|
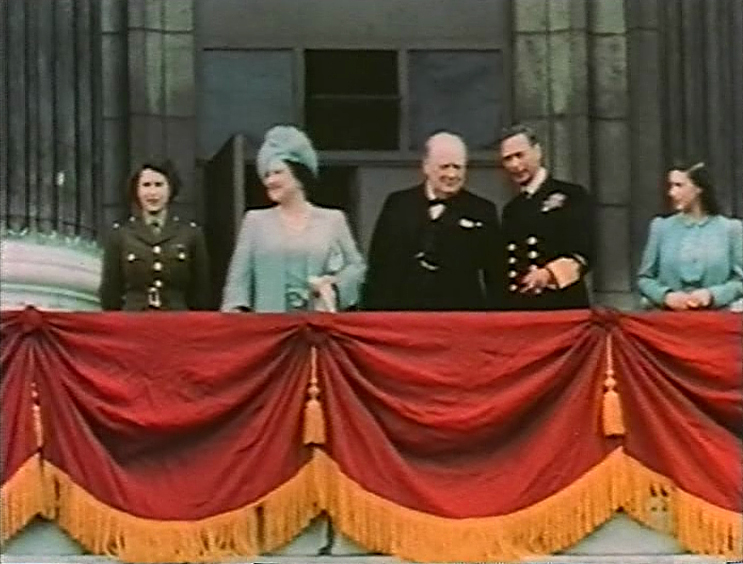
First Thatcher Ministry
Margaret Thatcher was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 4 May 1979 to 28 November 1990, during which time she led a Conservative majority government. She was the first woman to hold that office. During her premiership, Thatcher moved to liberalise the British economy through deregulation, privatisation, and the promotion of entrepreneurialism. This article details the first Thatcher ministry she led at the invitation of Queen Elizabeth II from 1979 to 1983. Formation Following the vote of no confidence against the Labour government and prime minister James Callaghan on 28 March 1979, a general election was called for 3 May 1979. The Winter of Discontent had seen the Labour government's popularity slump during the previous four months, and the opinion polls all pointed towards a Conservative victory. The Conservatives won the election with a majority of 44 seats and their leader Margaret Thatcher became the United Kingdom's first female prime minister. Thatcher in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher (; 13 October 19258 April 2013) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 1975 to 1990. She was the first female British prime minister and the longest-serving British prime minister of the 20th century. As prime minister, she implemented economic policies that became known as Thatcherism. A Soviet journalist dubbed her the "Iron Lady", a nickname that became associated with her uncompromising politics and leadership style. Thatcher studied chemistry at Somerville College, Oxford, and worked briefly as a research chemist, before becoming a barrister. She was elected Member of Parliament for Finchley in 1959. Edward Heath appointed her Secretary of State for Education and Science in his 1970–1974 government. In 1975, she defeated Heath in the Conservative Party leadership election to become Leader of the Opposition, the first woman to lead a major poli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callaghan Ministry
Callaghan most commonly refers to O'Callaghan, an Anglicized Irish surname. Callaghan may also refer to: Places * Callaghan, New South Wales, Australia * Callaghan, Edmonton, Canada * Callaghan, Virginia Callaghan is an Unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Alleghany County, Virginia, United States. The population as of the 2010 Census was 348. Humpback Covered Bridge and Wood Hall are listed on the U.S. National Regist ..., United States * Callaghan, Texas, United States Fictional characters * Clarissa Callaghan, from the video game '' Valkyria Chronicles III'' * Robert Callaghan, the main antagonist from the movie ''Big Hero 6'' See also * * Callahan (other) * Callihan, a surname {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Industry
Heavy industry is an industry that involves one or more characteristics such as large and heavy products; large and heavy equipment and facilities (such as heavy equipment, large machine tools, huge buildings and large-scale infrastructure); or complex or numerous processes. Because of those factors, heavy industry involves higher capital intensity than light industry does, and it is also often more heavily cyclical in investment and employment. Though important to economic development and industrialization of economies, heavy industry can also have significant negative side effects: both local communities and workers frequently encounter health risks, heavy industries tend to produce byproducts that both pollute the air and water, and the industrial supply chain is often involved in other environmental justice issues from mining and transportation. Because of their intensity, heavy industries are also significant contributors to greenhouse gas emissions that cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
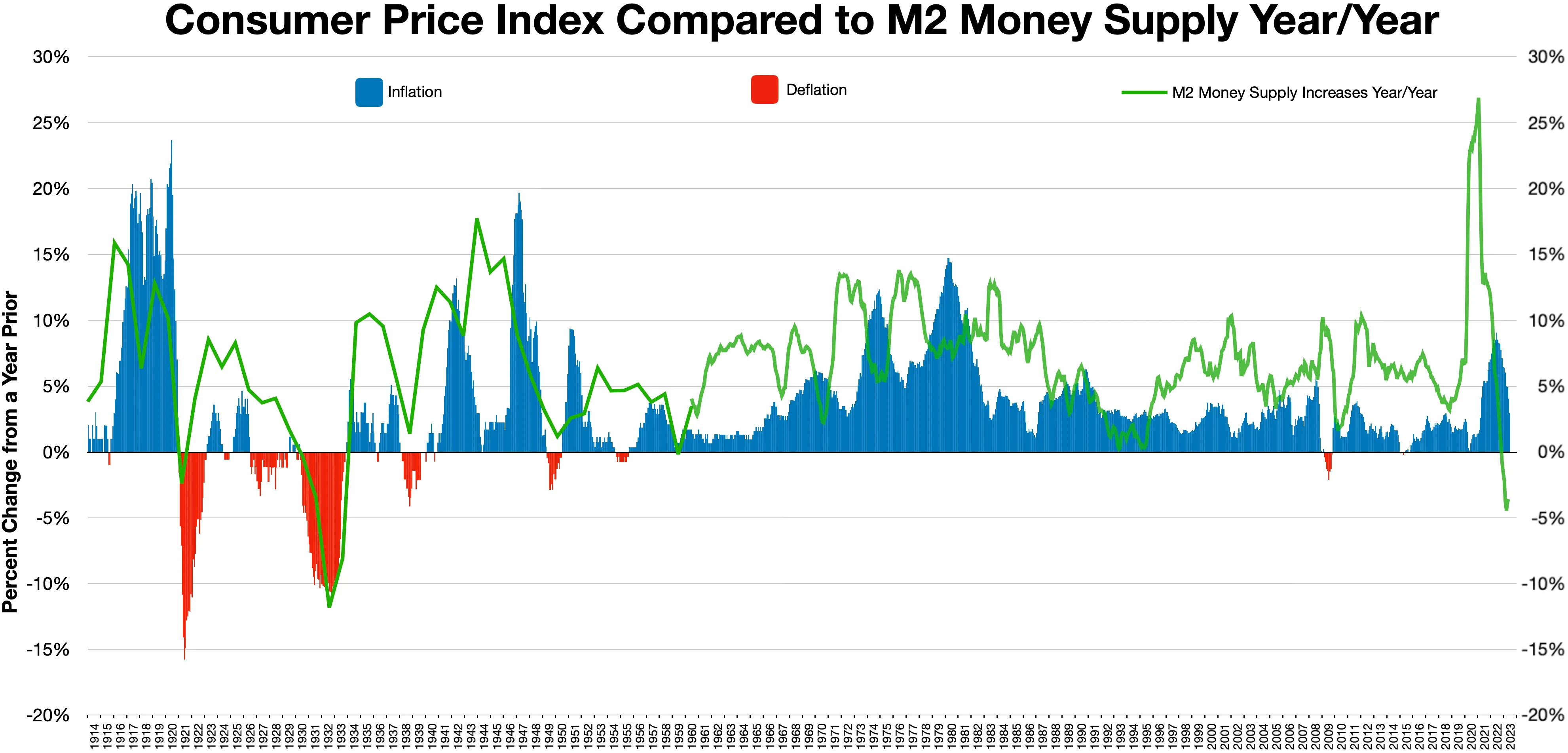
Monetarism
Monetarism is a school of thought in monetary economics that emphasizes the role of governments in controlling the amount of money in circulation. Monetarist theory asserts that variations in the money supply have major influences on national output in the short run and on price levels over longer periods. Monetarists assert that the objectives of monetary policy are best met by targeting the growth rate of the money supply rather than by engaging in discretionary monetary policy.Phillip Cagan, 1987. "Monetarism", '' The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', v. 3, Reprinted in John Eatwell et al. (1989), ''Money: The New Palgrave'', pp. 195–205, 492–97. Monetarism is commonly associated with neoliberalism. Monetarism today is mainly associated with the work of Milton Friedman, who was among the generation of economists to reject Keynesian economics and criticise Keynes's theory of fighting economic downturns using fiscal policy (government spending). Friedman and Anna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
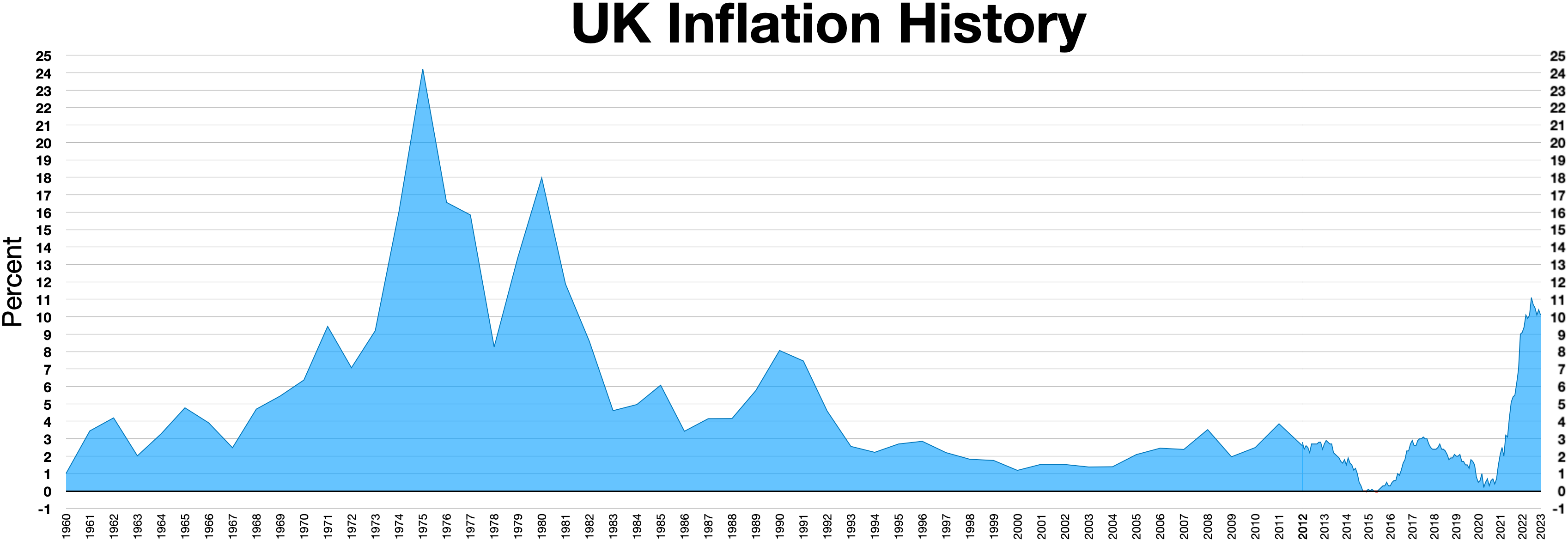
Winter Of Discontent
The Winter of Discontent was the period between November 1978 and February 1979 in the United Kingdom characterised by widespread strikes by private, and later public, sector trade unions demanding pay rises greater than the limits Prime Minister James Callaghan and his Labour Party government had been imposing, against Trades Union Congress (TUC) opposition, to control inflation. Some of these industrial disputes caused great public inconvenience, exacerbated by the coldest winter in 16 years, in which severe storms isolated many remote areas of the country. A strike by workers at Ford in late 1978 was settled with a pay increase of 17 per cent, well above the 5 per cent limit the government was holding its own workers to with the intent of setting an example for the private sector to follow, after a resolution at the Labour Party's annual conference urging the government not to intervene passed overwhelmingly. At the end of the year a road hauliers' strike began, coupled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979 Vote Of No Confidence In The Callaghan Ministry
A vote of no confidence in the British Labour government of James Callaghan occurred on 28 March 1979. The vote was brought by opposition leader Margaret Thatcher and was lost by the Labour government by one vote (311 votes to 310), which was announced at 10:19 pm. The result mandated a general election which was won by Thatcher's Conservative Party. The last time an election had been forced by the House of Commons was in 1924, when Ramsay MacDonald, the first Labour Prime Minister, lost a vote of confidence. Labour politician Roy Hattersley later remarked that the vote marked "the last rites" of ' old Labour'. Labour did not return to government for another 18 years. The BBC has referred to the vote as "one of the most dramatic nights in Westminster history". Background The general election at the end of February 1974 resulted in a hung parliament where Labour had slightly more seats than any other party but no overall majority. The Conservatives tried to negotiat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states during her lifetime, and was head of state of 15 realms at the time of her death. Her reign of 70 years and 214 days was the longest of any British monarch and the longest verified reign of any female monarch in history. Elizabeth was born in Mayfair, London, as the first child of the Duke and Duchess of York (later King George VI and Queen Elizabeth The Queen Mother). Her father acceded to the throne in 1936 upon the abdication of his brother Edward VIII, making the ten-year-old Princess Elizabeth the heir presumptive. She was educated privately at home and began to undertake public duties during the Second World War, serving in the Auxiliary Territorial Service. In November 1947, she Wedding of Princess Elizabeth and Philip Mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship is the creation or extraction of economic value. With this definition, entrepreneurship is viewed as change, generally entailing risk beyond what is normally encountered in starting a business, which may include other values than simply economic ones. An entrepreneur is an individual who creates and/or invests in one or more businesses, bearing most of the risks and enjoying most of the rewards.The process of setting up a business is known as entrepreneurship. The entrepreneur is commonly seen as an innovator, a source of new ideas, goods, services, and business/or procedures. More narrow definitions have described entrepreneurship as the process of designing, launching and running a new business, which is often similar to a small business, or as the "capacity and willingness to develop, organize and manage a business venture along with any of its risks to make a profit." The people who create these businesses are often referred to as entrepreneurs. While def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privatization
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when a heavily regulated private company or industry becomes less regulated. Government functions and services may also be privatised (which may also be known as "franchising" or "out-sourcing"); in this case, private entities are tasked with the implementation of government programs or performance of government services that had previously been the purview of state-run agencies. Some examples include revenue collection, law enforcement, water supply, and prison management. Another definition is that privatization is the sale of a state-owned enterprise or municipally owned corporation to private investors; in this case shares may be traded in the public market for the first time, or for the first time since an enterprise's previous nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deregulation
Deregulation is the process of removing or reducing state regulations, typically in the economic sphere. It is the repeal of governmental regulation of the economy. It became common in advanced industrial economies in the 1970s and 1980s, as a result of new trends in economic thinking about the inefficiencies of government regulation, and the risk that regulatory agencies would be controlled by the regulated industry to its benefit, and thereby hurt consumers and the wider economy. Economic regulations were promoted during the Gilded Age, in which progressive reforms were claimed as necessary to limit externalities like corporate abuse, unsafe child labor, monopolization, pollution, and to mitigate boom and bust cycles. Around the late 1970s, such reforms were deemed burdensome on economic growth and many politicians espousing neoliberalism started promoting deregulation. The stated rationale for deregulation is often that fewer and simpler regulations will lead to raised lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economy Of The United Kingdom
The economy of the United Kingdom is a highly developed social market and market-orientated economy. It is the sixth-largest national economy in the world measured by nominal gross domestic product (GDP), ninth-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP), and twenty second-highest by GDP per capita, constituting 3.3% of nominal world GDP. By PPP (purchasing power parity) terms, UK constitutes 2.34% of world GDP. The United Kingdom is one of the most globalised economies, and comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. In 2020, the UK was the fifth largest exporter in the world and the fifth-largest importer. It also had the third-largest inward foreign direct investment, and the fifth-largest outward foreign direct investment. In 2020, the UK's trade with the 27 member states of the European Union accounted for 49% of the country's exports and 52% of its imports. The service sector dominates, contributing 81% of GDP; the financial services industry is p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Liberalization
Economic liberalization (or economic liberalisation) is the lessening of government regulations and restrictions in an economy in exchange for greater participation by private entities. In politics, the doctrine is associated with classical liberalism and neoliberalism. Liberalization in short is "the removal of controls" to encourage economic development. Many countries have pursued and followed the path of economic liberalization in the 1980s, 1990s and in the 21st century, with the stated goal of maintaining or increasing their competitiveness as business environments. Liberalization policies may or often include the partial or complete privatization of government institutions and state-owned assets, greater labour market flexibility, lower tax rates for businesses, less restrictions on both domestic and foreign capital, open markets, etc. In support of liberalization, former British prime minister Tony Blair wrote that: "Success will go to those companies and countries whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



