|
First Battle Of Kharkov
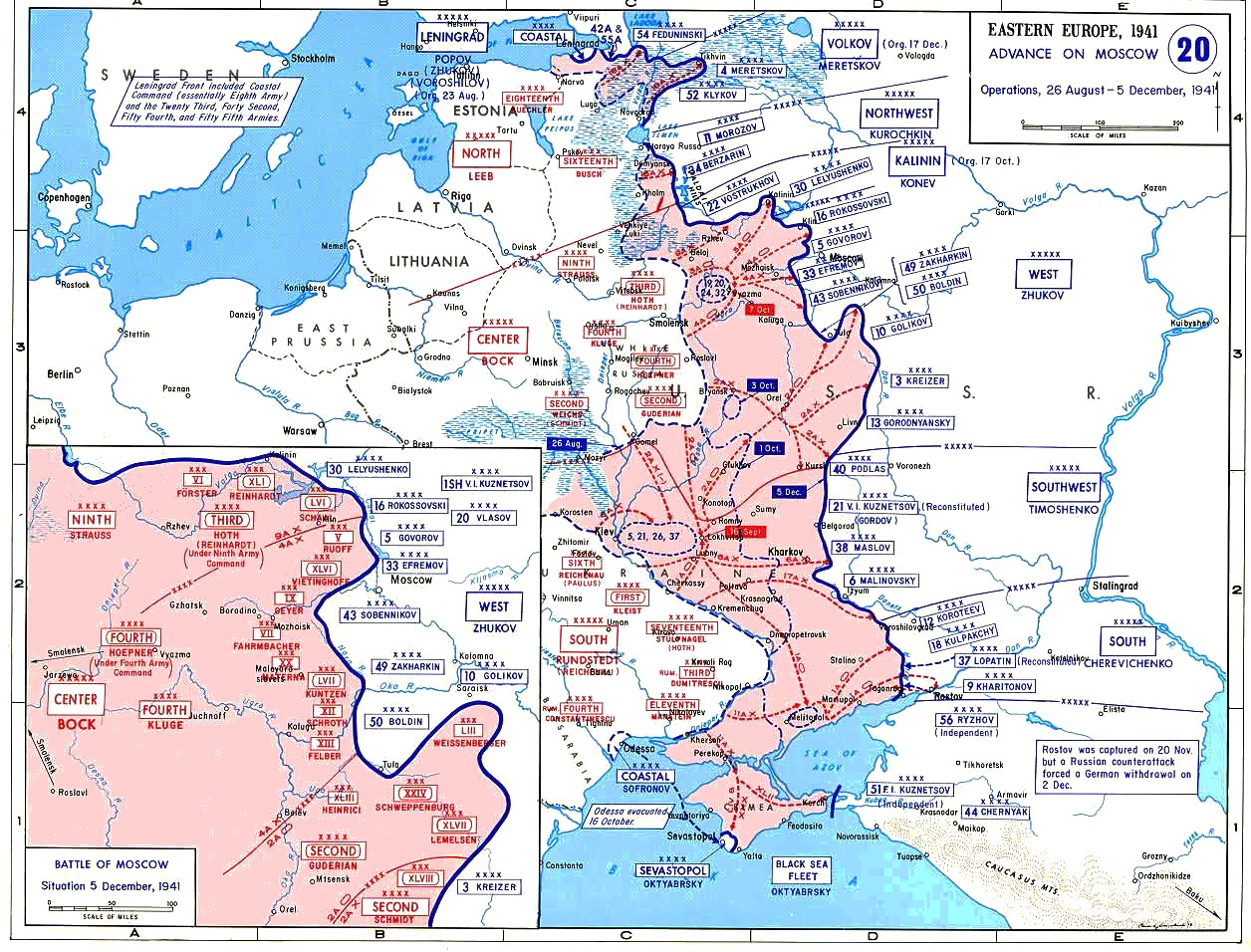
The First Battle of Kharkov, so named by Wilhelm Keitel, was the 1941 battle for the city of Kharkiv#German occupation, Kharkov, Ukrainian SSR, during the final phase of Operation Barbarossa between the German 6th Army (Wehrmacht), 6th Army of Army Group South and the Soviet Southwestern Front (Soviet Union), Southwestern Front. The Soviet 38th Army (Soviet Union), 38th Army was ordered to defend the city while its factories were dismantled for relocation farther east. The German 6th Army needed to take the city in order to close the widening gap to the German 17th Army (Wehrmacht), 17th Army. By 20 October the Germans had reached the western edge of the city, it was taken by the 57th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht), 57th Infantry Division by 24 October. At that time, however, most of Kharkov's industrial equipment had been evacuated or rendered useless by the Soviet authorities. Importance of Kharkov Kharkov's railroad system In the autumn of 1941, Kharkov was considered one o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Front (World War II)
The Eastern Front of World War II was a Theater (warfare), theatre of conflict between the European Axis powers against the Soviet Union (USSR), Polish Armed Forces in the East, Poland and other Allies of World War II, Allies, which encompassed Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Northern Europe, Northeast Europe (Baltic states, Baltics), and Southeast Europe (Balkans) from 22 June 1941 to 9 May 1945. It was known as the Great Patriotic War (term), Great Patriotic War in the Soviet Union – and still is in some of its successor states, while almost everywhere else it has been called the ''Eastern Front''. In present-day German and Ukrainian historiography the name German-Soviet War is typically used. The battles on the Eastern Front of the Second World War constituted the largest military confrontation in history. They were characterised by unprecedented ferocity and brutality, wholesale destruction, mass deportations, and immense loss of life due to combat, starvation, expos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th Army (Wehrmacht)
The 6th Army was a field army unit of the German Wehrmacht during World War II (1939–1945). It was widely remembered for being the most highly decorated German army unit until its defeat by the Red Army at the Battle of Stalingrad in the winter of 1942–1943. It also acquired a reputation for the war crimes (such as the massacre of more than 30,000 Jews at Babi Yar in September 1941) that it committed under the command of Field Marshal Walther von Reichenau during Operation Barbarossa. Western campaigns Originally numbered as the 10th Army, this Army formed on 10 October 1939 with General Walther von Reichenau in command. Its primary mission was to guard the western defenses of Germany against British and French attacks during the Polish campaign. During the invasion of the Low Countries the 6th Army saw active service linking up with paratroopers and destroying fortifications at Eben Emael, Liège, and Namur during the Battle of Belgium. The 6th Army was then involved in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Su-2
The Sukhoi Su-2 (russian: Сухой Су-2) was a Soviet reconnaissance and light bomber aircraft used in the early stages of World War II. It was the first airplane designed by Pavel Sukhoi. The basic design received an engine and armament upgrade (Su-4) and was modified for the ground-attack role (ShB). Development In 1936, Joseph Stalin released a requirement for a multipurpose combat aircraft. Codenamed Ivanov, the airplane had to be capable of performing reconnaissance and then attacking the targets it located. P. O. Sukhoi was working in the Tupolev OKB at the time and designed the "Ivanov" aircraft under the tutelage of Andrei Tupolev. The resulting ANT-51 flew on 25 August 1937 with M. M. Gromov at the controls. Powered by a 610 kW (820 hp) Shvetsov M-62 air-cooled radial engine, the ANT-51 reached 403 km/h (220 kn, 250 mph) at 4,700 m (15,420 ft). This was considered insufficient but since the basic design was sound, it was decided t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (russian: Наро́дный комиссариа́т вну́тренних дел, Naródnyy komissariát vnútrennikh del, ), abbreviated NKVD ( ), was the interior ministry of the Soviet Union. Established in 1917 as NKVD of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, the agency was originally tasked with conducting regular police work and overseeing the country's prisons and labor camps. It was disbanded in 1930, with its functions being dispersed among other agencies, only to be reinstated as an all-union commissariat in 1934. The functions of the OGPU (the secret police organization) were transferred to the NKVD around the year 1930, giving it a monopoly over law enforcement activities that lasted until the end of World War II. During this period, the NKVD included both ordinary public order activities, and secret police activities. The NKVD is known for its role in political repression and for carrying out the Great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kharkov Tractor Factory
Kharkiv Tractor Plant (KhTZ or HTZ) ( uk, Харківський тракторний завод, translit=Kharkivskyi Traktornyi Zavod) is an agricultural machinery manufacturer in the Ukrainian city of Kharkiv. Established in 1930-31, as a centerpiece of Stalin's First Five-Year Plan for Soviet industrialization (1927-1932), KhTZ was Ukraine's largest tractor manufacturer, producing both wheeled and tracked tractors. In 2016, the Ukrainian security service (SBU) alleged that at the Kremlin's direction the Russian owners were planning to decommission the enterprise. The industrial plant was reported destroyed by extensive shelling and resulting fires on the fourth day of the Russian Federation's invasion of Ukraine in late February 2022. History Building of the Plant in the First Five Year Plan The Kharkiv Tractor Plant, on the south-east edge of Kharkiv, was one of three major tractor plants (the others at Stalingrad and Chelyabinsk) built as one of "the giants of the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-34 Tank
The T-34 is a Soviet medium tank introduced in 1940. When introduced its 76.2 mm (3 in) tank gun was less powerful than its contemporaries while its 60-degree sloped armour provided good protection against Anti-tank warfare, anti-tank weapons. The Christie suspension was inherited from the design of American J. Walter Christie's M1928 tank, versions of which were sold turret-less to the Red Army and documented as "farm tractors", after being rejected by the U.S. Army. The T-34 had a profound effect on the conflict on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front in the World War II, Second World War, and had a short lasting impact on tank design. After the Germans encountered the tank in 1941 during Operation Barbarossa, German general Paul Ludwig Ewald von Kleist called it "the finest tank in the world" and Heinz Guderian affirmed the T-34's "vast superiority" over German tanks. Alfred Jodl, chief of operations staff of the German armed forces noted in his war diar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donbas
The Donbas or Donbass (, ; uk, Донба́с ; russian: Донба́сс ) is a historical, cultural, and economic region in eastern Ukraine. Parts of the Donbas are controlled by Russian separatist groups as a result of the Russo-Ukrainian War: the Donetsk People's Republic and the Luhansk People's Republic. The word ''Donbas'' is a portmanteau formed from "Donets Basin", an abbreviation of "Donets Coal Basin" ( uk, Донецький вугільний басейн, Donetskyi vuhilnyi basein; russian: Донецкий угольный бассейн, Donetskii ugolnyi bassein). The name of the coal basin is a reference to the Donets Ridge; the latter is associated with the Donets river. There are numerous definitions of the region's extent. It is now most commonly defined as the Donetsk and Luhansk regions of Ukraine. The historical coal mining region excluded parts of these oblasts, and included areas in Dnipropetrovsk Oblast and Southern Russia. A Euroregion of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dnieper
} The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and Belarus and the fourth-longest river in Europe, after the Volga, Danube, and Ural rivers. It is approximately long, with a drainage basin of . In antiquity, the river was part of the Amber Road trade routes. During the Ruin in the later 17th century, the area was contested between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russia, dividing Ukraine into areas described by its right and left banks. During the Soviet period, the river became noted for its major hydroelectric dams and large reservoirs. The 1986 Chernobyl disaster occurred on the Pripyat, immediately above that tributary's confluence with the Dnieper. The Dnieper is an important navigable waterway for the economy of Ukraine and is connected by the Dnieper–Bug Canal to other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historically been considered as a natural barrier between Eastern Europe and Western Asia. Mount Elbrus in Russia, Europe's highest mountain, is situated in the Western Caucasus. On the southern side, the Lesser Caucasus includes the Javakheti Plateau and the Armenian highlands, part of which is in Turkey. The Caucasus is divided into the North Caucasus and South Caucasus, although the Western Caucasus also exists as a distinct geographic space within the North Caucasus. The Greater Caucasus mountain range in the north is mostly shared by Russia and Georgia as well as the northernmost parts of Azerbaijan. The Lesser Caucasus mountain range in the south is occupied by several independent states, mostly by Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia, but also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a population of 2.4 million. The peninsula is almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukraine. To the east, the Crimean Bridge, constructed in 2018, spans the Strait of Kerch, linking the peninsula with Krasnodar Krai in Russia. The Arabat Spit, located to the northeast, is a narrow strip of land that separates the Sivash lagoons from the Sea of Azov. Across the Black Sea to the west lies Romania and to the south is Turkey. Crimea (called the Tauric Peninsula until the early modern period) has historically been at the boundary between the classical world and the steppe. Greeks colonized its southern fringe and were absorbed by the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
57th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 57th Infantry Division (german: 57. Infanterie-Division) was a German division in World War II. It was formed on 26 August 1939 in Landshut. History The 57th Infantry Division was formed in August 1939 as part of the second wave of German infantry divisions. During the German-Soviet invasion of Poland, the division remained in the Saarland. The division was moved into Poland as an occupational force in August 1940 until the initiation of Operation Barbarossa in June 1941. The division took part in the campaign as part of Army Group South, where it assaulted Kiev. Orders of Battle ;1939 *179th Infantry Regiment *199th Infantry Regiment *217th Infantry Regiment *157th Artillery Regiment *157th Engineer Battalion *157th Reconnaissance Battalion *157th Anti-tank Detachment *News department *157th Troops supply ;1944 *164th Grenadier Regiment *199th Grenadier Regiment *217th Grenadier Regiment *57th Fusilier Battalion *157th Artillery Regiment *157th Field-replacement Battal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th Army (Wehrmacht)
The German Seventeenth Army () was a field army of Nazi Germany during World War II. Operation Barbarossa On 22 June 1941, the 17th Army was part of Army Group South when Nazi Germany launched Operation Barbarossa and invaded the Soviet Union. From 1 July, the Hungarian "Mobile Corps" (''Gyorshadtest'') was subordinated to the 17th Army. Along with 1st Panzer Army, the 17th Army encircled Soviet forces in central Ukraine during the Battle of Uman. Approximately 100,000 Soviet troops were captured. The 17th Army participated in the Battle of Kiev. Army Group South was ordered to resume the offensive, with the objective of capturing Rostov-on-Don, the gateway to the Caucasus oil fields, and Kharkov, a major center of heavy industry for the Soviet Union. In October 1941, the army came under the command of Hermann Hoth, who was convicted post-war in the High Command Trial. Hoth was an active supporter of the war of annihilation (') against the Soviet Union. He called upon his men t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |