic progenitors. It acts by binding to and activating FLT3 (CD135) which is found on what (in mice) are called multipotent progenitor (MPP) and common lymphoid progenitor (CLP) cells. It also induces the mobilization of the hematopoietic progenitors and stem cells in vivo which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLT3
Cluster of differentiation antigen 135 (CD135) also known as fms like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT-3), receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3, or fetal liver kinase-2 (Flk2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FLT3'' gene. FLT3 is a cytokine receptor which belongs to the receptor tyrosine kinase class III. CD135 is the receptor for the cytokine Flt3 ligand (FLT3L). It is expressed on the surface of many hematopoietic progenitor cells. Signalling of FLT3 is important for the normal development of haematopoietic stem cells and progenitor cells. The FLT3 gene is one of the most frequently mutated genes in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). High levels of wild-type FLT3 have been reported for blast cells of some AML patients without FLT3 mutations. These high levels may be associated with worse prognosis. Structure FLT3 is composed of five extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains, an extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain, a juxtamembrane domain and a tyrosine-kinase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multipotent Progenitor
Lymphopoiesis (lĭm'fō-poi-ē'sĭs) (or lymphocytopoiesis) is the generation of lymphocytes, which are one of the five types of white blood cells (WBCs). It is more formally known as lymphoid hematopoiesis. Disruption in lymphopoiesis can lead to a number of lymphoproliferative disorders, such as the lymphomas and lymphoid leukemias. Terminology Lymphocytes are considered to be of the lymphoid lineage as opposed to other lineages of blood cells such as the myeloid lineage and the erythroid lineage. Nomenclature, the system of naming things properly, is not trivial in this case because although lymphocytes are found in the bloodstream and originate in the bone marrow, they principally belong to the separate lymphatic system which interacts with the blood circulation. Lymphopoiesis is now usually used interchangeably with the term "lymphocytopoiesis" - the making of lymphocytes - but other sources may distinguish between the two, stating that "lymphopoiesis" additionally refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
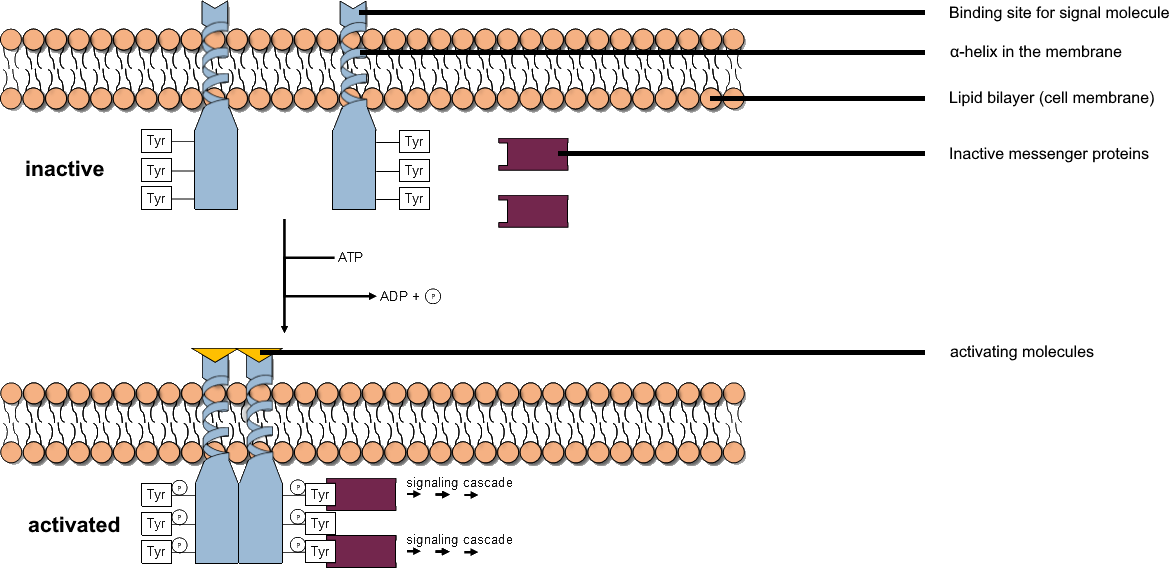
Tyrosine Kinase
A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the tyrosine residues of specific proteins inside a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions. Tyrosine kinases belong to a larger class of enzymes known as protein kinases which also attach phosphates to other amino acids such as serine and threonine. Phosphorylation of proteins by kinases is an important mechanism for communicating signals within a cell (signal transduction) and regulating cellular activity, such as cell division. Protein kinases can become mutated, stuck in the "on" position, and cause unregulated growth of the cell, which is a necessary step for the development of cancer. Therefore, kinase inhibitors, such as imatinib and osimertinib, are often effective cancer treatments. Most tyrosine kinases have an associated protein tyrosine phosphatase, which removes the phosphate group. Reaction Protein kinases are a group of enzymes that possess a catal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STAT5A
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''STAT5A'' gene. ''STAT5A'' orthologs have been identified in several placentals for which complete genome data are available. Structure STAT5a shares the same six functional domains as the other members of the STAT family. It contains 20 amino acids unique to its C-terminal domain and is 96% similar to its homolog, STAT5b. The six functional domains and their corresponding amino acid positions are as follows: * N-Terminal domain (aa1-144): stabilized interactions to form tetramers * Coiled-coil domain (aa145-330): interacts with chaperones and facilitates protein-protein interactions for transcriptional regulation * DNA binding domain (aa331-496): permits binding to consensus gamma-interferon activation sequence (GAS) * Linker domain (aa497-592): stabilizes DNA binding * Src Homology 2 domain (aa593-685): mediates receptor-specific recruitment and STAT dimerization via phosphoryla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAP Kinase
A mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK or MAP kinase) is a type of protein kinase that is specific to the amino acids serine and threonine (i.e., a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase). MAPKs are involved in directing cellular responses to a diverse array of stimuli, such as mitogens, osmotic stress, heat shock and proinflammatory cytokines. They regulate cell functions including proliferation, gene expression, differentiation, mitosis, cell survival, and apoptosis. MAP kinases are found in eukaryotes only, but they are fairly diverse and encountered in all animals, fungi and plants, and even in an array of unicellular eukaryotes. MAPKs belong to the CMGC (CDK/MAPK/GSK3/CLK) kinase group. The closest relatives of MAPKs are the cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). Discovery The first mitogen-activated protein kinase to be discovered was ERK1 (MAPK3) in mammals. Since ERK1 and its close relative ERK2 (MAPK1) are both involved in growth factor signaling, the family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoxanthine
Hypoxanthine is a naturally occurring purine derivative. It is occasionally found as a constituent of nucleic acids, where it is present in the anticodon of tRNA in the form of its nucleoside inosine. It has a tautomer known as 6-hydroxypurine. Hypoxanthine is a necessary additive in certain cells, bacteria, and parasite cultures as a substrate and nitrogen source. For example, it is commonly a required reagent in malaria parasite cultures, since ''Plasmodium falciparum'' requires a source of hypoxanthine for nucleic acid synthesis and energy metabolism. In August 2011, a report, based on NASA studies with meteorites found on Earth, was published suggesting hypoxanthine and related organic molecules, including the DNA and RNA components adenine and guanine, may have been formed extraterrestrially in outer space. The '' Pheretima aspergillum'' worm, used in Chinese medicine preparations, contains hypoxanthine. Reactions It is one of the products of the action of xanthine oxidase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mast Cell
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a part of the immune and neuroimmune systems. Mast cells were discovered by Paul Ehrlich in 1877. Although best known for their role in allergy and anaphylaxis, mast cells play an important protective role as well, being intimately involved in wound healing, angiogenesis, immune tolerance, defense against pathogens, and vascular permeability in brain tumours. The mast cell is very similar in both appearance and function to the basophil, another type of white blood cell. Although mast cells were once thought to be tissue-resident basophils, it has been shown that the two cells develop from different hematopoietic lineages and thus cannot be the same cells. Structure Mast cells are very similar to basophil granulocytes (a class of white ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. Malaria is caused by single-celled microorganisms of the ''Plasmodium'' group. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. The mosquito bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito's saliva into a person's blood. The parasites travel to the liver where they mature and reproduce. Five species of ''Plasmodium'' can infect and be spread by h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and the adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in those tissues that are in contact with the external environment, such as the skin (where there is a specialized dendritic cell type called the Langerhans cell) and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the ''dendrites'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance, these are structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and the adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in those tissues that are in contact with the external environment, such as the skin (where there is a specialized dendritic cell type called the Langerhans cell) and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the ''dendrites'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance, these are structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) are a rare type of immune cell that are known to secrete large quantities of type 1 interferon (IFNs) in response to a viral infection. They circulate in the blood and are found in peripheral lymphoid organs. They develop from bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells and constitute 2% of nucleated cells) and bone marrow and evidence (i.e. cytopenias) of bone marrow failure. Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasm has a high rate of recurrence following initial treatments with various chemotherapy regimens. In consequence, the disease has a poor overall prognosis and newer chemotherapeutic and novel non-chemotherapeutic drug regimens to improve the situation are under study. Role in immunity Upon stimulation and subsequent activation of TLR7 and TLR9, these cells produce large amounts (up to 1,000 times more than other cell type) of type I interferon (mainly IFN-α and IFN-β), which are critical anti-viral compounds mediating a wide range of ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell in a cell lineage. They are found in both embryonic and adult organisms, but they have slightly different properties in each. They are usually distinguished from progenitor cells, which cannot divide indefinitely, and precursor or blast cells, which are usually committed to differentiating into one cell type. In mammals, roughly 50–150 cells make up the inner cell mass during the blastocyst stage of embryonic development, around days 5–14. These have stem-cell capability. ''In vivo'', they eventually differentiate into all of the body's cell types (making them pluripotent). This process starts with the differentiation into the three germ layers – the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm – at the gastrulation stage. However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |