|
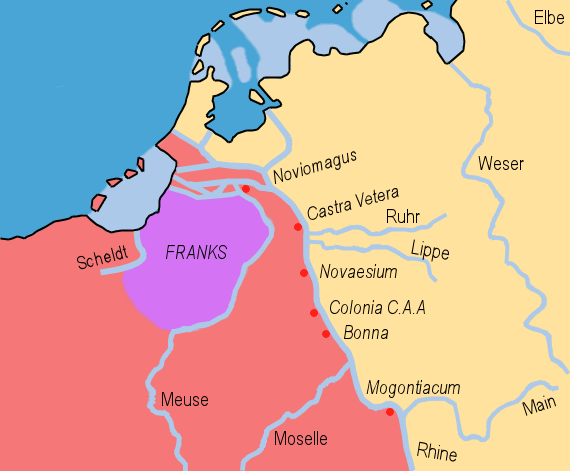
Firang
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, Weapons and Ornaments: Germanic Material Culture in Pre-Carolingian Central Europe, 400-750. BRILL, 2001, p.42. Later the term was associated with Romanized Germanic dynasties within the collapsing Western Roman Empire, who eventually commanded the whole region between the rivers Loire and Rhine. They imposed power over many other post-Roman kingdoms and Germanic peoples. Beginning with Charlemagne in 800, Frankish rulers were given recognition by the Catholic Church as successors to the old rulers of the Western Roman Empire. Although the Frankish name does not appear until the 3rd century, at least some of the original Frankish tribes had long been known to the Romans under their own names, both as allies providing soldiers, and as enem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merovingian Dynasty
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gaulish Romans under their rule. They conquered most of Gaul, defeating the Visigoths (507) and the Burgundians (534), and also extended their rule into Raetia (537). In Germania, the Alemanni, Bavarii and Saxons accepted their lordship. The Merovingian realm was the largest and most powerful of the states of western Europe following the breaking up of the empire of Theodoric the Great. The dynastic name, medieval Latin or ("sons of Merovech"), derives from an unattested Frankish form, akin to the attested Old English , with the final -''ing'' being a typical Germanic patronymic suffix. The name derives from King Merovech, whom many legends surround. Unlike the Anglo-Saxon royal genealogies, the Merovingians never claimed descent from a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippinid clans of the 7th century AD. The dynasty consolidated its power in the 8th century, eventually making the offices of mayor of the palace and '' dux et princeps Francorum'' hereditary, and becoming the ''de facto'' rulers of the Franks as the real powers behind the Merovingian throne. In 751 the Merovingian dynasty which had ruled the Germanic Franks was overthrown with the consent of the Papacy and the aristocracy, and Pepin the Short, son of Martel, was crowned King of the Franks. The Carolingian dynasty reached its peak in 800 with the crowning of Charlemagne as the first Emperor of the Romans in the West in over three centuries. His death in 814 began an extended period of fragmentation of the Carolingian Empire and decline that w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaric I
Alaric I (; got, 𐌰𐌻𐌰𐍂𐌴𐌹𐌺𐍃, , "ruler of all"; c. 370 – 410 AD) was the first king of the Visigoths, from 395 to 410. He rose to leadership of the Goths who came to occupy Moesia—territory acquired a couple of decades earlier by a combined force of Goths and Alans after the Battle of Adrianople. Alaric began his career under the Gothic soldier Gainas and later joined the Roman army. Once an ally of Rome under the Roman emperor Theodosius, Alaric helped defeat the Franks and other allies of a would-be Roman usurper. Despite losing many thousands of his men, he received little recognition from Rome and left the Roman army disappointed. After the death of Theodosius and the disintegration of the Roman armies in 395, he is described as king of the Visigoths. As the leader of the only effective field force remaining in the Balkans, he sought Roman legitimacy, never quite achieving a position acceptable to himself or to the Roman authorities. He operated m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregory Of Tours
Gregory of Tours (30 November 538 – 17 November 594 AD) was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours, which made him a leading prelate of the area that had been previously referred to as Gaul by the Romans. He was born Georgius Florentius and later added the name Gregorius in honour of his maternal great-grandfather. He is the primary contemporary source for Merovingian history. His most notable work was his ''Decem Libri Historiarum'' (''Ten Books of Histories''), better known as the ''Historia Francorum'' (''History of the Franks''), a title that later chroniclers gave to it. He is also known for his accounts of the miracles of saints, especially four books of the miracles of Martin of Tours. St. Martin's tomb was a major pilgrimage destination in the 6th century, and St. Gregory's writings had the practical effect of promoting highly organized devotion. Biography Gregory was born in Clermont, in the Auvergne region of central Gaul. He was born into the upper stratum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegidius
Aegidius (died 464 or 465) was the ruler of the short-lived Kingdom of Soissons from 461 to 464/465AD. Before his ascension, he became ''magister militum per Gallias'' (Master of the Soldiers for Gaul) serving under Majorian, in 458AD. An ardent supporter of Majorian, Aegidius rebelled against Ricimer when he assassinated Majorian and replaced him with Libius Severus; Aegidius may have pledged his allegiance to Leo I the Thracian, Leo I, the Eastern Roman Emperor. Aegidius repeatedly threatened to invade Italy and dethrone Libius Severus, but never actually launched such an invasion; historians have suggested he was unwilling to launch an invasion due to the pressure of the Visigoths, or else because it would leave Gaul exposed. Aegidius launched several campaigns against the Visigoths and the Burgundians, recapturing Lyons from the Burgundians in 458, and routing the Visigoths at the Battle of Orleans (463), Battle of Orleans. He died suddenly after a major victory against the V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clovis I
