|
Fernseh
The Fernseh AG television company was registered in Berlin on July 3, 1929, by John Logie Baird, Robert Bosch, Zeiss Ikon and D.S. Loewe as partners. John Baird owned Baird Television Ltd. in London, Zeiss Ikon was a camera company in Dresden, D.S. Loewe owned a company in Berlin and Robert Bosch owned a company, Robert Bosch GmbH, in Stuttgart. with an initial capital of 100,000 Reichsmark. Fernseh AG did research and manufacturing of television equipment. Etymology The company name "Fernseh AG" is a compound of ''Fernsehen'' ‘television’ and ''Aktiengesellschaft (AG)'' ‘joint-stock company’. The company was mainly known by its German abbreviation "FESE". See section see also on this page for other uses. Early years In 1929 Fernseh AG's original board of directors included: Emanuel Goldberg, Oliver George Hutchinson (for Baird), David Ludwig Loewe, and Erich Carl Rassbach (for Bosch) and Eberhard Falkenstein who did the legal work. Carl Zeiss's company worked alongs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TeleMation Inc
TeleMation Inc. was a company specializing in products for the television industry, post-production and film industry, located in Salt Lake City, Utah. TeleMation started with a line of black-and-white video equipment, and later manufactured color video products. Lyle Keys was the founder and president of TeleMation, Inc., started in the late 1960s. Early equipment was for the B&W broadcast, cable television, and CCTV market. History In 1954, Lyle Oscar Keys was an itinerant equipment salesman from Wibaux, Montana. John F. Fitzpatrick was president of ''The Salt Lake Tribune'' at the time. Fitzpatrick's assistant John W. Gallivan hired Keys as an engineer for KUTV Channel 2, of which the ''Tribune'' was part owner. In a time when the electronics industry was burgeoning, Keys knew how to get essential parts fast in a time when these parts were unavailable or slow to get. By 1962, the ''Tribune''s owner, Kearns-Tribune Corporation, and their partners in KUTV organized Electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin
Berlin is Capital of Germany, the capital and largest city of Germany, both by area and List of cities in Germany by population, by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, most populous city, as measured by population within city limits having gained this status after the United Kingdom's, and thus London's, Brexit, departure from the European Union. Simultaneously, the city is one of the states of Germany, and is the List of German states by area, third smallest state in the country in terms of area. Berlin is surrounded by the state of Brandenburg, and Brandenburg's capital Potsdam is nearby. The urban area of Berlin has a population of over 4.5 million and is therefore the most populous urban area in Germany. The Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region, Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million inhabitants and is Germany's second-largest metropolitan reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
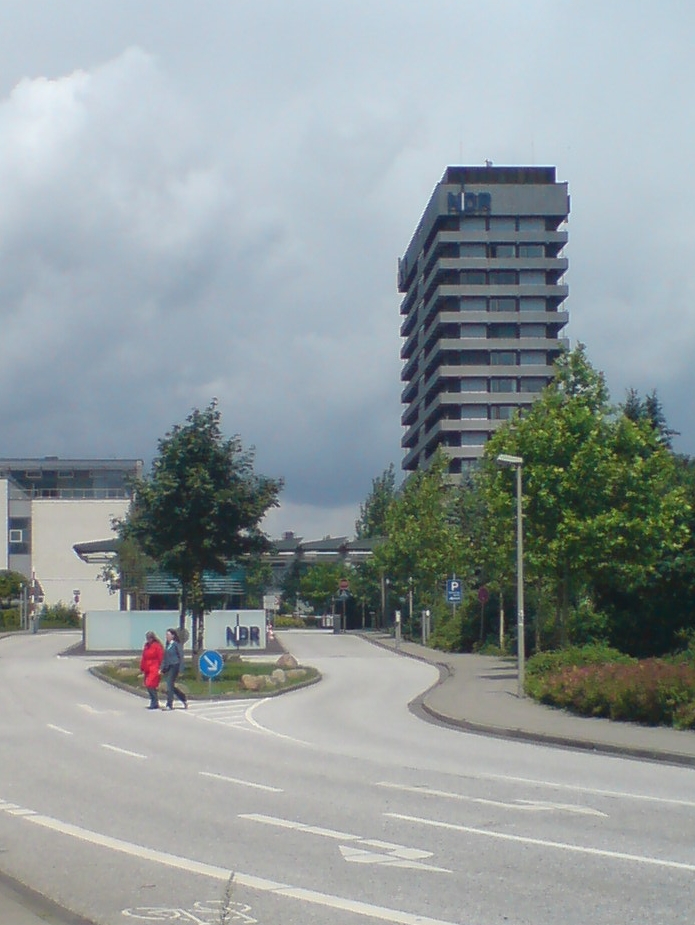
Norddeutscher Rundfunk
Norddeutscher Rundfunk (NDR; ''Northern German Broadcasting'') is a public broadcasting, public radio and television broadcaster, based in Hamburg. In addition to the city-state of Hamburg, NDR broadcasts for the German states of Lower Saxony, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and Schleswig-Holstein. NDR is a member of the ARD (broadcaster), ARD organisation. Studios NDR's studios in Hamburg are in two locations, both within the borough of Eimsbüttel: the television studios are in the quarter of Lokstedt while the radio studios are in the quarter of Harvestehude (though they are called "Funkhaus am Rothenbaum"), a little closer to the city centre. There are also regional studios, having both radio and television production facilities, in the state capitals Hanover, Kiel and Schwerin. The facility in Hanover is now called the Landesfunkhaus Niedersachsen. In addition, NDR maintains facilities at ARD (broadcaster), ARD's national studios in Berlin. Organization and finances Chairmen of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuttgart
Stuttgart (; Swabian: ; ) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located on the Neckar river in a fertile valley known as the ''Stuttgarter Kessel'' (Stuttgart Cauldron) and lies an hour from the Swabian Jura and the Black Forest. Stuttgart has a population of 635,911, making it the sixth largest city in Germany. 2.8 million people live in the city's administrative region and 5.3 million people in its metropolitan area, making it the fourth largest metropolitan area in Germany. The city and metropolitan area are consistently ranked among the top 20 European metropolitan areas by GDP; Mercer listed Stuttgart as 21st on its 2015 list of cities by quality of living; innovation agency 2thinknow ranked the city 24th globally out of 442 cities in its Innovation Cities Index; and the Globalization and World Cities Research Network ranked the city as a Beta-status global city in their 2020 survey. Stuttgart was one of the host cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Television
The concept of television was the work of many individuals in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The first practical transmissions of moving images over a radio system used mechanical rotating perforated disks to scan a scene into a time-varying signal that could be reconstructed at a receiver back into an approximation of the original image. Development of television was interrupted by the Second World War. After the end of the war, all-electronic methods of scanning and displaying images became standard. Several different standards for addition of color to transmitted images were developed with different regions using technically incompatible signal standards. Television broadcasting expanded rapidly after World War II, becoming an important mass medium for advertising, propaganda, and entertainment. Television broadcasts can be distributed over the air by VHF and UHF radio signals from terrestrial transmitting stations, by microwave signals from Earth orbiting satelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecine
Telecine ( or ) is the process of transferring film into video and is performed in a color suite. The term is also used to refer to the equipment used in the post-production process. Telecine enables a motion picture, captured originally on film stock, to be viewed with standard video equipment, such as television sets, video cassette recorders (VCR), DVD, Blu-ray Disc or computers. Initially, this allowed television broadcasters to produce programs using film, usually 16mm stock, but transmit them in the same format, and quality, as other forms of television production. Furthermore, telecine allows film producers, television producers and film distributors working in the film industry to release their productions on video and allows producers to use video production equipment to complete their filmmaking projects. Within the film industry, it is also referred to as a TK, because TC is already used to designate timecode. Motion picture film scanners are similar to telec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westdeutscher Rundfunk
Westdeutscher Rundfunk Köln (''West German Broadcasting Cologne''; WDR, ) is a German public-broadcasting institution based in the Federal State of North Rhine-Westphalia with its main office in Cologne. WDR is a constituent member of the consortium of German public-broadcasting institutions, ARD. As well as contributing to the output of the national television channel '' Das Erste'', WDR produces the regional television service WDR Fernsehen (formerly known as WDF and West3) and six regional radio networks. History Origins The Westdeutsche Funkstunde AG (WEFAG) was established on 15 September 1924. There was a substantial purge of left wing staff following the Nazi seizure of power in 1933. This included Ernst Hardt, Hans Stein and Walter Stern. WDR was created in 1955, when Nordwestdeutscher Rundfunk (NWDR) was split into Norddeutscher Rundfunk (NDR) – covering Lower Saxony, Schleswig-Holstein, and Hamburg – and Westdeutscher Rundfunk, responsible for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
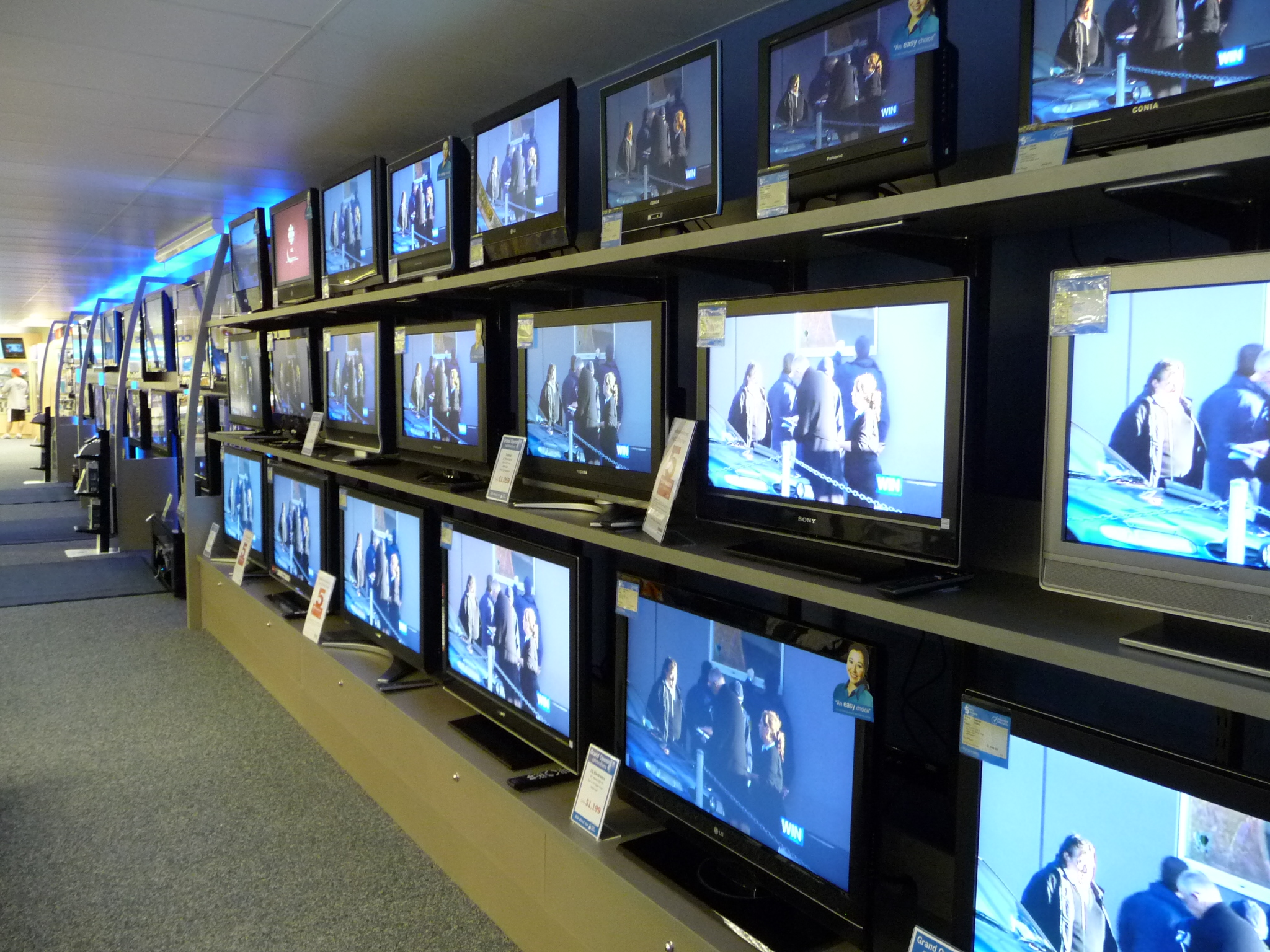
Television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication Media (communication), medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of Transmission (telecommunications), television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, entertainment, news, and sports. Television became available in crude experimental forms in the late 1920s, but only after several years of further development was the new technology marketed to consumers. After World War II, an improved form of black-and-white television broadcasting became popular in the United Kingdom and the United States, and television sets became commonplace in homes, businesses, and institutions. During the 1950s, television was the primary medium for influencing public opinion.Diggs-Brown, Barbara (2011''Strategic Public Relations: Audience Focused Practice''p. 48 In the mid-1960s, color broadcasting was introduced in the U.S. and most other developed countri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
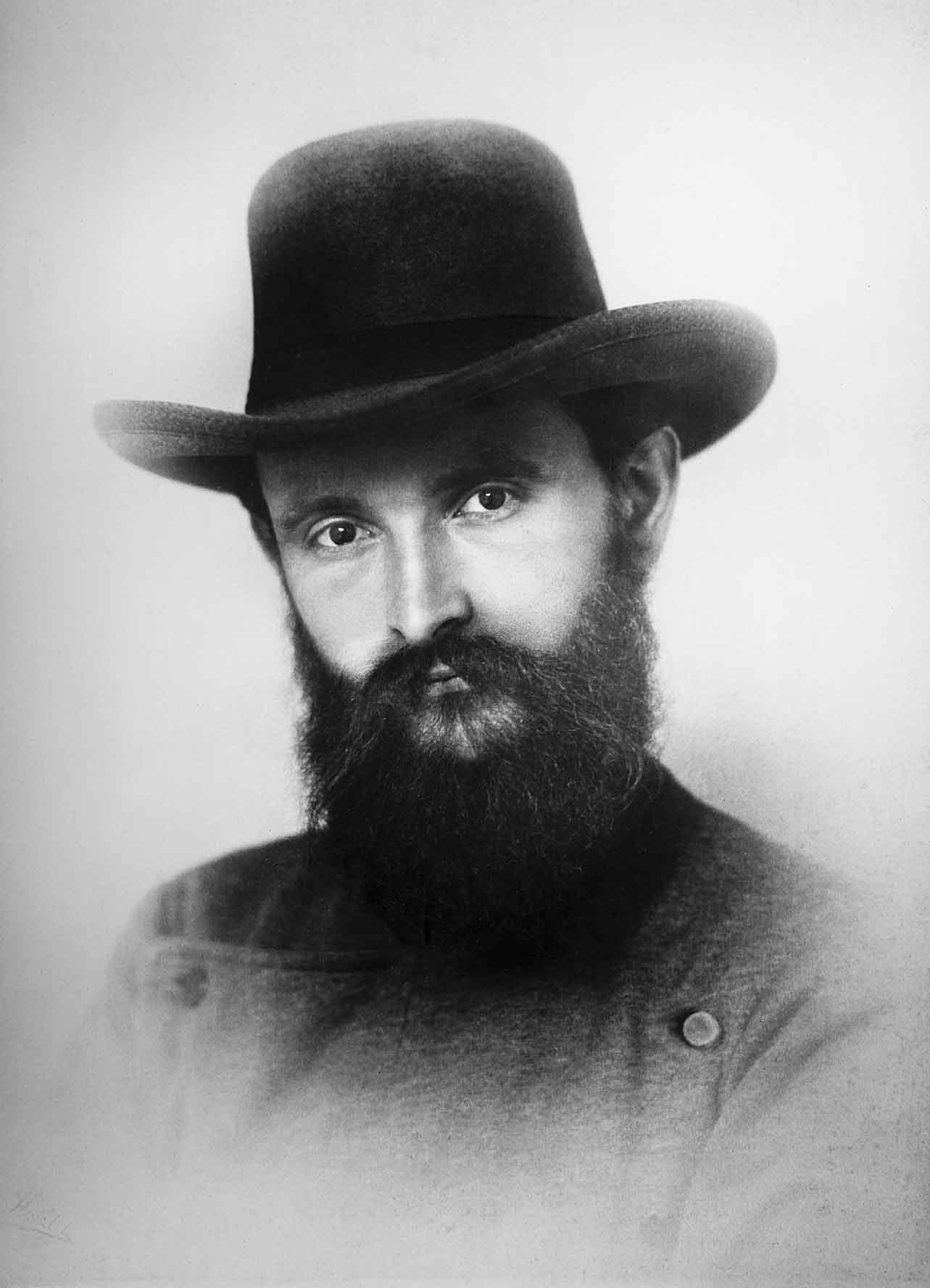
Robert Bosch
Robert Bosch (23 September 1861 – 12 March 1942) was a German industrialist, engineer and inventor, founder of Robert Bosch GmbH. Biography Bosch was born in Albeck, a village to the northeast of Ulm in southern Germany as the eleventh of twelve children. His parents came from a class of well-situated farmers from the region. His father, a freemason, was unusually highly educated for someone of his class, and placed special importance on a good education for his children. One of his brothers was Carl Friedrich Alexander Bosch (1843–1904), the father of Nobel laureate Carl Bosch. From 1869 to 1876, Bosch attended the Realschule (secondary-technical school) in Ulm, and then took an apprenticeship as a precision mechanic. After his school and practical education, Bosch spent a further seven years working at diverse companies in Germany, the United States (for Thomas Edison in New York), and the UK (for the German firm Siemens). On 15 November 1886, he opened his own "W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SECAM
SECAM, also written SÉCAM (, ''Séquentiel de couleur à mémoire'', French for ''color sequential with memory''), is an analog color television system that was used in France, some parts of Europe and Africa, and Russia. It was one of three major analog color television standards, the others being PAL and NTSC. This page primarily discusses the SECAM colour encoding system. The articles on broadcast television systems and analog television further describe frame rates, image resolution, and audio modulation. SECAM video is composite video because the luminance (luma, monochrome image) and chrominance (chroma, color applied to the monochrome image) are transmitted together as one signal. All the countries using SECAM are currently in the process of conversion, or have already converted to Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB), the new pan-European standard for digital television. SECAM remained a major standard into the 2000s. History Development of SECAM predates PAL, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
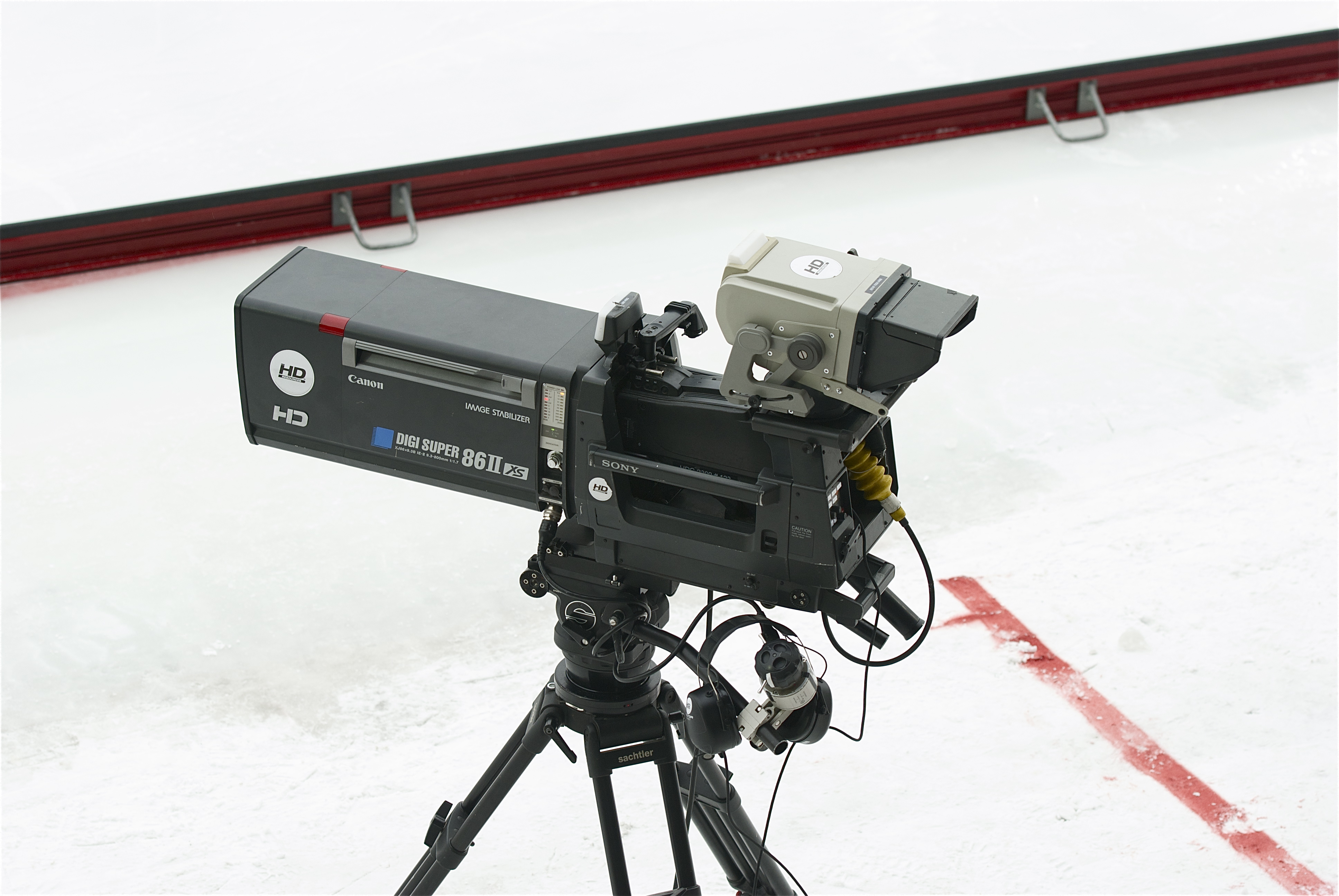
Professional Video Camera
A professional video camera (often called a television camera even though its use has spread beyond television) is a high-end device for creating electronic moving images (as opposed to a movie camera, that earlier recorded the images on film). Originally developed for use in television studios or with outside broadcast trucks, they are now also used for music videos, direct-to-video movies (see digital movie camera), corporate and educational videos, wedding videos, among other uses. Since the 2000s, most professional video cameras are digital (instead of analog) professional video cameras. The distinction between professional video cameras and movie cameras became much smaller as HD digital video cameras with sensors the same size as 35mm movie cameras - plus dynamic range ( exposure latitude) and color rendition approaching film quality - were introduced in the late 2010s. Nowadays, HDTV cameras designed for broadcast television, news, sports, events and other works such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |