|
Floating Island
A floating island is a mass of floating aquatic plants, mud, and peat ranging in thickness from several centimeters to a few meters. Floating islands are a common natural phenomenon that are found in many parts of the world. They exist less commonly as an artificial phenomenon. Floating islands are generally found on marshlands, lakes, and similar wetland locations, and can be many hectares in size. Natural occurrences Sometimes referred to as ''tussocks'', ''floatons'', or ''suds'', natural floating islands are composed of vegetation growing on a buoyant mat of plant roots or other organic detritus. In aquatic regions of Northwestern Europe several hundred hectares or thousand acres of floating meadows (German ''Schwingrasen'', Dutch ''trilveen'') have been preserved, which are partly used as agricultural land, partly as nature reserves. They typically occur when growths of cattails, bulrush, sedge, and reeds extend outward from the shoreline of a wetland area. As the wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Floating Island
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena. The word ''nature'' is borrowed from the Old French ''nature'' and is derived from the Latin word ''natura'', or "essential qualities, innate disposition", and in ancient times, literally meant "birth". In ancient philosophy, ''natura'' is mostly used as the Latin translation of the Greek word ''physis'' (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics of plants, animals, and other features of the world to develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pumice Raft
A pumice raft is a floating raft of pumice created by some eruptions of submarine volcanoes or coastal subaerial volcanoes. Biologists suggest that animals and plants have migrated from island to island on pumice rafts. Pumice rafts have unique characteristics such as the highest surface-area-to-volume ratio known for any rock type, long term flotation and beaching in the tidal zone, exposure to a variety of conditions, including dehydration, and an ability to absorb many potentially advantageous elements/compounds. For at least these reasons, astrobiologists have hypothetically proposed pumice rafts as an ideal substrate for the origin of life. Notable examples Pumice rafts drifted to Fiji in 1979 and 1984 from eruptions around Tonga, and some were reportedly wide. Volcanic activity in the South Pacific near Tonga on August 12, 2006 caused the emergence of a new island. The crew of the ''Maiken'', a yacht that had left the northern Tongan islands group of Vava'u in August ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiral Island
Spiral Island was a floating artificial island built in Mexico by British artist Richart "Reishee" Sowa. It was destroyed by Hurricane Emily in 2005. A replacement, Joyxee Island, had been open for tours since 2008, but closed after it was damaged by storms and the local authority ordered its removal. Spiral Island was featured in newspapers and TV documentaries around the world, including in Japan and South Korea, as well as an episode of the ''Ripley's Believe It or Not!'' TV series, and on the MTV program ''Extreme Cribs'' in 2011. Spiral Island The first Spiral island was located in a lagoon near Puerto Aventuras, on the Caribbean coast of Mexico south of Cancún; Richart Sowa began constructing it in 1998. He filled nets with empty discarded plastic bottles to support a structure of plywood and bamboo, on which he poured sand and planted numerous plants, including mangroves. The island sported a two-story house, a solar oven, a self-composting toilet, and three beaches. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquaponics
Aquaponics is a food production system that couples aquaculture (raising aquatic animals such as fish, crayfish, snails or prawns in tanks) with hydroponics (cultivating plants in water) whereby the nutrient-rich aquaculture water is fed to hydroponically grown plants. As existing hydroponic and aquaculture farming techniques form the basis of all aquaponic systems, the size, complexity, and types of foods grown in an aquaponic system can vary as much as any system found in either distinct farming discipline. History Aquaponics has ancient roots, although there is some debate on its first occurrence: *Aztec cultivated agricultural islands known as '' chinampas'' in a system considered by some to be an early form of aquaponics for agricultural use, where plants were raised on stationary (or sometime movable) islands in lake shallows and waste materials dredged from the Chinampa canals and surrounding cities were used to manually irrigate the plants. * South China and the whol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinampa
Chinampa ( nah, chināmitl ) is a technique used in Mesoamerican agriculture which relies on small, rectangular areas of fertile arable land to grow crops on the shallow lake beds in the Valley of Mexico. They are built up on wetlands of a lake or freshwater swamp for agricultural purposes, and their proportions ensure optimal moisture retention. The United Nations designated it a Globally Important Agricultural Heritage System in 2018. The Aztecs created the very first Chinampa. Although different technologies existed during the Post-classic and Colonial periods in the basin, chinampas have raised many questions on agricultural production and political development. After the Aztec Triple Alliance formed, the conquest of southern basin city-states, such as Xochimilco, was one of the first strategies of imperial expansion. Before this time, farmers maintained small-scale chinampas adjacent to their households and communities in the freshwater lakes of Xochimilco and Chalco. Chinam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
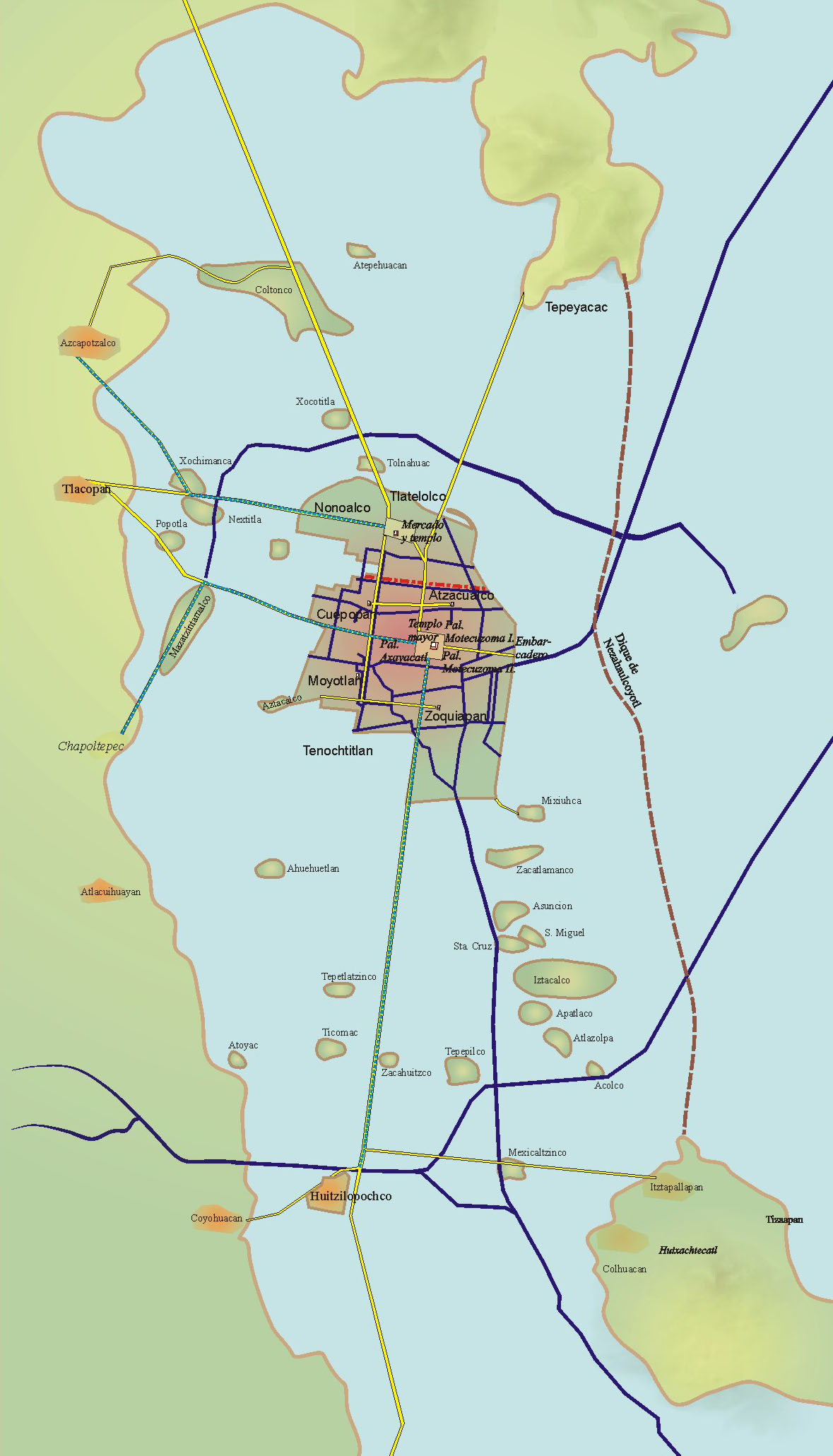
Tenochtitlan
, ; es, Tenochtitlan also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, ; es, México-Tenochtitlan was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear. The date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th anniversary of the city. The city was built on an island in what was then Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. The city was the capital of the expanding Aztec Empire in the 15th century until it was captured by the Spanish in 1521. At its peak, it was the largest city in the pre-Columbian Americas. It subsequently became a '' cabecera'' of the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Today, the ruins of are in the historic center of the Mexican capital. The World Heritage Site of contains what remains of the geography (water, boats, floating gardens) of the Mexica capital. was one of two Mexica (city-states or polities) on the island, the other being . The city is located in modern-day Mexico City. Etymolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl, Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Aztec culture was organized into city-states (''altepetl''), some of which joined to form alliances, political confederations, or empires. The Aztec Empire was a confederation of three city-states established in 1427: Tenochtitlan, city-state of the Mexica or Tenochca; Texcoco (altepetl), Texcoco; and Tlacopan, previously part of the Tepanec empire, whose dominant power was Azcapotzalco (altepetl), Azcapotzalco. Although the term Aztecs is often narrowly restricted to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, it is also broadly used to refer to Nahuas, Nahua polities or peoples of central Pre-Columbian Mexico, Mexico in the preh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colla People
The Qulla (Quechuan for ''south'', Hispanicized and mixed spellings: ''Colla, Kolla'') are an indigenous people of western Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina living in west of Jujuy and west of Salta Province. The 2004 Complementary Indigenous Survey reported 53,019 Qulla households living in Argentina. They moved freely between the borders of Argentina and Bolivia. Their lands are part of the yungas or high altitude forests at the edge of the Amazon rainforest. History The Qulla have lived in their region for centuries. Sillustani is a prehistoric Qulla cemetery in Peru, with elaborate stone ''chullpas''. Several groups made up the Qulla people, including the Zenta, and Gispira. The Qulla came into contact with Spaniards in 1540. They resisted Spanish invasion for many years but ultimately lost the Santiago Estate to the Spanish. One particularly famous rebel leader was Ñusta Willaq, a female warrior who fought the Spanish in 1780. With Argentinian independence in 1810, the situatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inca
The Inca Empire (also known as the Incan Empire and the Inka Empire), called ''Tawantinsuyu'' by its subjects, (Quechua for the "Realm of the Four Parts", "four parts together" ) was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The Inca civilization arose from the Peruvian highlands sometime in the early 13th century. The Spanish began the conquest of the Inca Empire in 1532 and by 1572, the last Inca state was fully conquered. From 1438 to 1533, the Incas incorporated a large portion of western South America, centered on the Andean Mountains, using conquest and peaceful assimilation, among other methods. At its largest, the empire joined modern-day Peru, what are now western Ecuador, western and south central Bolivia, northwest Argentina, the southwesternmost tip of Colombia and a large portion of modern-day Chile, and into a state comparable to the historical empires of Eurasia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Totora (plant)
Totora (''Schoenoplectus californicus'' subsp. ''tatora'') is a subspecies of the giant bulrush sedge. It is found in South America, notably on Lake Titicaca, the middle coast of Peru and on Easter Island in the Pacific Ocean. The genus ''Schoenoplectus'' is closely related to ''Scirpus'' and sometimes included therein. This plant can reach a height of and commonly reaches .Iltis, A., and P. Mourguiart (1992). Higher Plants: Distribution and biomass. Pp. 242-253 in: Dejoux, C., eds. (1992). Lake Titicaca: a synthesis of limnological knowledge. The word totora comes from the Quechua language. The people of the mid-coast region of Peru have used totora to build their caballitos de totora, small rowed and straddled fishing vessels, for at least 3,000 years. The Uru people, an indigenous people predating the Inca civilisation, live on Lake Titicaca upon floating islands fashioned from this plant. The Uru people also use the totora plant to make boats (''balsas'') of the bundled d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg , image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg , other_symbol = Great Seal of the State , other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal , national_motto = "Firm and Happy for the Union" , national_anthem = "National Anthem of Peru" , march = "March of Flags" , image_map = PER orthographic.svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Lima , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Peruvian Spanish, Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages = , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2017 , demonym = Peruvians, Peruvian , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Semi-presidential system, semi-presidential republic , leader_title1 = President of Peru, President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Titicaca
Lake Titicaca (; es, Lago Titicaca ; qu, Titiqaqa Qucha) is a large freshwater lake in the Andes mountains on the border of Bolivia and Peru. It is often called the highest navigable lake in the world. By volume of water and by surface area, it is also the largest lake in South America.Grove, M. J., P. A. Baker, S. L. Cross, C. A. Rigsby and G. O. Seltzer 2003 Application of Strontium Isotopes to Understanding the Hydrology and Paleohydrology of the Altiplano, Bolivia-Peru. ''Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology'' 194:281-297. Lake Titicaca has a surface elevation of . The "highest lake" claim is generally considered to refer to commercial craft. Numerous smaller bodies of water (that are not considered lakes) around the world are at higher elevations. For many years, the largest vessel afloat on the lake was the 2,200-ton (2,425 U.S. tons), SS ''Ollanta''. Today, the largest vessel is most likely the similarly sized train barge/float ''Manco Capac'', operated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)