|
Fir River
Fir River is a river in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The river's source is in the east central part of the province in the heart of the Pasquia Hills, which is one of four landforms that make up the Manitoba Escarpment. It flows in a southward direction until it meets up with the Red Deer River south of the town of Hudson Bay in Hudson Bay Regional Park. The river is in the boreal forest. Fir River is in the Nelson River drainage basin. Fir River begins at a small lake in the south-east corner of Wildcat Hill Provincial Park in the Pasquia Hills. The lake is in a small valley just west of Bankside Lake, which flows into Man River. While Fir River heads south towards Red Deer River, Man River eventually makes its way northward and is in the Saskatchewan River watershed. Wildcat Hill (), while in the Man River watershed, is only about 4 miles north of Fir River's source. The Pasquia River's source is just on the north-east side of Bankside Lake and it flows north-ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces And Territories Of Canada
Within the geographical areas of Canada, the ten provinces and three territories are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada (which upon Confederation was divided into Ontario and Quebec)—united to form a federation, becoming a fully independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the world's second-largest country by area. The major difference between a Canadian province and a territory is that provinces receive their power and authority from the ''Constitution Act, 1867'' (formerly called the ''British North America Act, 1867''), whereas territorial governments are creatures of statute with powers delegated to them by the Parliament of Canada. The powers flowing from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasquia River
Pasquia River is a river in the Canadian provinces of Manitoba and Saskatchewan. It begins in Saskatchewan in the Pasquia Hills and traverses boreal forests and muskeg in the Boreal Plains Ecozone, moving from the Mid-Boreal Upland of the Pasquia Hills east to the Mid-Boreal Lowland. It meets the Saskatchewan River in Manitoba at The Pas. Near the river's mouth, several small dams, dykes, and other water control structures have been built to control water flows. Description Pasquia River begins at a small lake in the Rural Municipality of Hudson Bay No. 394 at the eastern boundary of Wildcat Hill Provincial Park in the Pasquia Hills. Coming out of the hills, it crosses Highway 9 and flows in an easterly direction towards the Manitoba border. At the Highway 9 bridge, there is a picnic area and access to the river from the Pasquia River Recreation Site (). As the river nears the border with Manitoba, it begins to flow north paralleling it. At Nosamwokwu Lake, the river turns e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
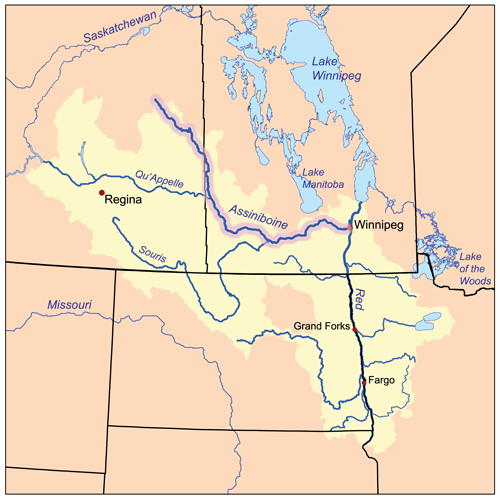
Assiniboine River Fur Trade
Fur trading on the Assiniboine River and the general area west of Lake Winnipeg began as early as 1731. Geography Lake Winnipeg was a major junction for the fur trade routes. See Canadian canoe routes (early). To the southeast the route ran to Grand Portage and the French center at Montreal. To the northeast the Hayes River led to the English base on Hudson Bay. To the northwest the Saskatchewan River led west to the Rocky Mountains. From this river another route led northwest to the even richer Athabasca Country. West of Lake Winnipeg is the chain of lakes that look like a single lake on large maps (Cedar Lake (Manitoba), Lake Winnipegosis and Lake Manitoba). West of this is the Assiniboine River. The Assiniboine flows southeast and then the east to Winnipeg, Manitoba where it meets the Red River of the North which flows north into Lake Winnipeg. Further west the Qu'Appelle River flows east to meet the Assiniboine. South of the Qu'Appelle is the Souris River which was not im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etomami River
Etomami River is a river in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The river originates in the Porcupine Hills and flows northward towards the town of Hudson Bay and into the Red Deer River. "Etomami" is a First Nations word that means "a place that three rivers join." It is in reference to the spot along the Red Deer River where the mouths of the Etomami and Fir Rivers meet the Red Deer River. Description The river begins at the north end of Etomami Lake in the RM of Preeceville No. 334 and flows northward through a deep-cut valley into the RM of Hudson Bay No. 394 following the Canadian National Railway and Highway 9. Its mouth is located on the Red Deer River on the south side of the town of Hudson Bay in the Hudson Bay Regional Park. The regional park itself is the site of an historical North West Company fur trading fort called Fort Red Deer River. Upstream from the park along the river and Highway 9 is Dagg Creek Recreation Site (52°38′30″N, 102°24′9″W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourism In Saskatchewan
There are numerous heritages and cultural attractions in the province of Saskatchewan. Museums, dinosaur digs, aboriginal cultural and heritage sites, art galleries, professional sport venues, spas, handcraft, antique and tea shops, agricultural tours, theatre and archaeological sites comprise over 600 varied Saskatchewan institutions. There are two national parks located in the province of Saskatchewan: Grasslands National Park, Prince Albert National Park. There are also four National Historic Sites operated by Parks Canada in Saskatchewan including Fort Walsh National Historic Site, Batoche National Historic Site, Fort Battleford National Historic Site and Motherwell Homestead National Historic Site. There are 37 provincial parks, provincial recreation areas, natural areas and a Heritage rangeland are also protected on a provincial level. Saskatchewan also has two major cities, Regina and Saskatoon. Regina is home to the Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP) Academy at Depo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson Bay Drainage Basin
The Hudson Bay drainage basin is the drainage basin in northern North America where surface water empties into Hudson Bay and adjoining waters. Spanning an area of about , the basin is almost totally in Canada (spanning parts of the Prairies, central and northern Canada), with a small portion in the United States (in Montana, the Dakotas, and Minnesota). The watershed's connection to the Labrador Sea is at the Hudson Strait's mouth between Resolution Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region and Cape Chidley on the Labrador Peninsula. The watershed's headwaters to the south-west are on the Continental Divide of the Americas, bounded at Triple Divide Peak to the south, and Snow Dome to the north. The western and northern boundary of the watershed is the Arctic Divide, and the southern and eastern boundary is the Laurentian Divide. left, Rupert's Land, granted as a commercial monopoly to the Hudson's Bay Company in 1670 Hudson Bay is often considered part of the Arctic Ocean. For ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Rivers Of Saskatchewan
This is a list of rivers of Saskatchewan, a province of Canada. The largest and most notable rivers are listed at the start, followed by rivers listed by drainage basin and then alphabetically. Principal river statistics ''SourcStatistics Canada' Rivers by drainage basin *Arctic Ocean watershed ** Fond du Lac River ** Cree River ***Rapid River (Cree River tributary) ** Geikie River (Wollaston Lake) ** Clearwater River ***Graham Creek (Alberta) **Firebag River *Hudson Bay drainage basin **Assiniboine River ***Qu'Appelle River ****Moose Jaw River *****Avonlea Creek *****Thunder Creek **** Last Mountain Creek ***** Arm River *****Lanigan Creek ****Pheasant Creek ****Wascana Creek *** Whitesand River **** Spirit Creek ****Yorkton Creek ***** Crescent Creek ***Souris River **** Graham Creek ****Antler River ****Des Lacs River **** Gainsborough Creek ****Moose Mountain Creek **** Long Creek ****Pipestone Creek ** Churchill River *** Beaver River ****Doré ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snowmobile
A snowmobile, also known as a Ski-Doo, snowmachine, sled, motor sled, motor sledge, skimobile, or snow scooter, is a motorized vehicle designed for winter travel and recreation on snow. It is designed to be operated on snow and ice and does not require a road or trail, but most are driven on open terrain or trails. Snowmobiling is a sport that many people have taken on as a serious hobby. Older snowmobiles could generally accommodate two people; however, most snowmobiles manufactured since the 1990s have been designed to only accommodate one person. Snowmobiles built with the ability to accommodate two people are referred to as "2-up" snowmobiles or "touring" models and make up an extremely small share of the market. Most snowmobiles do not have any enclosures, except for a windshield, and their engines normally drive a continuous track at the rear. Skis at the front provide directional control. Early snowmobiles used simple rubber tracks, but modern snowmobiles' tracks are usu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All-terrain Vehicle
An all-terrain vehicle (ATV), also known as a light utility vehicle (LUV), a quad bike, or simply a quad, as defined by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI); is a vehicle that travels on low-pressure tires, with a seat that is straddled by the operator, along with handlebars for steering control. As the name implies, it is designed to handle a wider variety of terrain than most other vehicles. Although it is a street-legal vehicle in some countries, it is not street-legal within most states, territories and provinces of Australia, the United States or Canada. By the current ANSI definition, ATVs are intended for use by a single operator, although some companies have developed ATVs intended for use by the operator and one passenger. These ATVs are referred to as tandem ATVs. The rider sits on and operates these vehicles like a motorcycle, but the extra wheels give more stability at slower speeds. Although most are equipped with three or four wheels, six-wheel mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Protected Areas Of Saskatchewan
This is a list of protected areas of Saskatchewan. National parks Provincial parks The Government of Canada, federal government transferred control of natural resources to the Western Canada, western provinces in 1930 with the Natural Resources Acts. At that time, the Saskatchewan government set up its own Department of Natural Resources. In an attempt to get people working and to encourage tourism during the Great Depression, several projects were set up by the government, including setting up a provincial park system in 1931. The founding parks include Cypress Hills, Duck Mountain, Good Spirit Lake, Moose Mountain, Katepwa Point, and Little Manitou Lake#Manitou and District Regional Park, Little Manitou. Greenwater Lake was added in 1932. Two more parks were added by the end of the 1930s and Little Manitou ceased to be a provincial park in 1956 and in 1962, it became a regional park. The list of parks, and their types, come from The Parks Act. Regional park ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Red Deer River
Hudson Bay Regional Park is a regional park in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It is located on the south side of the town of Hudson Bay in the RM of Hudson Bay No. 394 along the shores of the Red Deer River. The park is the site of a North West Company fur trading fort called Fort Red Deer River that was built in 1790. About downstream, near Erwood, was a Hudson's Bay Company trading post that was built in 1757. Hudson Bay Regional Park is composed about 900 acres of land split up between the main park on the south side of the town of Hudson Bay and along the Red Deer River and three former provincial recreation sites, Ruby Lake, Dagg Creek, and Greenbush River. The park is in the Porcupine Provincial Forest and at the edge of a pre-historic glacial lake called Lake Agassiz. Hudson Bay park The main part of the park is located at the junction of Fir, Red Deer, and Etomami Rivers and features camping, golfing, baseball diamonds, picnicking, hiking, fishing, and cros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |