|
Flapwheel
A flapwheel and the related flap disk is an abrasive disk, used for metal finishing. Unlike the simpler flat disks, made from a circular flat sheet of a coated abrasive, a flapwheel is made of multiple overlapping small pieces or 'flaps', bonded to a central hub. Advantages The advantages of a flapwheel over a traditional disk are twofold: * The separate flaps each attack the workpiece surface at a slightly different angle, and this varies slightly with tool angle. This avoids the common problem with flat sheets, where they produce repeated identical scratches. * Abrasive wear is distributed more evenly across the flaps, and through the length of each flap. Flaps wear from their outer ends and the sheet carrier cuts back as the abrasive coating is worn away. The wheel remains useful even as the flaps erode. Compared to flat sheets, that are discarded after only a small area of the abrasive is truly worn-out, this is a much more efficient use of the abrasive material. Developmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drill Flapwheel
A drill is a tool used for making round holes or driving fasteners. It is fitted with a bit, either a drill or driverchuck. Hand-operated types are dramatically decreasing in popularity and cordless battery-powered ones proliferating due to increased efficiency and ease of use. Drills are commonly used in woodworking, metalworking, construction, machine tool fabrication, construction and utility projects. Specially designed versions are made for miniature applications. History Around 35,000 BC, ''Homo sapiens'' discovered the benefits of the application of rotary tools. This would have rudimentarily consisted of a pointed rock being spun between the hands to bore a hole through another material. This led to the hand drill, a smooth stick, that was sometimes attached to flint point, and was rubbed between the palms. This was used by many ancient civilizations around the world including the Mayans. The earliest perforated artifacts, such as bone, ivory, shells, and antlers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coated Abrasive
upright=1.35, Sheets of sandpaper with different grit sizes (40 (coarse), 80, 150, 240, 600 (fine)). Sandpaper and glasspaper are names used for a type of coated abrasive that consists of sheets of paper or cloth with abrasive material glued to one face. There are many varieties of sandpaper, with variations in the paper or backing, the material used for the grit, grit size, and the bond. In the modern manufacture of these products, sand and glass have been replaced by other abrasives such as aluminium oxide or silicon carbide. It is common to use the name of the abrasive when describing the paper, e.g. "aluminium oxide paper", or "silicon carbide paper". Sandpaper is produced in a range of grit sizes and is used to remove material from surfaces, whether to make them smoother (for example, in painting and wood finishing), to remove a layer of material (such as old paint), or sometimes to make the surface rougher (for example, as a preparation for gluing). The grit size of sand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flap Disk
Flap may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Flap'' (film), a 1970 American film * Flap, a boss character in the arcade game ''Gaiapolis'' * Flap, a minor character in the film '' Little Nemo: Adventures in Slumberland'' Biology and healthcare * Flap (surgery), a surgical technique involving movement of vascularized tissue ** Free flap, a specific kind of surgical flap * 5-lipoxygenase activating protein (FLAP) Computing and networks * The phenomenon of some variable or resource oscillating or alternating rapidly between two states ** Route flapping, when a network router flips between different routes ** Link flap, errant behavior in a communications link Engineering and design * Flap (aeronautics), a lift augmentation device on an airplane wing, often near the trailing edge * Flapping, the up-and-down motion of a helicopter rotor * Flap, any hinged plate often used as a cover or a simple one-way valve ** Sluice or flap gate, a pressure driven water flow co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Turbine
A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part (known as the gas generator or core) and are, in the direction of flow: * a rotating gas compressor * a combustor * a compressor-driving turbine. Additional components have to be added to the gas generator to suit its application. Common to all is an air inlet but with different configurations to suit the requirements of marine use, land use or flight at speeds varying from stationary to supersonic. A propelling nozzle is added to produce thrust for flight. An extra turbine is added to drive a propeller (turboprop) or ducted fan (turbofan) to reduce fuel consumption (by increasing propulsive efficiency) at subsonic flight speeds. An extra turbine is also required to drive a helicopter rotor or land-vehicle transmission (turboshaft), marine propeller or electrical generator (power turbine). Greater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Investment Casting
Investment casting is an industrial process based on lost-wax casting, one of the oldest known metal-forming techniques. The term "lost-wax casting" can also refer to modern investment casting processes. Investment casting has been used in various forms for the last 5,000 years. In its earliest forms, beeswax was used to form patterns necessary for the casting process. Today, more advanced waxes, refractory materials and specialist alloys are typically used for making patterns. Investment casting is valued for its ability to produce components with accuracy, repeatability, versatility and integrity in a variety of metals and high-performance alloys. The fragile wax patterns must withstand forces encountered during the mould making. Much of the wax used in investment casting can be reclaimed and reused. Lost-foam casting is a modern form of investment casting that eliminates certain steps in the process. Investment casting is so named because the process invests (surrounds) the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
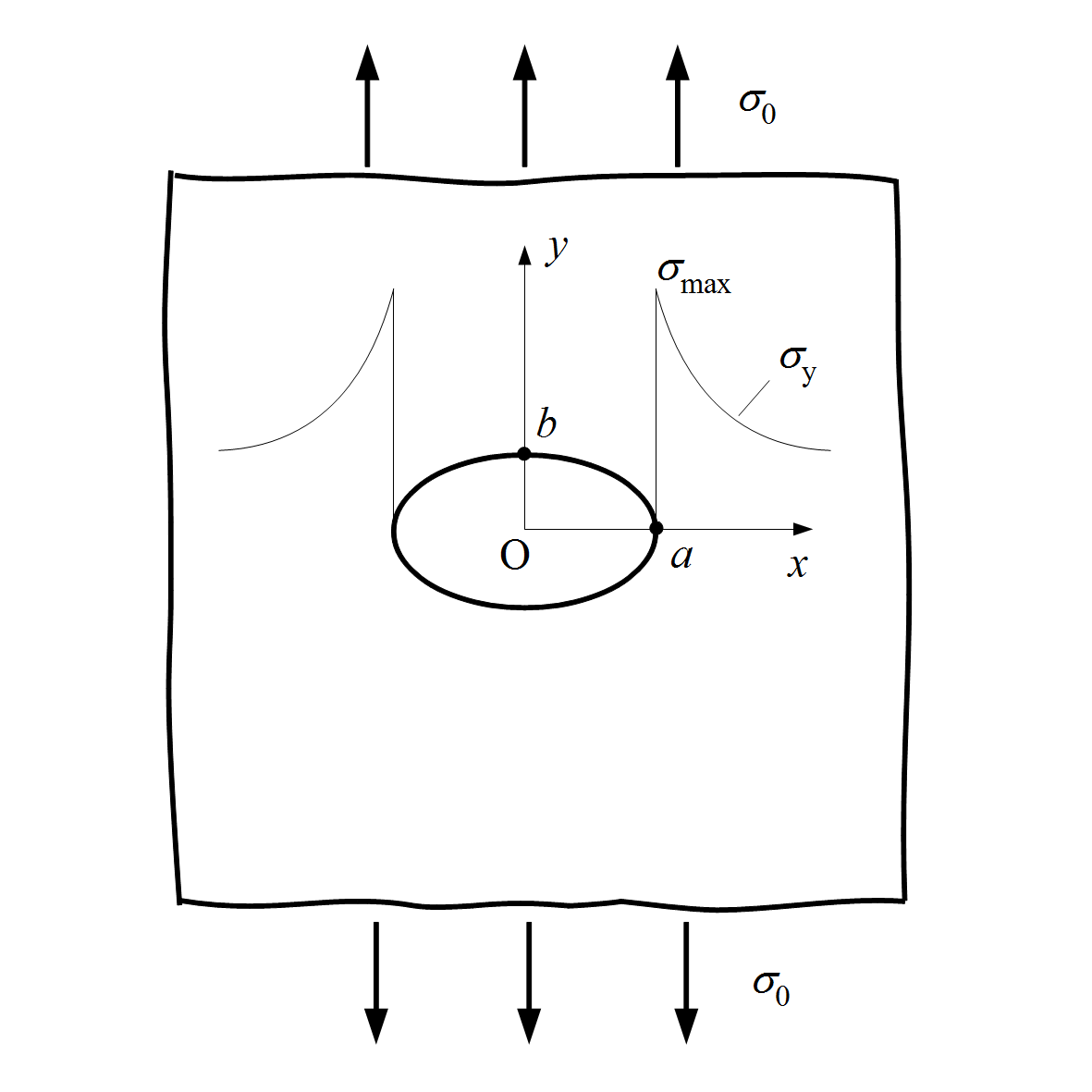
Stress Riser
In solid mechanics, a stress concentration (also called a stress raiser or a stress riser) is a location in an object where the stress is significantly greater than the surrounding region. Stress concentrations occur when there are irregularities in the geometry or material of a structural component that cause an interruption to the flow of stress. This arises from such details as holes, grooves, notches and fillets. Stress concentrations may also occur from accidental damage such as nicks and scratches. The degree of concentration of a discontinuity under typically tensile loads can be expressed as a non-dimensional stress concentration factor K_t, which is the ratio of the highest stress to the nominal far field stress. For a circular hole in an infinite plate, K_t = 3. The stress concentration factor should not be confused with the stress intensity factor, which is used to define the effect of a crack on the stresses in the region around a crack tip. For ductile materials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buffing Machine
Polishing and buffing are finishing processes for smoothing a workpiece's surface using an abrasive and a work wheel or a leather strop. Technically, ''polishing'' refers to processes that uses an abrasive that is glued to the work wheel, while ''buffing'' uses a loose abrasive applied to the work wheel. Polishing is a more aggressive process, while buffing is less harsh, which leads to a smoother, brighter finish.Oberg, p. 1439. A common misconception is that a polished surface has a mirror-bright finish, however, most mirror-bright finishes are actually buffed. Polishing is often used to enhance the appearance of an item, prevent contamination of instruments, remove oxidation, create a reflective surface, or prevent corrosion in pipes. In metallography and metallurgy, polishing is used to create a flat, defect-free surface for examination of a metal's microstructure under a microscope. Silicon-based polishing pads or a diamond solution can be used in the polishing process. Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
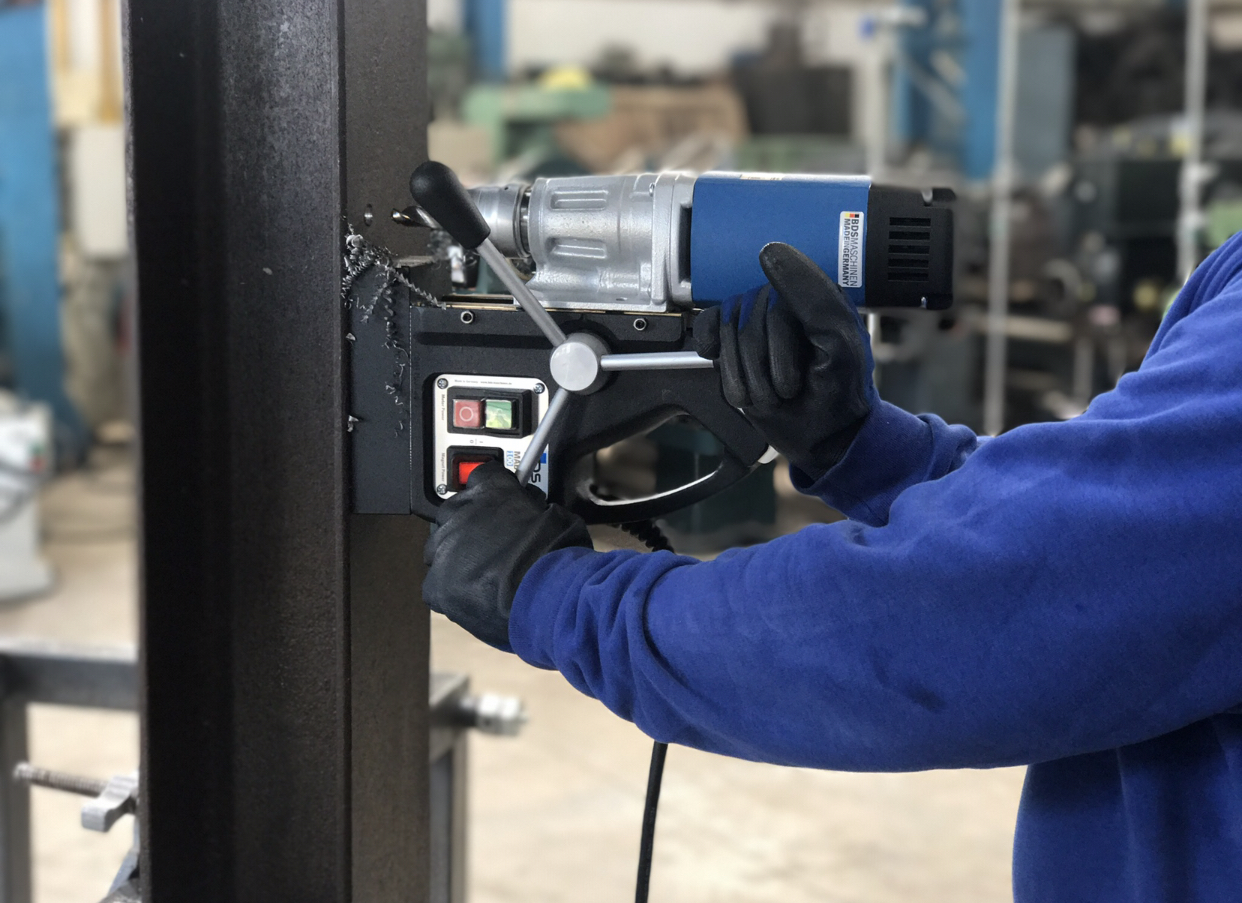
Electric Drill
A drill is a tool used for making round holes or driving fasteners. It is fitted with a bit, either a drill or driverchuck. Hand-operated types are dramatically decreasing in popularity and cordless battery-powered ones proliferating due to increased efficiency and ease of use. Drills are commonly used in woodworking, metalworking, construction, machine tool fabrication, construction and utility projects. Specially designed versions are made for miniature applications. History Around 35,000 BC, ''Homo sapiens'' discovered the benefits of the application of rotary tools. This would have rudimentarily consisted of a pointed rock being spun between the hands to bore a hole through another material. This led to the hand drill, a smooth stick, that was sometimes attached to flint point, and was rubbed between the palms. This was used by many ancient civilizations around the world including the Mayans. The earliest perforated artifacts, such as bone, ivory, shells, and antler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Grinder
An angle grinder, also known as a side grinder or disc grinder, is a handheld power tool used for grinding (abrasive cutting) and polishing. Although developed originally as tools for rigid abrasive discs, the availability of an interchangeable power source has encouraged their use with a wide variety of cutters and attachments. Angle grinders can be powered by an electric motor or compressed air. The motor drives a geared head at a right-angle on which is mounted an abrasive disc or a thinner cut-off disc, either of which can be replaced when worn. Angle grinders typically have an adjustable guard and a side-handle for two-handed operation. Certain angle grinders, depending on their speed range, can be used as sanders, employing a sanding disc with a backing pad or disc. The backing system is typically made of hard plastic, phenolic resin, or medium-hard rubber depending on the amount of flexibility desired. Angle grinders are standard equipment in metal fabrication shops an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |