|
Filippo S. Gilij
Filippo Salvatore Gilii (Spanish: Felipe Salvador Gilij) (1721–1789) was an Italian Jesuit priest who lived in the Province of Venezuela (in present day central Venezuela) on the Orinoco River. Gilii is a highly celebrated figure in early South American linguistics due to his advanced insights into the nature of languages. Gilii was born in Legogne, Italy (Umbria region). Most of what is known about the ethnology of the Tamanaco Indians was recorded by Gilii. One of his most notable works was ''Saggio di Storia Americana, o sia Storia Naturale, Civile, e Sacra De regni, e delle provincie Spagnuole di Terra-ferma nell' America meridionale'', first published in four volumes in 1768. Commemorative stamp showing him were issued in 1998 by the Venezuelan government. Linguistic insights Gilii recognized sound correspondences (e.g. between : : in the Cariban family) and predated William Jones' third discourse suggesting genealogical relationships between languages. Unlike Jone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilii Saggio Di Storia Americana 1780 Title Page
Filippo Salvatore Gilii (Spanish: Felipe Salvador Gilij) (1721–1789) was an Italian Jesuit priest who lived in the Province of Venezuela (in present day central Venezuela) on the Orinoco River. Gilii is a highly celebrated figure in early South American linguistics due to his advanced insights into the nature of languages. Gilii was born in Legogne, Italy (Umbria region). Most of what is known about the ethnology of the Tamanaco Indians was recorded by Gilii. One of his most notable works was ''Saggio di Storia Americana, o sia Storia Naturale, Civile, e Sacra De regni, e delle provincie Spagnuole di Terra-ferma nell' America meridionale'', first published in four volumes in 1768. Commemorative stamp showing him were issued in 1998 by the Venezuelan government. Linguistic insights Gilii recognized sound correspondences (e.g. between : : in the Cariban family) and predated William Jones' third discourse suggesting genealogical relationships between languages. Unlike J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Death
In linguistics, language death occurs when a language loses its last native speaker. By extension, language extinction is when the language is no longer known, including by second-language speakers. Other similar terms include linguicide, the death of a language from natural or political causes, and rarely glottophagy, the absorption or replacement of a minor language by a major language. Language death is a process in which the level of a speech community's linguistic competence in their language variety decreases, eventually resulting in no native or fluent speakers of the variety. Language death can affect any language form, including dialects. Language death should not be confused with language attrition (also called language loss), which describes the loss of proficiency in a first language of an individual.Crystal, David (2000) ''Language Death''. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. p. 19 In the modern period (–present; following the rise of colonialism), language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorenzo Hervás Y Panduro
Lorenzo may refer to: People * Lorenzo (name) Places Peru * San Lorenzo Island (Peru), sometimes referred to as the island of Lorenzo United States * Lorenzo, Illinois * Lorenzo, Texas * San Lorenzo, California, formerly Lorenzo * Lorenzo State Historic Site, house in New York State listed on the National Register of Historic Places Art, entertainment, and media ;Films and television * ''Lorenzo'' (film), an animated short film * ''Lorenzo's Oil'', a film based on a true story about a boy suffering from Adrenoleukodystrophy and his parents' journey to find a treatment. * ''Lorenzo's Time'', a 2012 Philippine TV series that aired on ABS-CBN ;Music *Lorenzo (rapper), French rapper * "Lorenzo", a 1996 song by Phil Collins Other uses * List of storms named Lorenzo * Lorenzo patient record systems, a type of electronic health record in the United Kingdom See also * San Lorenzo (other) * De Lorenzo * di Lorenzo di Lorenzo or Di Lorenzo is an Italian surname. Notable peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classification Of Indigenous Languages Of The Americas
This is a list of different language classification proposals developed for the indigenous languages of the Americas. The article is divided into North, Central, and South America sections; however, the classifications do not correspond to these divisions. North America ''Glottolog'' 4.1 (2019) ''Glottolog'' 4.1 (2019) recognizes 42 independent families and 31 isolates in North America (73 total). The vast majority are (or were) spoken in the United States, with 26 families and 26 isolates (52 total). ;North American languages families proposed in ''Glottolog'' 4.1 ;Families (42) #Otomanguean (180) #Arawakan (78) # Uto-Aztecan (69) #Algic (46) # Athabaskan-Eyak-Tlingit (45) #Mayan (33) #Chibchan (27) #Salishan (25) # Mixe-Zoque (19) #Siouan (18) #Eskimo–Aleut (12) # Totonacan (12) # Cochimi-Yuman (11) #Iroquoian (11) # Miwok-Costanoan (11) #Kiowa-Tanoan (8) #Muskogean (7) # Pomoan (7) # Chumashan (6) #Wakashan (6) #Caddoan (5) #Misumalpan (5) #Sahaptian (5) # Xincan (5) #C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arhuacan
The Chibchan languages (also Chibchan, Chibchano) make up a language family indigenous to the Isthmo-Colombian Area, which extends from eastern Honduras to northern Colombia and includes populations of these countries as well as Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama. The name is derived from the name of an extinct language called ''Chibcha'' or ''Muysccubun'', once spoken by the people who lived on the Altiplano Cundiboyacense of which the city of Bogotá was the southern capital at the time of the Spanish Conquista. However, genetic and linguistic data now indicate that the original heart of Chibchan languages and Chibchan-speaking peoples might not have been in Colombia, but in the area of the Costa Rica-Panama border, where the greatest variety of Chibchan languages has been identified. External relations A larger family called ''Macro-Chibchan'', which would contain the Misumalpan languages, Xinca, and Lenca, was found convincing by Kaufman (1990). Pache (2018) suggests a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warao Language
Warao (also known as Guarauno, Guarao, Warrau) is the native language of the Warao people. A language isolate, it is spoken by about 33,000 people primarily in northern Venezuela, Guyana and Suriname. It is notable for its unusual object–subject–verb word order. The 2015 Venezuelan film '' Gone with the River'' was spoken in Warao. Classification Warao appears to be a language isolate, unrelated to any recorded language in the region or elsewhere. Terrence Kaufman (1994) included it in his hypothetical Macro-Paezan family, but the necessary supporting work was never done. Julian Granberry connected many of the grammatical forms, including nominal and verbal suffixes, of Warao to the Timucua language of North Florida, also a language isolate. However, he has also derived Timucua morphemes from Muskogean, Chibchan, Paezan, Arawakan, and other Amazonian languages, suggesting multi-language creolization as a possible explanation for these similarities. Waroid hypothesis Gran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaruro Language
The Yaruro language (also spelled ''Llaruro'' or ''Yaruru''; also called Yuapín or Pumé) is an indigenous language spoken by Yaruro people, along the Orinoco, Cinaruco, Meta, and Apure rivers of Venezuela. It is not well classified; it may be an isolate, or distantly related to the extinct Esmeralda language. Genetic relations Pache (2016) considers Yaruro to be related to the Chocoan languages, citing evidence from lexical and sound correspondences. Some shared lexical items between Yaruro and Chocoan (Pache (2016) cites Yaruro and Epena forms from the Intercontinental Dictionary Series): : Language contact Jolkesky (2016) notes that there are lexical similarities with the Saliba-Hodi, Arawak The Arawak are a group of indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. Specifically, the term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to the Lokono of South America and the Taíno, who historically lived in the Greate ..., Bora-Muinane, Choko, Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guajiboan
Guajiboan (also Guahiban, Wahívoan, Guahiboan) is a language family spoken in the Orinoco River region in eastern Colombia and southwestern Venezuela, a savanna region known as the Llanos. Family division Guajiboan consists of 5 languages: * Macaguane (also known as Hitnü, Macaguán, Makawane, Agualinda, Agualinda Guahibo, Támude) * Southwest Guajiboan ** Guayabero (also known as Cunimía, Mítiwa, Mitúa, Mitu, Hiw, Jiw, Wayavero, Guaviare) ** Churuya (also known as Bisanigua, Guaigua) ''(†)'' * Central Guajiboan ** Guajibo (also known as Guahibo, Sikuani, Sicuani, Chiricoa, Hiwi, Jiwi, Jivi, Wahivo, Wahibo, Guaybo, Goahibo, Guaigua, Guayba, Goahiva) *** Waü (west) *** Newütjü (also known as Tigrero) *** Parawá (east) *** Hamorúa (also known as Amorúa, Jamorúa) *** Dome (also known as Playero, Cajaro) ** Cuiva (also known as Wamonae, Cuiba, Kuiba, Deja, Cuiba-Wámonae) *** Pimenepiwi (Meta river) *** Aitopiwi (Ariporo river) *** Yaraüraxi (Capanaparo river) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guamo Language
Guamo ( Wamo or Guamotey) is an extinct language of Venezuela. Kaufman (1990) finds a connection with the Chapacuran languages convincing. Varieties Varieties that may have been dialects or closely related languages: *Guamo of San José - on the Santo Domingo River, Zamora *Dazaro - once spoken in Zamora on the Guanare River *Guamontey - once spoken from the mouth of the Zárate River to the Apure River (unattested) *Tayaga - once spoken between the Arauca River and Apure River, in Apure State (unattested) *Atapaima - once spoken at the mouth of the Guanaparo River, Guárico State, Venezuela (unattested) *Guárico - extinct principal language Guárico State, once spoken on the Guárico River, Portuguesa River, and Apure River (unattested) *Guire - once spoken on the middle course of the Tiznados River, Orituco River, and Guaritico River, Guarico State (unattested) *Payme - once spoken at the mouth of the Guárico River (unattested) Dialect comparison Loukotka (196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
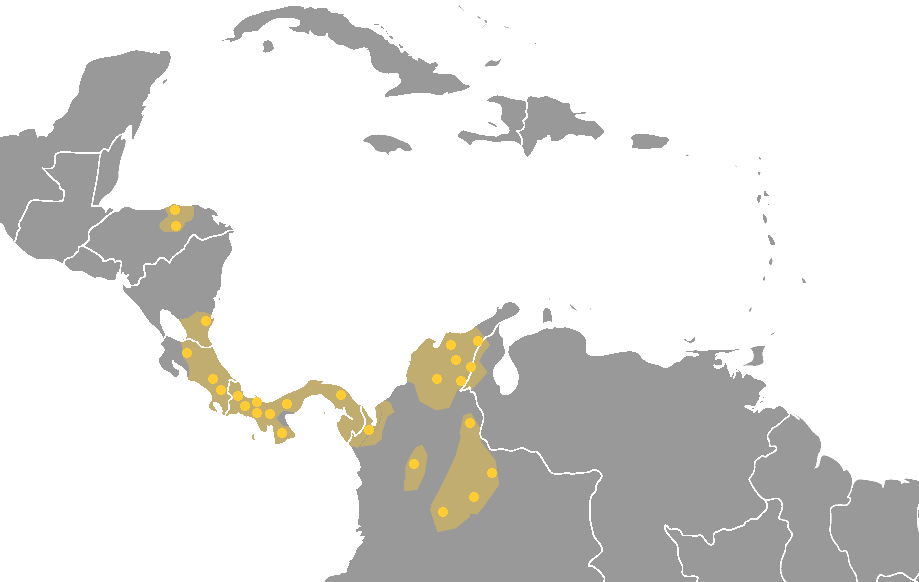
Maipurean
Arawakan (''Arahuacan, Maipuran Arawakan, "mainstream" Arawakan, Arawakan proper''), also known as Maipurean (also ''Maipuran, Maipureano, Maipúre''), is a language family that developed among ancient indigenous peoples in South America. Branches migrated to Central America and the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean and the Atlantic, including what is now the Bahamas. Almost all present-day South American countries are known to have been home to speakers of Arawakan languages, the exceptions being Ecuador, Uruguay, and Chile. Maipurean may be related to other language families in a hypothetical Macro-Arawakan stock. Name The name ''Maipure'' was given to the family by Filippo S. Gilij in 1782, after the Maipure language of Venezuela, which he used as a basis of his comparisons. It was renamed after the culturally more important Arawak language a century later. The term ''Arawak'' took over, until its use was extended by North American scholars to the broader Macro-Arawakan propo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |