|
Fibrotic
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is a pathological wound healing in which connective tissue replaces normal parenchymal tissue to the extent that it goes unchecked, leading to considerable tissue remodelling and the formation of permanent scar tissue. Repeated injuries, chronic inflammation and repair are susceptible to fibrosis where an accidental excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix components, such as the collagen is produced by fibroblasts, leading to the formation of a permanent fibrotic scar. In response to injury, this is called scarring, and if fibrosis arises from a single cell line, this is called a fibroma. Physiologically, fibrosis acts to deposit connective tissue, which can interfere with or totally inhibit the normal architecture and function of the underlying organ or tissue. Fibrosis can be used to describe the pathological state of excess deposition of fibrous tissue, as well as the process of connective tissue deposition in healing. Defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to as ''photomicroscopy''. At a basic level, photomicroscopy may be performed simply by connecting a camera to a microscope, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatic Stellate Cell
Hepatic stellate cells (HSC), also known as perisinusoidal cells or Ito cells (earlier ''lipocytes'' or ''fat-storing cells''), are pericytes found in the perisinusoidal space of the liver, also known as the space of Disse (a small area between the sinusoids and hepatocytes). The stellate cell is the major cell type involved in liver fibrosis, which is the formation of scar tissue in response to liver damage. Structure Hepatic stellate cells can be selectively stained with gold chloride, but their distinguishing feature in routine histological preparations is the presence of multiple lipid droplets in their cytoplasm. Cytoglobin expression has been shown to be a specific marker with which hepatic stellate cells can be distinguished from portal myofibroblasts in the damaged human liver. In murine (rats, mice) liver, reelin expressed by Ito cells has been shown to be a reliable marker in discerning them from other myofibroblasts. The expression of reelin is increased after liver inju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
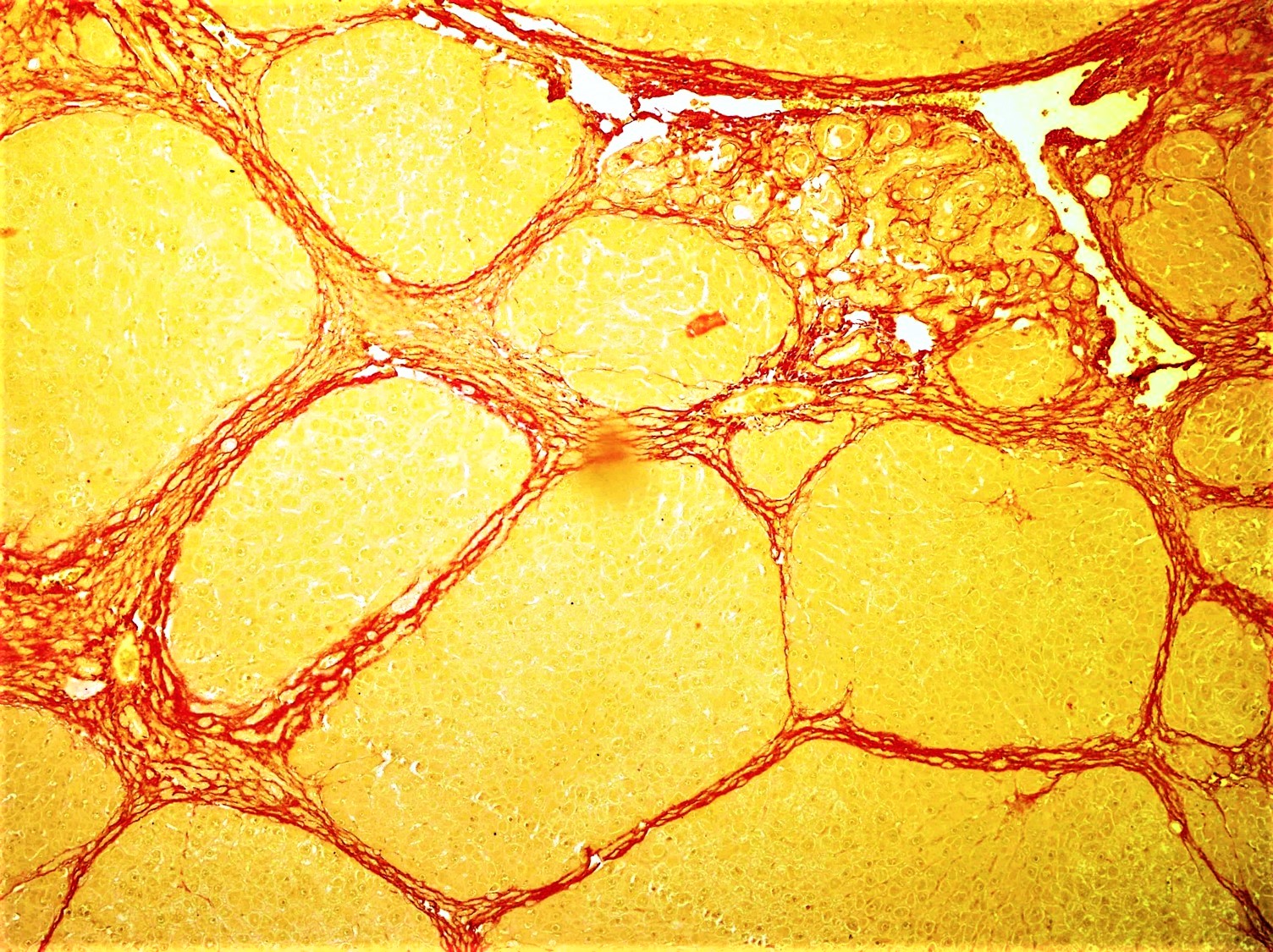
Bridging Fibrosis
In histology (microscopic anatomy), the lobules of liver, or hepatic lobules, are small divisions of the liver defined at the microscopic scale. The hepatic lobule is a building block of the liver tissue, consisting of a portal triad, hepatocytes arranged in linear cords between a capillary network, and a central vein. Lobules are different from the lobes of liver: they are the smaller divisions of the lobes. The two-dimensional microarchitecture of the liver can be viewed from different perspectives: The term "hepatic lobule", without qualification, typically refers to the classical lobule. Structure The hepatic lobule can be described in terms of metabolic "zones", describing the hepatic acinus (terminal acinus). Each zone is centered on the line connecting two portal triads and extends outwards to the two adjacent central veins. The periportal zone I is nearest to the entering vascular supply and receives the most oxygenated blood, making it least sensitive to ischemic in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation-induced Lung Injury
Radiation-induced lung injury (RILI) is a general term for damage to the lungs as a result of exposure to ionizing radiation. In general terms, such damage is divided into early inflammatory damage (''radiation pneumonitis'') and later complications of chronic scarring (''radiation fibrosis''). Pulmonary radiation injury most commonly occurs as a result of radiation therapy administered to treat cancer. Symptoms and signs The lungs are a radiosensitive organ, and radiation pneumonitis can occur leading to pulmonary insufficiency and death (100% after exposure to 50 gray of radiation), in a few months. Radiation pneumonitis is characterized by: *Loss of epithelial cells *Edema *Inflammation *Occlusions airways, air sacs and blood vessels *Fibrosis Symptoms of radiation pneumonitis include: fever, cough, chest congestion, shortness of breath Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
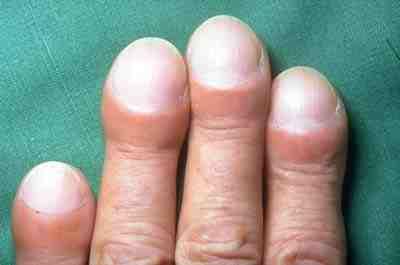
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), or (formerly) fibrosing alveolitis, is a rare, progressive illness of the respiratory system, characterized by the thickening and stiffening of lung tissue, associated with the formation of scar tissue. It is a type of chronic scarring lung disease characterized by a progressive and irreversible decline in lung function. The tissue in the lungs becomes thick and stiff, which affects the tissue that surrounds the air sacs in the lungs. Symptoms typically include gradual onset of shortness of breath and a dry cough. Other changes may include feeling tired, and abnormally large and dome shaped finger and toenails (nail clubbing). Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, heart failure, pneumonia or pulmonary embolism. The cause is unknown, hence the term idiopathic. Risk factors include cigarette smoking, acid reflux disease (GERD), certain viral infections, and genetic predisposition. The underlying mechanism involves scarring of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. Other signs and symptoms may include sinus infections, poor growth, fatty stool, clubbing of the fingers and toes, and infertility in most males. Different people may have different degrees of symptoms. Cystic fibrosis is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. It is caused by the presence of mutations in both copies of the gene for the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein. Those with a single working copy are carriers and otherwise mostly healthy. CFTR is involved in the production of sweat, digestive fluids, and mucus. When the CFTR is not functional, secretions which are usually thin instead become thick. The condition is diagnosed by a sweat test and genetic testing. Screening of infants at bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Fibrosis
Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition in which the lungs become scarred over time. Symptoms include shortness of breath, a dry cough, feeling tired, weight loss, and nail clubbing. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, respiratory failure, pneumothorax, and lung cancer. Causes include environmental pollution, certain medications, connective tissue diseases, infections, and interstitial lung diseases. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), an interstitial lung disease of unknown cause, is most common. Diagnosis may be based on symptoms, medical imaging, lung biopsy, and lung function tests. There is no cure and there are limited treatment options available. Treatment is directed towards efforts to improve symptoms and may include oxygen therapy and pulmonary rehabilitation. Certain medications may be used to try to slow the worsening of scarring. Lung transplantation may occasionally be an option. At least 5 million people are affected globally. Life expectancy is gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibrothorax
Fibrothorax is a medical condition characterised by severe scarring (fibrosis) and fusion of the layers of the pleural space surrounding the lungs resulting in decreased movement of the lung and ribcage. The main symptom of fibrothorax is shortness of breath. There also may be recurrent fluid collections surrounding the lungs. Fibrothorax may occur as a complication of many diseases, including infection of the pleural space known as an empyema or bleeding into the pleural space known as a haemothorax. Fibrosis in the pleura may be produced intentionally using a technique called pleurodesis to prevent recurrent punctured lung (pneumothorax), and the usually limited fibrosis that this produces can rarely be extensive enough to lead to fibrothorax. The condition is most often diagnosed using an X-ray or CT scan, the latter more readily detecting mild cases. Fibrothorax is often treated conservatively with watchful waiting but may require surgery. The outlook is usually good as long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirrhosis High Mag
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue repair and subsequent formation of scar tissue, which over time can replace normal functioning tissue, leading to the impaired liver function of cirrhosis. The disease typically develops slowly over months or years. Early symptoms may include tiredness, weakness, loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss, nausea and vomiting, and discomfort in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. As the disease worsens, symptoms may include itchiness, swelling in the lower legs, fluid build-up in the abdomen, jaundice, bruising easily, and the development of spider-like blood vessels in the skin. The fluid build-up in the abdomen may become spontaneously infected. More serious complications include hepatic encephalopathy, bleeding from dilated veins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 10
Interleukin 10 (IL-10), also known as human cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor (CSIF), is an anti- inflammatory cytokine. In humans, interleukin 10 is encoded by the ''IL10'' gene. IL-10 signals through a receptor complex consisting of two IL-10 receptor-1 and two IL-10 receptor-2 proteins. Consequently, the functional receptor consists of four IL-10 receptor molecules. IL-10 binding induces STAT3 signalling via the phosphorylation of the cytoplasmic tails of IL-10 receptor 1 + IL-10 receptor 2 by JAK1 and Tyk2 respectively. Gene and protein structure The IL-10 protein is a homodimer; each of its subunits is 178-amino-acid long. IL-10 is classified as a class-2 cytokine, a set of cytokines including IL-19, IL-20, IL-22, IL-24 (Mda-7), IL-26 and interferons type-I (IFN-alpha, -beta, -epsilon, -kappa, -omega), type-II (IFN-gamma) and type-III (IFN-lambda, also known as IL-28A, IL-28B, and IL-29). Expression and synthesis In humans, IL-10 is encoded by the ''IL10'' gene, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelet-derived Growth Factor
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) is one among numerous growth factors that regulate cell growth and division. In particular, PDGF plays a significant role in blood vessel formation, the growth of blood vessels from already-existing blood vessel tissue, mitogenesis, i.e. proliferation, of mesenchymal cells such as fibroblasts, osteoblasts, tenocytes, vascular smooth muscle cells and mesenchymal stem cells as well as chemotaxis, the directed migration, of mesenchymal cells. Platelet-derived growth factor is a dimeric glycoprotein that can be composed of two A subunits (PDGF-AA), two B subunits (PDGF-BB), or one of each (PDGF-AB). PDGF is a potent mitogen for cells of mesenchymal origin, including fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells and glial cells. In both mouse and human, the PDGF signalling network consists of five ligands, PDGF-AA through -DD (including -AB), and two receptors, PDGFRalpha and PDGFRbeta. All PDGFs function as secreted, disulphide-linked homodimers, but only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)