Clovis ( la, Chlodovechus; reconstructed Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first king of the Franks to unite all of the Frankish tribes under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a single king and ensuring that the kingship was passed down to his heirs. He is considered to have been the founder of the Merovingian dynasty, which ruled the Frankish kingdom for the next two centuries. Clovis succeeded his father, Childeric I, as a king of Salian Franks in 481, and eventually came to rule an area extending from what is now the southern Netherlands to northern France, corresponding in Roman terms to Gallia Belgica (northern Gaul). At the Battle of Soissons (486) he established his military dominance of the rump state of the fragmenting Western Roman Empire which was then under the command of Syagrius. By the time of his death in either 511 or 513, Clovis had conquered several smaller Frankish kingdoms in the northeast of Gaul inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Childeric I
Childeric I (; french: Childéric; la, Childericus; reconstructed Frankish: ''*Hildirīk''; – 481 AD) was a Frankish leader in the northern part of imperial Roman Gaul and a member of the Merovingian dynasty, described as a king (Latin ''rex''), both on his Roman-style seal ring, which was buried with him, and in fragmentary later records of his life. He was father of Clovis I, who acquired effective control over all or most Frankish kingdoms, and a significant part of Roman Gaul. Biography Childeric's father is recorded by several sources including Gregory of Tours to have been Merovech, whose name is the basis of the Merovingian dynasty. Gregory reports that Merovech was reputed by some to be a descendant of Chlodio who was an earlier Frankish king who had conquered Roman Gaulish areas first in the Silva Carbonaria, then in Tournai, Cambrai and as far south as the Somme. This is roughly the definition of the Roman province of ''Belgica Secunda'' (approximately the "Belgium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western States of Germany, state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 million people in the Cologne Bonn Region, urban region. Centered on the left bank of the Rhine, left (west) bank of the Rhine, Cologne is about southeast of NRW's state capital Düsseldorf and northwest of Bonn, the former capital of West Germany. The city's medieval Catholic Cologne Cathedral (), the third-tallest church and tallest cathedral in the world, constructed to house the Shrine of the Three Kings, is a globally recognized landmark and one of the most visited sights and pilgrimage destinations in Europe. The cityscape is further shaped by the Twelve Romanesque churches of Cologne, and Cologne is famous for Eau de Cologne, that has been produced in the city since 1709, and "col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ripuarian Franks
Ripuarian or Rhineland Franks (Latin: ''Ripuarii'' or ''Ribuarii'') were one of the two main groupings of early Frankish people, and specifically it was the name eventually applied to the tribes who settled in the old Roman territory of the Ubii, with its capital at Cologne on the Rhine river in modern Germany. Their western neighbours were the Salii, or "Salian Franks", who were named already in late Roman records, and settled with imperial permission within the Roman Empire in what is today the southern part of the Netherlands, and Belgium, and later expanded their influence into the northern part of France above the Loire river, creating the Frankish empire of Francia. Both the Salii and Ripuarii were new names and represented new groupings of older tribal groups on the Roman Rhine border. The ancestors of the Ripuarii originally lived on the right bank of the Rhine, where there had been a long history of friendly and unfriendly contact. Under pressure from their northern enemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salian Franks
The Salian Franks, also called the Salians (Latin: ''Salii''; Greek: Σάλιοι, ''Salioi''), were a northwestern subgroup of the early Franks who appear in the historical record in the fourth and fifth centuries. They lived west of the Lower Rhine in what was then the Roman Empire and today the Netherlands and Belgium. The traditional historiography sees the Salians as one of the main divisions of the Franks alongside the Ribuarians. Recent scholarship, however, has often questioned the ethnic significance of both these terms. Etymology Various etymologies are proposed. The ethnonym is unrelated to the name for the dancing priests of Mars, who were also called Salii. In line with theories that the Salians already existed as a tribe outside the Roman Empire, the name may have derived from the name of the IJssel river, formerly called ''Hisloa'' or ''Hisla'', and in ancient times, ''Sala'', which may be the Salians' original residence. Today this area is called Salland. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Istvaeonic
Weser-Rhine Germanic is a proposed group of prehistoric West Germanic dialects which would have been both directly ancestral to Dutch language, Dutch, as well as being a notable substratum influencing West Central German dialects. The term was introduced by the German linguist Friedrich Maurer (linguist), Friedrich Maurer as a replacement for the older term Istvaeonic, with which it is essentially synonymous. The term ''Rhine-Weser-Germanic'' is sometimes preferred. Nomenclature The term ''Istvaeonic'' is derived from the Istvaeones, Istvæones (or Istvaeones), a culturo-linguistic grouping of Germanic tribes, mentioned by Tacitus in his ''Germania (book), Germania''. Pliny the Elder further specified its meaning by claiming that the Istævones lived near the Rhine. Maurer used Pliny to refer to the dialects spoken by the Franks and Chatti around the northwestern banks of the Rhine, which were presumed to be descendants of the earlier Istvaeones. The Weser is a river in Germany, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)