|
Five Discourses Of Matthew
In Christianity, the term Five Discourses of Matthew refers to five specific discourses by Jesus within the Gospel of Matthew.''The Cradle, the Cross, and the Crown: An Introduction to the New Testament'' by Andreas J. Köstenberger, L. Scott Kellum 2009 pages 194-196 The five discourses are listed as the following: the ''Sermon on the Mount'', the ''Mission Discourse'', the '' Parabolic Discourse'', the '' Discourse on the Church,'' and the ''Discourse on End Times''. Each of the discourses has a shorter parallel in the Gospel of Mark or the Gospel of Luke. Structure Biblical scholars generally agree on the existence of the five separate discourses, although discussions and differences of opinion exist about specific details.''The Gospel of Matthew'' by Craig S. Keener 2009 pages 37-38''Preaching Matthew's Gospel'' by Richard A. Jensen 1998 pages 25 & 158 There are occurrences of the closing formula "when Jesus had finished speaking": 7:28, 11:1, 13:53, 19:1, and 26:1. Most s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Christianity. The New Testament's background, the first division of the Christian Bible, is called the Old Testament, which is based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible; together they are regarded as sacred scripture by Christians. The New Testament is a collection of Christian texts originally written in the Koine Greek language, at different times by various authors. While the Old Testament canon varies somewhat between different Christian denominations, the 27-book canon of the New Testament has been almost universally recognized within Christianity since at least Late Antiquity. Thus, in almost all Christian traditions today, the New Testament consists of 27 books: * 4 canonical gospels (Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John) * The Acts of the Apostl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Leaven
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
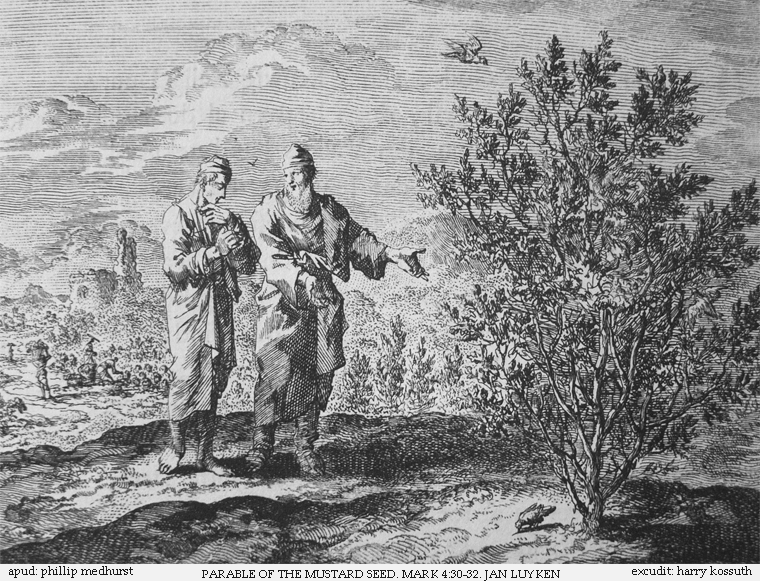
Parable Of The Mustard Seed
The Parable of the Mustard Seed is one of the shorter parables of Jesus. It appears in Matthew ( 13:31–32), Mark ( 4:30–32), and Luke ( 13:18–19). In the Gospels of Matthew and Luke, it is immediately followed by the Parable of the Leaven, which shares this parable's theme of the Kingdom of Heaven growing from small beginnings. It also appears in the non-canonical Gospel of Thomas (verse 20). Narrative In the Gospel of Matthew the parable is as follows: In the Gospel of Mark: In the Gospel of Luke: Interpretation The plant referred to here (Greek , ) is generally considered to be black mustard, a large annual plant up to tall, but growing from a proverbially small seed (this smallness is also used to refer to faith in Matthew 17:20 and Luke 17:6). According to rabbinical sources, Jews did not grow the plant in gardens, and this is consistent with Matthew's description of it growing in a field. Luke tells the parable with the plant in a garden instead; this is pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
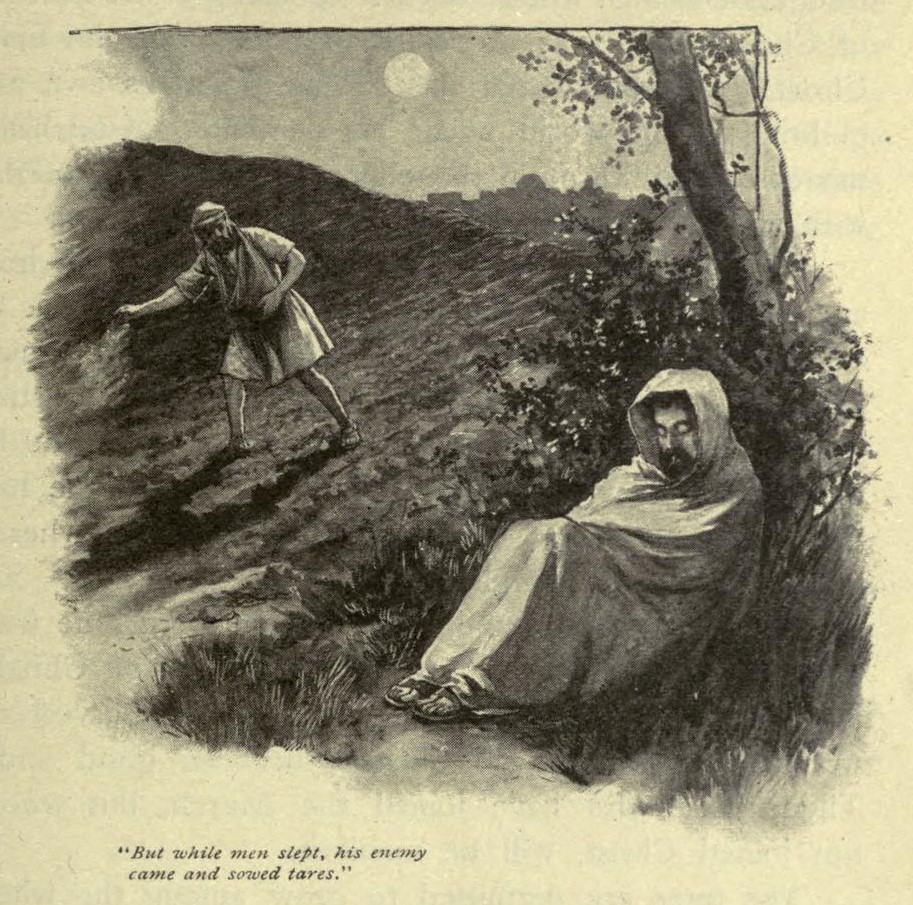
The Tares
The Parable of the Tares or Weeds (KJV: ''tares'', WNT: ''darnel'', DRB: ''cockle'') is a parable of Jesus which appears in . The parable relates how servants eager to pull up weeds were warned that in so doing they would root out the wheat as well and were told to let both grow together until the harvest. Later in Matthew, the weeds are identified with "the children of the evil one", the wheat with "the children of the Kingdom", and the harvest with "the end of the age". A shorter, compressed version of the parable is found without any interpretation in the apocryphal Gospel of Thomas. Narrative The parable in the Gospel of Matthew goes as follows: Analysis The word translated "tares" in the King James Version is (''zizania''), plural of (''zizanion''). This word is thought to mean darnel (''Lolium temulentum''), a ryegrass which looks much like wheat in its early stages of growth. The Weymouth New Testament, a translation of the resultant Greek, translates the word as "Darn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israelites
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan. The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele of ancient Egypt, dated to about 1200 BCE. According to the modern archaeological account, the Israelites and their culture branched out of the Canaanite peoples and their cultures through the development of a distinct monolatristic—and later monotheistic—religion centred on the national god Yahweh.Mark Smith in "The Early History of God: Yahweh and Other Deities of Ancient Israel" states "Despite the long regnant model that the Canaanites and Israelites were people of fundamentally different culture, archaeological data now casts doubt on this view. The material culture of the region exhibits numerous common points between Israelites and Canaanites in the Iron I period (c. 1200–1000 BCE). The record would suggest that the Isra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bible (American Standard)/Matthew
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a variety of forms originally written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Koine Greek. These texts include instructions, stories, poetry, and prophecies, among other genres. The collection of materials that are accepted as part of the Bible by a particular religious tradition or community is called a biblical canon. Believers in the Bible generally consider it to be a product of divine inspiration, but the way they understand what that means and interpret the text can vary. The religious texts were compiled by different religious communities into various official collections. The earliest contained the first five books of the Bible. It is called the Torah in Hebrew and the Pentateuch (meaning ''five books'') in Greek; the second oldest part was a coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Commission
In Christianity, the Great Commission is the instruction of the resurrected Jesus Christ to his disciples to spread the gospel to all the nations of the world. The Great Commission is outlined in Matthew 28:16– 20, where on a mountain in Galilee Jesus calls on his followers to make disciples of and baptize all nations in the name of the Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit. The Great Commission is similar to the episodes of the commissioning of the Twelve Apostles found in the other Synoptic Gospels, though with significant differences. Luke also has Jesus during his ministry dispatching disciples, including the seventy disciples, sending them to all the nations and giving them power over demons. The dispersion of the Apostles in the traditional ending of Mark is thought to be a 2nd-century summary based on Matthew and Luke. It has become a tenet in Christian theology emphasizing ministry, missionary work, evangelism, and baptism. The apostles are said to have disp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twelve Apostles
In Christian theology and ecclesiology, the apostles, particularly the Twelve Apostles (also known as the Twelve Disciples or simply the Twelve), were the primary disciples of Jesus according to the New Testament. During the life and ministry of Jesus in the 1st century AD, the apostles were his closest followers and became the primary teachers of the gospel message of Jesus. There is also an Eastern Christian tradition derived from the Gospel of Luke of there having been as many as seventy apostles during the time of Jesus' ministry. The commissioning of the Twelve Apostles during the ministry of Jesus is described in the Synoptic Gospels. After his resurrection, Jesus sent eleven of them (as Judas Iscariot by then had died) by the Great Commission to spread his teachings to all nations. This event has been called the dispersion of the Apostles. In the Pauline epistles, Paul, although not one of the original twelve, described himself as an apostle, saying he was called b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ben Sira
Ben Sira also known as Shimon ben Yeshua ben Eliezer ben Sira (שמעון בן יהושע בן אליעזר בן סירא) or Yeshua Ben Sirach (), was a Hellenistic Jewish scribe, sage, and allegorist from Seleucid-controlled Jerusalem of the Second Temple period. He is the author of ''Sirach'', also known as the "Book of Ecclesiasticus". He wrote his work in Hebrew, possibly in Alexandria in Egypt in the Ptolemaic Kingdom c. 180–175 BCE, where he is thought to have established a school. While Ben Sira is sometimes claimed to be a contemporary of Simeon the Just, it is more likely that his contemporary was High Priest Simon II (219–199 BCE) and this is due to confusion with his father, Yeshua'. A medieval text, the ''Alphabet of Sirach'', was falsely attributed to him. Name In the Koine Greek text of the Book of Sirach, the author's father is called "Jesus the son of Sirach of Jerusalem". Jesus is the Anglicized form of the Greek name Ἰησοῦς, the equivalent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)


.jpg)


