|
Flag Of The Greek Orthodox Church
The Ecumenical Patriarchate and Mount Athos, and also the Greek Orthodox Churches in the diaspora under the Patriarchate use a black double-headed eagle in a yellow field as their flag or emblem. The eagle is depicted as clutching a sword and an orb with a crown above and between its two heads. An earlier variant of the flag, used in the 1980s, combined the double-headed eagle design with the blue-and-white stripes of the flag of Greece. Tomislav Todorović, 2 June 2015 The design is sometimes dubbed the "Byzantine imperial flag", and is considered—inaccurately—to have been the actual historical banner of the . The double-headed eagle was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of Greece
The national flag of Greece, popularly referred to as the "blue and white one" ( el, Γαλανόλευκη, ) or the "sky blue and white" (, ), is officially recognised by Greece as one of its national symbols and has nine equal horizontal stripes of blue alternating with white. There is a blue canton in the upper hoist-side corner bearing a white cross; the cross symbolises Eastern Orthodox Christianity. The blazon of the flag is Azure, four bars Argent; on a canton of the field a Greek cross throughout of the second. The official flag ratio is 2:3. The shade of blue used in the flag has varied throughout its history, from light blue to dark blue, the latter being increasingly used since the late 1960s. It was officially adopted by the First National Assembly at Epidaurus on 13 January 1822. The nine stripes do not have any official meaning; the most popular theory says that they represent the syllables of the phrase ("Freedom or Death"), the five blue stripes for the syllabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of Greece
The national flag of Greece, popularly referred to as the "blue and white one" ( el, Γαλανόλευκη, ) or the "sky blue and white" (, ), is officially recognised by Greece as one of its national symbols and has nine equal horizontal stripes of blue alternating with white. There is a blue canton in the upper hoist-side corner bearing a white cross; the cross symbolises Eastern Orthodox Christianity. The blazon of the flag is Azure, four bars Argent; on a canton of the field a Greek cross throughout of the second. The official flag ratio is 2:3. The shade of blue used in the flag has varied throughout its history, from light blue to dark blue, the latter being increasingly used since the late 1960s. It was officially adopted by the First National Assembly at Epidaurus on 13 January 1822. The nine stripes do not have any official meaning; the most popular theory says that they represent the syllables of the phrase ("Freedom or Death"), the five blue stripes for the syllabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of The Greek Orthodox Church
The Ecumenical Patriarchate and Mount Athos, and also the Greek Orthodox Churches in the diaspora under the Patriarchate use a black double-headed eagle in a yellow field as their flag or emblem. The eagle is depicted as clutching a sword and an orb with a crown above and between its two heads. An earlier variant of the flag, used in the 1980s, combined the double-headed eagle design with the blue-and-white stripes of the flag of Greece. Tomislav Todorović, 2 June 2015 The design is sometimes dubbed the "Byzantine imperial flag", and is considered—inaccurately—to have been the actual historical banner of the . The double-headed eagle was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaiologos
The House of Palaiologos ( Palaiologoi; grc-gre, Παλαιολόγος, pl. , female version Palaiologina; grc-gre, Παλαιολογίνα), also found in English-language literature as Palaeologus or Palaeologue, was a Byzantine Greek family that rose to nobility and produced the last and longest-ruling dynasty in the history of the Byzantine Empire. Their rule as Emperors and Autocrats of the Romans lasted almost two hundred years, from 1259 to the Fall of Constantinople in 1453. The origins of the family are unclear. Their own medieval origin stories ascribed them an ancient and prestigious origin in ancient Roman Italy, descended from some of the Romans that had accompanied Constantine the Great to Constantinople upon its foundation in 330. It is more likely that they originated significantly later in Anatolia since the earliest known member of the family, possibly its founder, Nikephoros Palaiologos, served as a commander there in the second half of the 11th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Orthodoxy
The term Greek Orthodox Church (Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also called 'Eastern Orthodox,' 'Greek Catholic,' or generally 'the Greek Church. The narrower meaning designates "any of several independent churches within the worldwide communion of asternOrthodox Christianity that retain the use of the Greek language in formal ecclesiastical settings". Etymology Historically, the term "Greek Orthodox" has been used to describe all Eastern Orthodox churches, since the term "Greek" can refer to the heritage of the Byzantine Empire. During the first eight centuries of Christian history, most major intellectual, cultural, and social developments in the Christian Church took place in the Byzantine Empire or its sphere of influence, where the Greek language was widely spoken and used for most theological writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Hoc Signo Vinces
"''In hoc signo vinces''" (, ) is a Latin phrase conventionally translated into English as "In this sign thou shalt conquer". The Latin phrase itself renders, rather loosely, the Greek phrase "", transliterated as "''en toútōi níka''" (, ), literally meaning "in this, conquer". History Lucius Caecilius Firmianus Lactantius was an early Christian author (c. 240 – c. 320) who became an advisor to the first Christian Roman emperor, Constantine I (and tutor to his son), guiding the Emperor's religious policy as it developed during his reign. His work ''De Mortibus Persecutorum'' has an apologetic character, but has been treated as a work of history by Christian writers. Here Lactantius preserves the story of Constantine's vision of the Chi Rho before his conversion to Christianity. The full text is found in only one manuscript, which bears the title, ''Lucii Caecilii liber ad Donatum Confessorem de Mortibus Persecutorum''. The bishop Eusebius of Caesaria, a historian, st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthodox Church Of Greece
The Church of Greece ( el, Ἐκκλησία τῆς Ἑλλάδος, Ekklēsía tē̂s Helládos, ), part of the wider Greek Orthodox Church, is one of the autocephalous churches which make up the communion of Eastern Orthodox Christianity. Its canonical territory is confined to the borders of Greece prior to the Balkan Wars of 1912–1913 ("Old Greece"), with the rest of Greece (the "New Lands", Crete, and the Dodecanese) being subject to the jurisdiction of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople. However, most of the dioceses of the Metropolises of the New Lands are ''de facto'' administered as part of the Church of Greece for practical reasons, under an agreement between the churches of Athens and Constantinople. The primate of the Church of Greece is the archbishop of Athens and All Greece. Prevailing religion of Greece Adherence to the Eastern Orthodox Church was established as a definitive hallmark of Greek ethnic identity in the first modern Greek constitution, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Flags And Insignia
For most of its history, the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire did not know or use heraldry in the Western European sense of permanent motifs transmitted through hereditary right. Various large aristocratic families employed certain symbols to identify themselves; the use of the cross, and of icons of Christ, the Theotokos and various saints is also attested on seals of officials, but these were often personal rather than family emblems. . Likewise, various emblems ( el, σημεῖα, ''sēmeia''; ''σημεῖον'', ''sēmeion'') were used in official occasions and for military purposes, such as banners or shields displaying various motifs such as the cross or the '' labarum''.. Despite the abundance of pre-heraldic symbols in Byzantine society from the 10th century, only through contact with the Crusaders in the 12th century (when heraldry was becoming systematized in Western Europe), and particularly following the Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) and the establishment of Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
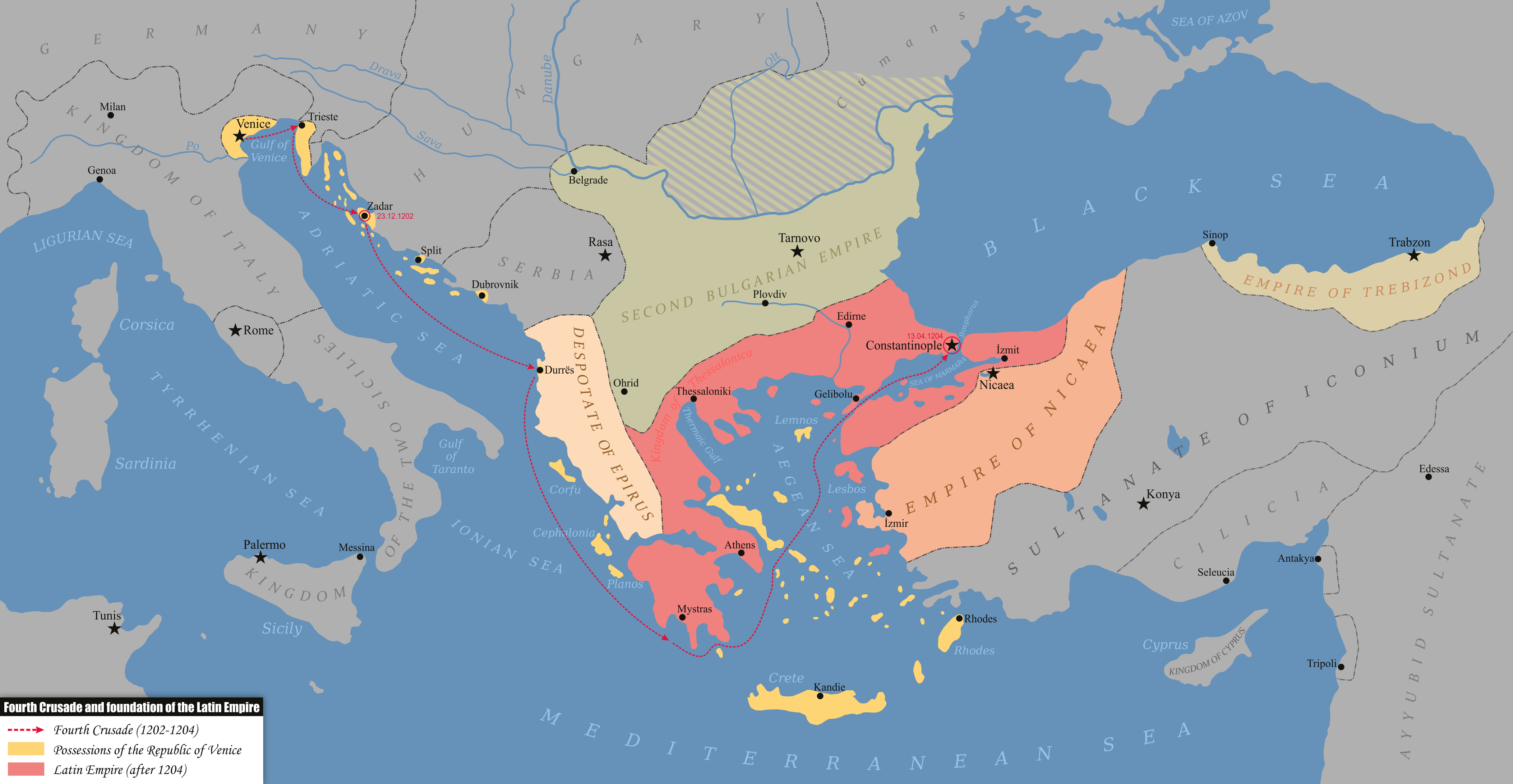
Empire Of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond, or Trapezuntine Empire, was a monarchy and one of three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire, along with the Despotate of the Morea and the Principality of Theodoro, that flourished during the 13th through to the 15th century, consisting of the far northeastern corner of Anatolia (the Pontus) and the southern Crimea. The empire was formed in 1204 with the help of the Georgian queen Tamar after the Georgian expedition in Chaldia and Paphlagonia, commanded by Alexios Komnenos a few weeks before the sack of Constantinople. Alexios later declared himself Emperor and established himself in Trebizond (modern day Trabzon, Turkey). Alexios and David Komnenos, grandsons and last male descendants of deposed Emperor Andronikos I Komnenos, pressed their claims as "Roman emperors" against Byzantine Emperor Alexios V Doukas. The later Byzantine emperors, as well as Byzantine authors, such as George Pachymeres, Nicephorus Gregoras and to some extent Trapezun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komnenos
Komnenos ( gr, Κομνηνός; Latinized Comnenus; plural Komnenoi or Comneni (Κομνηνοί, )) was a Byzantine Greek noble family who ruled the Byzantine Empire from 1081 to 1185, and later, as the Grand Komnenoi (Μεγαλοκομνηνοί, ''Megalokomnenoi'') founded and ruled the Empire of Trebizond (1204–1461). Through intermarriages with other noble families, notably the Doukai, Angeloi, and Palaiologoi, the Komnenos name appears among most of the major noble houses of the late Byzantine world. Origins The 11th-century Byzantine historian Michael Psellos reported that the Komnenos family originated from the village of Komne in Thrace—usually identified with the "Fields of Komnene" () mentioned in the 14th century by John Kantakouzenos—a view commonly accepted by modern scholarship. The first known member of the family, Manuel Erotikos Komnenos, acquired extensive estates at Kastamon in Paphlagonia, which became the stronghold of the family in the 11th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Flags And Insignia
For most of its history, the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire did not know or use heraldry in the Western European sense of permanent motifs transmitted through hereditary right. Various large aristocratic families employed certain symbols to identify themselves; the use of the cross, and of icons of Christ, the Theotokos and various saints is also attested on seals of officials, but these were often personal rather than family emblems. . Likewise, various emblems ( el, σημεῖα, ''sēmeia''; ''σημεῖον'', ''sēmeion'') were used in official occasions and for military purposes, such as banners or shields displaying various motifs such as the cross or the '' labarum''.. Despite the abundance of pre-heraldic symbols in Byzantine society from the 10th century, only through contact with the Crusaders in the 12th century (when heraldry was becoming systematized in Western Europe), and particularly following the Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) and the establishment of Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeologoi Eagle XV C Byzantine Miniature
The House of Palaiologos ( Palaiologoi; grc-gre, Παλαιολόγος, pl. , female version Palaiologina; grc-gre, Παλαιολογίνα), also found in English-language literature as Palaeologus or Palaeologue, was a Byzantine Greek family that rose to nobility and produced the last and longest-ruling dynasty in the history of the Byzantine Empire. Their rule as Emperors and Autocrats of the Romans lasted almost two hundred years, from 1259 to the Fall of Constantinople in 1453. The origins of the family are unclear. Their own medieval origin stories ascribed them an ancient and prestigious origin in ancient Roman Italy, descended from some of the Romans that had accompanied Constantine the Great to Constantinople upon its foundation in 330. It is more likely that they originated significantly later in Anatolia since the earliest known member of the family, possibly its founder, Nikephoros Palaiologos, served as a commander there in the second half of the 11th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)