|
Fish Reproduction
Fish reproductive organs include testes and ovaries. In most species, gonads are paired organs of similar size, which can be partially or totally fused. There may also be a range of secondary organs that increase reproductive fitness. The genital papilla is a small, fleshy tube behind the anus in some fishes, from which the sperm or eggs are released; the sex of a fish can often be determined by the shape of its papilla. Anatomy Testes Most male fish have two testes of similar size. In the case of sharks, the testes on the right side is usually larger. The primitive jawless fish have only a single testis, located in the midline of the body, although even this forms from the fusion of paired structures in the embryo. Under a tough membranous shell, the tunica albuginea, the testis of some teleost fish, contains very fine coiled tubes called seminiferous tubules. The tubules are lined with a layer of cells (germ cells) that from puberty into old age, develop into sperm cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betta Spawning
''Betta'' is a large genus of small, active, often colorful, freshwater ray-finned fishes, in the gourami family (Osphronemidae). The best known ''Betta'' species is ''B. splendens,'' commonly known as the Siamese fighting fish and often kept as an aquarium pet. Characteristics All ''Betta'' species are small fishes, but they vary considerably in size, ranging from under 2.5 cm (1 in) total length in ''B. chanoides'' to 14 cm (5.5 in) in the Akar betta (''B. akarensis''). Bettas are anabantoids, which means they can breathe atmospheric air using a unique organ called the labyrinth. This accounts for their ability to thrive in low-oxygen water conditions that would kill most other fish, such as rice paddies, slow-moving streams, drainage ditches, and large puddles. The bettas exhibit two kinds of spawning behaviour: some build bubble nests, such as ''B. splendens'', while others are mouthbrooders, such as ''B. picta''. The mouthbrooding species are sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing s. It is also common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seminiferous Tubule
Seminiferous tubules are located within the testes, and are the specific location of meiosis, and the subsequent creation of male gametes, namely spermatozoa. Structure The epithelium of the tubule consists of a type of sustentacular cells known as Sertoli cells, which are tall, columnar type cells that line the tubule. In between the Sertoli cells are spermatogenic cells, which differentiate through meiosis to sperm cells. Sertoli cells function to nourish the developing sperm cells. They secrete androgen-binding protein, a binding protein which increases the concentration of testosterone. There are two types: convoluted and straight, convoluted toward the lateral side, and straight as the tubule comes medially to form ducts that will exit the testis. The seminiferous tubules are formed from the testis cords that develop from the primitive gonadal cords, formed from the gonadal ridge. Function Spermatogenesis, the process for producing spermatozoa, takes place in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatogonia
A spermatogonium (plural: ''spermatogonia'') is an undifferentiated male germ cell. Spermatogonia undergo spermatogenesis to form mature spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules of the testis. There are three subtypes of spermatogonia in humans: *Type A (dark) cells, with dark nuclei. These cells are reserve spermatogonial stem cells which do not usually undergo active mitosis. *Type A (pale) cells, with pale nuclei. These are the spermatogonial stem cells that undergo active mitosis. These cells divide to produce Type B cells. *Type B cells, which undergo growth and become primary spermatocytes. Anticancer drugs Anticancer drugs such as doxorubicin and vincristine can adversely affect male fertility by damaging the DNA of proliferative spermatogonial stem cells. Experimental exposure of rat undifferentiated spermatogonia to doxorubicin and vincristine indicated that these cells are able to respond to DNA damage by increasing their expression of DNA repair genes, and tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Higher Vertebrates
Amniotes are a clade of tetrapod vertebrates that comprises sauropsids (including all reptiles and birds, and extinct parareptiles and non-avian dinosaurs) and synapsids (including pelycosaurs and therapsids such as mammals). They are distinguished from the other tetrapod clade — the amphibians — by the development of three extraembryonic membranes (amnion for embryoic protection, chorion for gas exchange, and allantois for metabolic waste disposal or storage), thicker and more keratinized skin, and costal respiration (breathing by expanding/constricting the rib cage). All three main features listed above, namely the presence of an amniotic buffer, water-impermeable cutes and a robust respiratory system, are very important for amniotes to live on land as true terrestrial animals – the ability to reproduce in locations away from water bodies, better homeostasis in drier environments, and more efficient air respiration to power terrestrial locomotions, although the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Urethral Orifice (male)
The urinary meatus, (, ) also known as the external urethral orifice, is the opening of the urethra. It is the point where urine exits the urethra in both sexes and where semen exits the urethra in males. The meatus has varying degrees of sensitivity to touch. The meatus is located on the glans of the penis or in the vulval vestibule. In human males The male external urethral orifice is the external opening or urinary meatus, normally located at the tip of the glans penis, at its junction with the frenular delta. It presents as a vertical slit, possibly bounded on either side by two small labia-like projections, and continues longitudinally along the front aspect of the glans, which facilitates the flow of urine micturition. In some cases, the opening may be more rounded. This can occur naturally or may also occur as a side effect of excessive skin removal during circumcision. The meatus is a sensitive part of the male reproductive system. In human females The female extern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
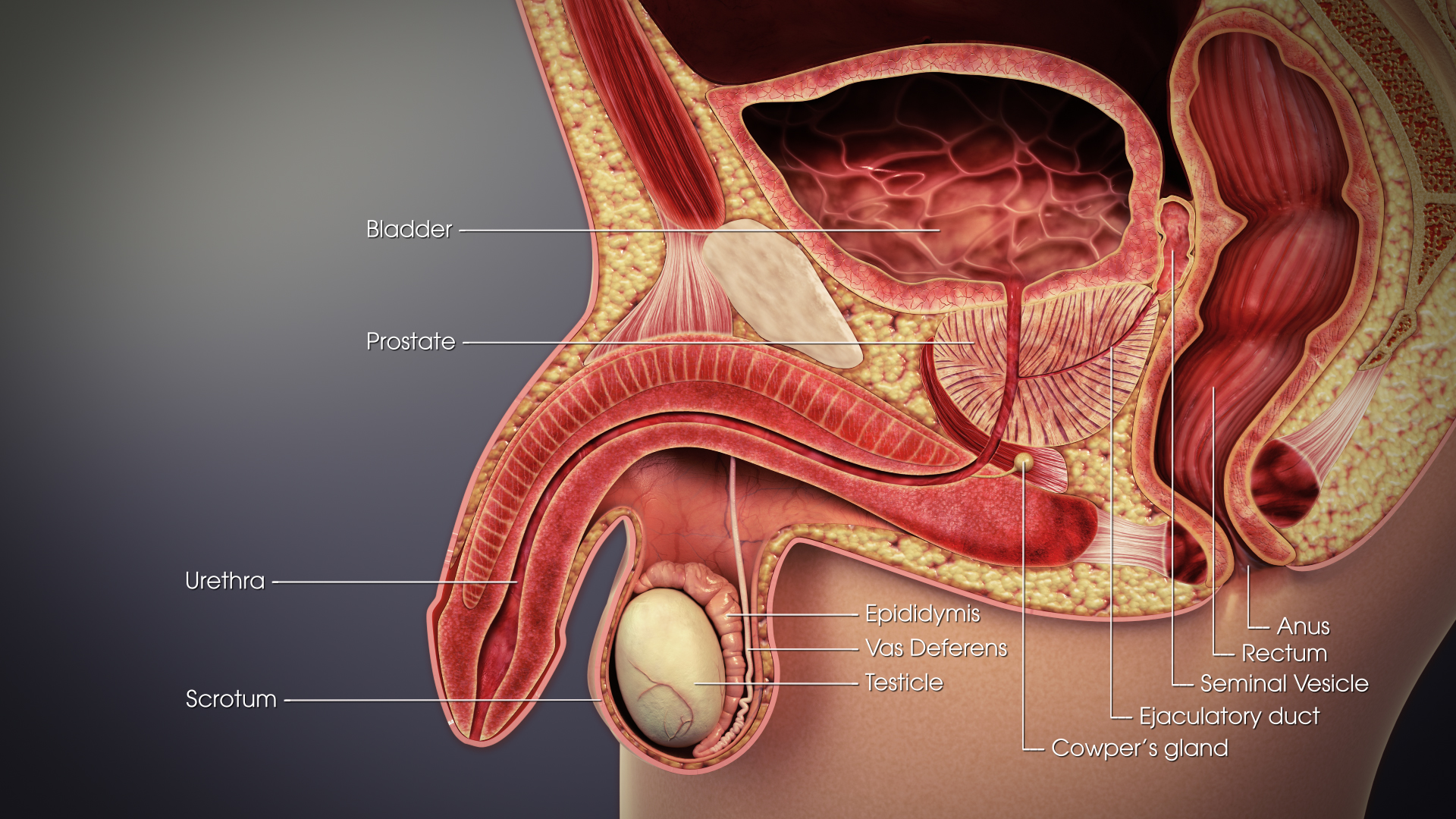
Urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus. Females use their urethra only for urinating, but males use their urethra for both urination and ejaculation. The external urethral sphincter is a striated muscle that allows voluntary control over urination. The internal sphincter, formed by the involuntary smooth muscles lining the bladder neck and urethra, receives its nerve supply by the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. The internal sphincter is present both in males and females. Structure The urethra is a fibrous and muscular tube which connects the urinary bladder to the external urethral meatus. Its length differs between th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vas Deferens
The vas deferens or ductus deferens is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. The ducts transport sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts in anticipation of ejaculation. The vas deferens is a partially coiled tube which exits the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal. Etymology ''Vas deferens'' is Latin, meaning "carrying-away vessel"; the plural version is ''vasa deferentia''. ''Ductus deferens'' is also Latin, meaning "carrying-away duct"; the plural version is ''ducti deferentes''. Structure There are two vasa deferentia, connecting the left and right epididymis with the seminal vesicles to form the ejaculatory duct in order to move sperm. The (human) vas deferens measures 30–35 cm in length, and 2–3 mm in diameter. The vas deferens is continuous proximally with the tail of the epididymis. The vas deferens exhibits a tortuous, convoluted initial/proximal section (which measures 2–3 cm in length). Distally, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testis. This process starts with the mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of the tubules. These cells are called spermatogonial stem cells. The mitotic division of these produces two types of cells. Type A cells replenish the stem cells, and type B cells differentiate into primary spermatocytes. The primary spermatocyte divides meiotically (Meiosis I) into two secondary spermatocytes; each secondary spermatocyte divides into two equal haploid spermatids by Meiosis II. The spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa (sperm) by the process of spermiogenesis. These develop into mature spermatozoa, also known as sperm cells. Thus, the primary spermatocyte gives rise to two cells, the secondary spermatocytes, and the two secondary spermatocytes by their subdivision produce four spermatozoa and four haploid cells. Sperma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epididymis
The epididymis (; plural: epididymides or ) is a tube that connects a testicle to a vas deferens in the male reproductive system. It is a single, narrow, tightly-coiled tube in adult humans, in length. It serves as an interconnection between the multiple efferent ducts at the rear of a testicle (proximally), and the vas deferens (distally). Anatomy The epididymis is situated posterior and somewhat lateral to the testis. The epididymis is invested completely by the tunica vaginalis (which is continuous with the tunica vaginalis covering the testis). The epididymis can be divided into three main regions: * The head ( la, caput). The head of the epididymis receives spermatozoa via the efferent ducts of the mediastinium of the testis at the superior pole of the testis. The head is characterized histologically by a thick epithelium with long stereocilia (described below) and a little smooth muscle. It is involved in absorbing fluid to make the sperm more concentrated. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efferent Ducts
The efferent ducts (or efferent ductules or ductuli efferentes or ductus efferentes or vasa efferentia) connect the rete testis with the initial section of the epididymis.Hess 2018 There are two basic designs for efferent ductule structure: * a) multiple entries into the epididymis, as seen in most large mammals. In humans and other large mammals, there are approximately 15 to 20 efferent ducts, which also occupy nearly one third of the head of the epididymis. * b) single entry, as seen in most small animals such as rodents, where by the 3–6 ductules merge into a single small ductule prior to entering the epididymis. The ductuli are unilaminar and composed of columnar ciliated and non-ciliated (absorptive) cells. The ciliated cells serve to stir the luminal fluids, possibly to help ensure homogeneous absorption of water from the fluid produced by the testis, which results in an increase in the concentration of luminal sperm. The epithelium is surrounded by a band of smooth m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediastinum Testis
The mediastinum testis is a network of fibrous connective tissue that extends from the top to near the bottom of each testis. It is wider above than below. Numerous imperfect septa are given off from its front and sides, which radiate toward the surface of the testes and are attached to the tunica albuginea. These divide the interior of the testes into a number of incomplete spaces called lobules. These are somewhat cone-shaped, being broad at their bases at the surface of the gland, and becoming narrower as they converge to the mediastinum. The mediastinum supports the rete testis The rete testis ( ) is an anastomosing network of delicate tubules located in the hilum of the testicle ( mediastinum testis) that carries sperm from the seminiferous tubules to the efferent ducts. It is the counterpart of the rete ovarii in f ... and blood vessels of the testis in their passage to and from the substance of the gland. Additional images File:gray1145.png, Transverse section thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)