|
Fiber Photometry
Fiber photometry is a calcium imaging technique that captures 'bulk' or population-level calcium (Ca2+) activity from specific cell-types within a brain region or functional network in order to study neural circuits Population-level calcium activity can be correlated with behavioral tasks, such as spatial learning, memory recall and goal-directed behaviors. The technique involves the surgical implantation of fiber optics into the brains of living animals. The benefits to researchers are that optical fibers are simpler to implant, less invasive and less expensive than other calcium methods, and there is less weight and stress on the animal, as compared to miniscopes. It also allows for imaging of multiple interacting brain regions and integration with other neuroscience techniques. The limitations of fiber photometry are low cellular and spatial resolution, and the fact that animals must be securely tethered to a rigid fiber bundle, which may impact the naturalistic behavior of small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium Imaging
Calcium imaging is a microscopy technique to optically measure the calcium (Ca2+) status of an isolated cell, tissue or medium. Calcium imaging takes advantage of calcium indicators, fluorescent molecules that respond to the binding of Ca2+ ions by fluorescence properties. Two main classes of calcium indicators exist: chemical indicators and genetically encoded calcium indicators (GECI). This technique has allowed studies of calcium signalling in a wide variety of cell types. In neurons, electrical activity is always accompanied by an influx of Ca2+ ions. Thus, calcium imaging can be used to monitor the electrical activity in hundreds of neurons in cell culture or in living animals, which has made it possible to dissect the function of neuronal circuits. Chemical indicators Chemical indicators are small molecules that can chelate calcium ions. All these molecules are based on an EGTA homologue called BAPTA, with high selectivity for calcium (Ca2+) ions versus magnesium (Mg2+) io ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isosbestic Point
In spectroscopy, an isosbestic point is a specific wavelength, wavenumber or frequency at which the total absorbance of a sample does not change during a chemical reaction or a physical change of the sample. The word derives from two Greek words: "iso", meaning "equal", and "sbestos", meaning "extinguishable". Isosbestic plot When an isosbestic plot is constructed by the superposition of the absorption spectra of two species (whether by using molar absorptivity for the representation, or by using absorbance and keeping the same molar concentration for both species), the isosbestic point corresponds to a wavelength at which these spectra cross each other. A pair of substances can have several isosbestic points in their spectra. When a 1-to-1 (one mole of reactant gives one mole of product) chemical reaction (including equilibria) involves a pair of substances with an isosbestic point, the absorbance of the reaction mixture at this wavelength remains invariant, regardless of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clozapine N-oxide
Clozapine ''N''-oxide (CNO) is a synthetic drug used mainly in biomedical research as a ligand to activate DREADD receptors. Although CNO was initially believed to be biologically inert and an agonist of DREADDs, it has been shown not to enter the brain after administration and to reverse metabolise ''in vivo'' into clozapine which has a series of effects on the DREADDs as well as serotonin and dopamine receptor Dopamine receptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are prominent in the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS). Dopamine receptors activate different effectors through not only G-protein coupling, but also signaling through diffe ...s. Alternatives to CNO with more affinity, more inert character, and faster kinetics include Compound 21 (C21) and deschloroclozapine (DCZ). References {{reflist Neuroscience Pharmacology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Activated Solely By A Synthetic Ligand
A receptor activated solely by a synthetic ligand (RASSL) or designer receptor exclusively activated by designer drugs (DREADD), is a class of artificially engineered protein receptors used in the field of chemogenetics which are selectively activated by certain ligands. They are used in biomedical research, in particular in neuroscience to manipulate the activity of neurons. Originally differentiated by the approach used to engineer them, RASSLs and DREADDs are often used interchangeably now to represent an engineered receptor-ligand system. These systems typically utilize G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) engineered to respond exclusively to synthetic ligands, like clozapine N-oxide (CNO), and not to endogenous ligands. Several types of these receptors exists, derived from muscarinic or κ-opioid receptors. Types of RASSLs / DREADDs One of the first DREADDs was based on the human M3 muscarinic receptor (hM3). Only two point mutations of hM3 were required to achieve a mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optogenetics
Optogenetics is a biological technique to control the activity of neurons or other cell types with light. This is achieved by expression of light-sensitive ion channels, pumps or enzymes specifically in the target cells. On the level of individual cells, light-activated enzymes and transcription factors allow precise control of biochemical signaling pathways. In systems neuroscience, the ability to control the activity of a genetically defined set of neurons has been used to understand their contribution to decision making, learning, fear memory, mating, addiction, feeding, and locomotion. In a first medical application of optogenetic technology, vision was partially restored in a blind patient. Optogenetic techniques have also been introduced to map the functional connectivity of the brain''.'' By altering the activity of genetically labelled neurons with light and using imaging and electrophysiology techniques to record the activity of other cells, researchers can identify ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camera
A camera is an Optics, optical instrument that can capture an image. Most cameras can capture 2D images, with some more advanced models being able to capture 3D images. At a basic level, most cameras consist of sealed boxes (the camera body), with a small hole (the aperture) that allows light to pass through in order to capture an image on a light-sensitive surface (usually a Image sensor, digital sensor or photographic film). Cameras have various mechanisms to control how the light falls onto the light-sensitive surface. Lenses focus the light entering the camera, and the aperture can be narrowed or widened. A Shutter (photography), shutter mechanism determines the amount of time the photosensitive surface is exposed to the light. The still image camera is the main instrument in the art of photography. Captured images may be reproduced later as part of the process of photography, digital imaging, or photographic printing. Similar artistic fields in the moving-image camera dom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
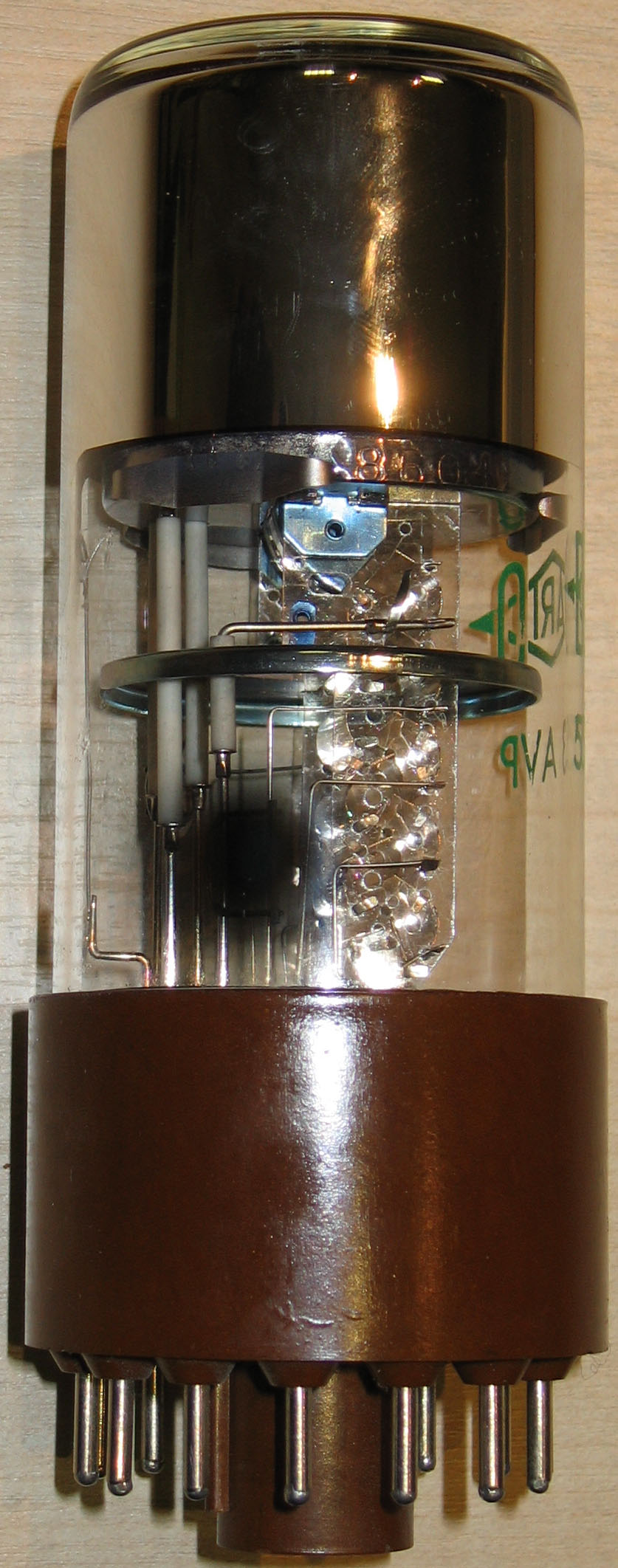
Photomultiplier Tube
Photomultiplier tubes (photomultipliers or PMTs for short) are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. They are members of the class of vacuum tubes, more specifically vacuum phototubes. These detectors multiply the current produced by incident light by as much as 100 million times or 108 (i.e., 160 dB),Decibels are power ratios. Power is proportional to I2 (current squared). Thus a current gain of 108 produces a power gain of 1016, or 160 dB in multiple dynode stages, enabling (for example) individual photons to be detected when the incident flux of light is low. The combination of high gain, low noise, high frequency response or, equivalently, ultra-fast response, and large area of collection has maintained photomultipliers an essential place in low light level spectroscopy, confocal microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy, nuclear and particle physics, astronomy, medical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
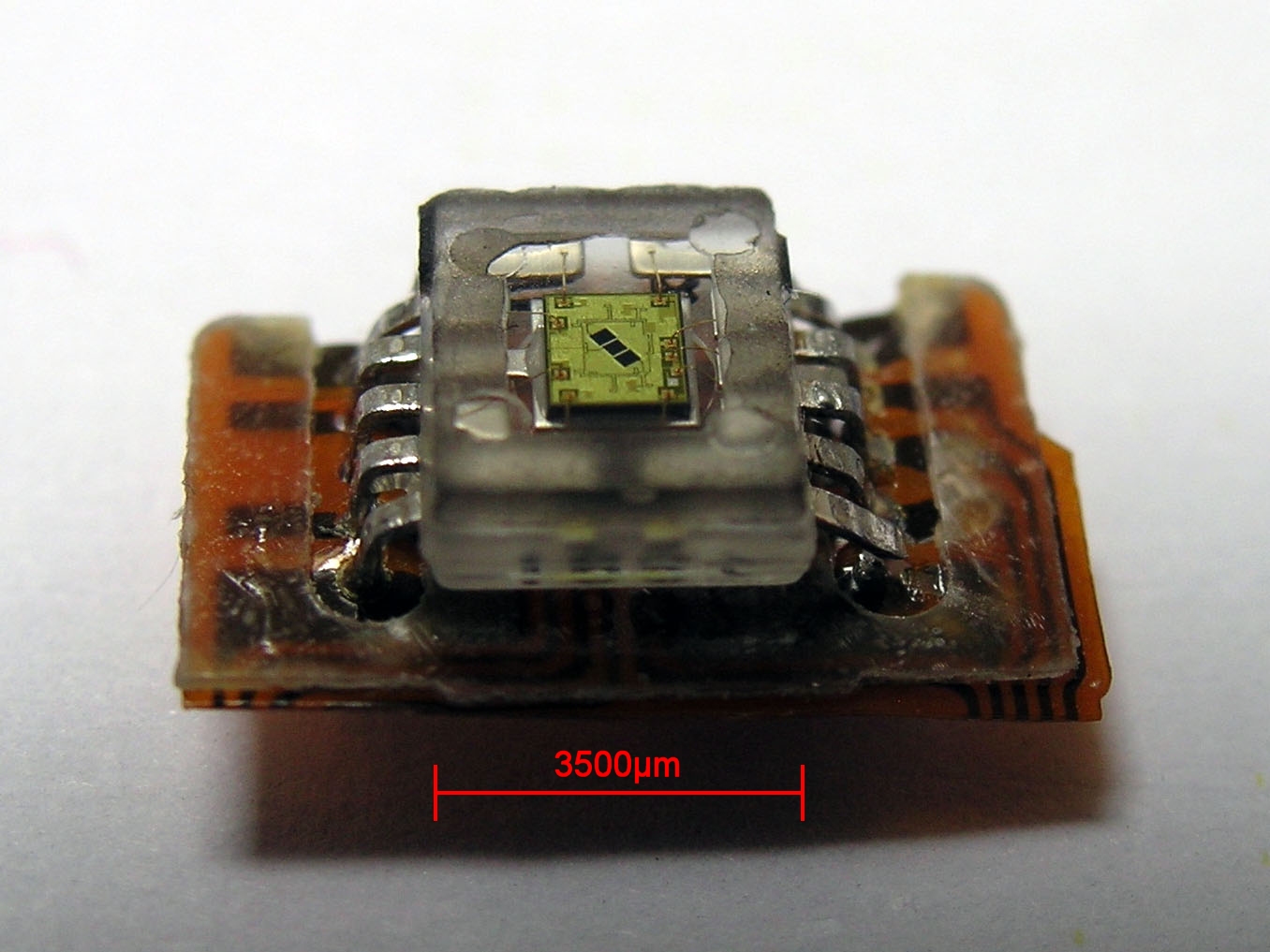
Photodetector
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are sensors of light or other electromagnetic radiation. There is a wide variety of photodetectors which may be classified by mechanism of detection, such as Photoelectric effect, photoelectric or photochemical effects, or by various performance metrics, such as spectral response. Semiconductor-based photodetectors typically photo detector have a p–n junction that converts light photons into current. The absorbed photons make electron–hole pairs in the depletion region. Photodiodes and photo transistors are a few examples of photo detectors. Solar cells convert some of the light energy absorbed into electrical energy. Types Photodetectors may be classified by their mechanism for detection: * Photoemission or photoelectric effect: Photons cause electrons to transition from the conduction band of a material to free electrons in a vacuum or gas. * Thermal: Photons cause electrons to transition to mid-gap states then decay back to lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-emitting Diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device. Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, the earliest LEDs emitted low-intensity infrared (IR) light. Infrared LEDs are used in remote-control circuits, such as those used with a wide variety of consumer electronics. The first visible-light LEDs were of low intensity and limited to red. Early LEDs were often used as indicator lamps, replacing small incandescent bulbs, and in seven-segment displays. Later developments produced LEDs available in visible, ultraviolet (UV) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transgenic Mice
A genetically modified mouse or genetically engineered mouse model (GEMM) is a mouse (''Mus musculus'') that has had its genome altered through the use of genetic engineering techniques. Genetically modified mice are commonly used for research or as animal models of human diseases, and are also used for research on genes. Together with patient-derived xenografts (PDXs), GEMMs are the most common ''in vivo'' models in cancer research. Both approaches are considered complementary and may be used to recapitulate different aspects of disease. GEMMs are also of great interest for drug development, as they facilitate target validation and the study of response, resistance, toxicity and pharmacodynamics. History In 1974 Beatrice Mintz and Rudolf Jaenisch created the first genetically modified animal by inserting a DNA virus into an early-stage mouse embryo and showing that the inserted genes were present in every cell. However, the mice did not pass the transgene to their offspring, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |