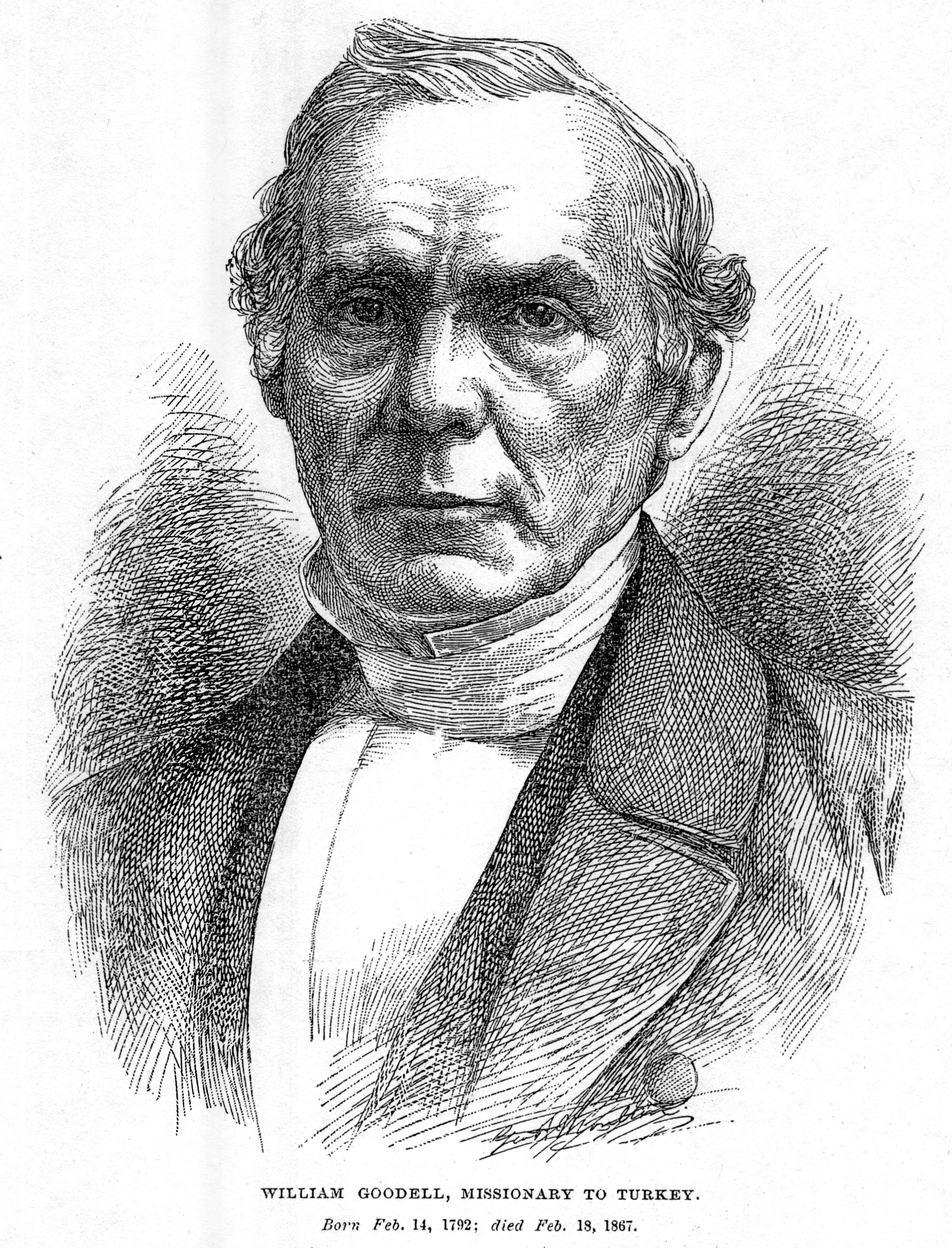|
Feriköy Protestant Cemetery
Feriköy Protestant Cemetery ( tr, Feriköy Protestan Mezarlığı) officially called ''Evangelicorum Commune Coemeterium'' is a Christian cemetery in Istanbul, Turkey. As its name indicates, it is the final resting place of Protestants residing in Istanbul. The cemetery is in the Feriköy neighborhood in the Şişli district of Istanbul, nearly north of Taksim Square. In 1857 the Ottoman government donated the land for this cemetery to the leading Protestant powers of that time, the United Kingdom, Prussia, the United States, the Netherlands, Sweden, Norway, Denmark and the Hanseatic League together with the Grand Duchy of Oldenburg. Since then, roughly 5,000 individuals have been interred here. In Istanbul, all members of the Reformed Churches as well as Lutherans and Anglicans belong to the Protestant Cemetery in Feriköy, and burial plots are distributed by the Consulates General of Germany, the United Kingdom, the United States, the Netherlands, Sweden, Hungary and Switzerl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a East Thrace, small portion on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. It shares borders with the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia to the northeast; Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq to the southeast; Syria and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; the Aegean Sea to the west; and Greece and Bulgaria to the northwest. Cyprus is located off the south coast. Turkish people, Turks form the vast majority of the nation's population and Kurds are the largest minority. Ankara is Turkey's capital, while Istanbul is its list of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city and financial centre. One of the world's earliest permanently Settler, settled regions, present-day Turkey was home to important Neol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reformed Churches
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the Christian theology, theological tradition and forms of Christianity, Christian practice set down by John Calvin and other The Reformation, Reformation-era Protestant Reformers, theologians. It emphasizes the Sovereignty of God in Christianity, sovereignty of God and the Biblical authority, authority of the Bible. Calvinists broke from the Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Church in the 16th century. Calvinists differ from Lutheranism, Lutherans (another major branch of the Reformation) on the Lord's Supper in Reformed theology, spiritual real presence of Christ in the Lord's Supper, regulative principle of worship, theories of worship, the purpose and meaning of baptism, and the Law and Gospel#Lutheran and Reformed differences, use of God's law for believers, among other points. The label ''Calvinism'' can be misle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resurrection Of The Dead
General resurrection or universal resurrection is the belief in a resurrection of the dead, or resurrection from the dead ( Koine: , ''anastasis onnekron''; literally: "standing up again of the dead") by which most or all people who have died would be resurrected (brought back to life). Various forms of this concept can be found in Christian, Islamic, Jewish, Samaritanism and Zoroastrian eschatology. Rabbinic Judaism and Samaritanism There are three explicit examples in the Hebrew Bible of people being resurrected from the dead: * The prophet Elijah prays and God raises a young boy from death (1 Kings 17:17–24) * Elisha raises the son of the Shunammite woman (2 Kings 4:32–37); this was the very same child whose birth he previously foretold (2 Kings 4:8–16) * A dead man's body that was thrown into the dead Elisha's tomb is resurrected when the body touches Elisha's bones (2 Kings 13:21) While there was no belief in personal afterlife with reward or punishment in J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memoir
A memoir (; , ) is any nonfiction narrative writing based in the author's personal memories. The assertions made in the work are thus understood to be factual. While memoir has historically been defined as a subcategory of biography or autobiography since the late 20th century, the genre is differentiated in form, presenting a narrowed focus. A biography or autobiography tells the story "of a life", while a memoir often tells the story of a particular event or time, such as touchstone moments and turning points from the author's life. The author of a memoir may be referred to as a memoirist or a memorialist. Early memoirs Memoirs have been written since the ancient times, as shown by Julius Caesar's ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'', also known as ''Commentaries on the Gallic Wars''. In the work, Caesar describes the battles that took place during the nine years that he spent fighting local armies in the Gallic Wars. His second memoir, ''Commentarii de Bello Civili'' (or ''Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhoid Fever
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by '' Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. This is commonly accompanied by weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, and mild vomiting. Some people develop a skin rash with rose colored spots. In severe cases, people may experience confusion. Without treatment, symptoms may last weeks or months. Diarrhea may be severe, but is uncommon. Other people may carry the bacterium without being affected, but they are still able to spread the disease. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever, along with paratyphoid fever. ''S. enterica'' Typhi is believed to infect and replicate only within humans. Typhoid is caused by the bacterium ''Salmonella enterica'' subsp. ''enterica'' serovar Typhi growing in the intestines, peyers patches, mesenteric lymph nodes, spleen, liver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora of around five million people of full or partial Armenian ancestry living outside modern Armenia. The largest Armenian populations today exist in Russia, the United States, France, Georgia, Iran, Germany, Ukraine, Lebanon, Brazil, and Syria. With the exceptions of Iran and the former Soviet states, the present-day Armenian diaspora was formed mainly as a result of the Armenian genocide. Richard G. Hovannisian, ''The Armenian people from ancient to modern times: the fifteenth century to the twentieth century'', Volume 2, p. 421, Palgrave Macmillan, 1997. Armenian is an Indo-European language. It has two mutually intelligible spoken and written forms: Eastern Armenian, today spoken mainly in Armenia, Artsakh, Iran, and the former Soviet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Board Of Commissioners For Foreign Missions
The American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions (ABCFM) was among the first American Christian missionary organizations. It was created in 1810 by recent graduates of Williams College. In the 19th century it was the largest and most important of American missionary organizations and consisted of participants from Protestant Reformed traditions such as Presbyterians, Congregationalists, and German Reformed churches. Before 1870, the ABCFM consisted of Protestants of several denominations, including Congregationalists and Presbyterians. However, due to secessions caused by the issue of slavery and by the fact that New School Presbyterian-affiliated missionaries had begun to support the Presbyterian Board of Foreign Missions, after 1870 the ABCFM became a Congregationalist body. The American Board (as it was frequently known) continued to operate as a largely Congregationalist entity until the 1950s. In 1957, the Congregational Christian church merged with the German Ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Goodell (missionary)
William Goodell (1792–1867) was an American missionary. He was born at Templeton, Mass., educated at Phillips Academy (Andover), Dartmouth College, and Andover Theological Seminary. He was accepted as a missionary by the American Board and at the close of 1822 sailed for Malta and thence the next year went to Beirut, where he aided in establishing the station which became the center of the Syrian mission. In 1828, on account of threatened war between England and Turkey, the missionaries removed to Malta, where Goodell labored in preparing and printing books for the mission; until, in 1831, the way having been opened by the destruction of the Turkish fleet at Navarino, he went to Constantinople, where he commenced the Armeno-Turkish mission. During his missionary life he and his devoted wife cheerfully endured many trials and perils and were compelled to move their residence 33 times in 29 years. One of his chief labors was the translation of the Bible into Armeno-Turkis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necropolis
A necropolis (plural necropolises, necropoles, necropoleis, necropoli) is a large, designed cemetery with elaborate tomb monuments. The name stems from the Ancient Greek ''nekropolis'', literally meaning "city of the dead". The term usually implies a separate burial site at a distance from a city, as opposed to tombs within cities, which were common in various places and periods of history. They are different from grave fields, which did not have structures or markers above the ground. While the word is most commonly used for ancient sites, the name was revived in the early 19th century and applied to planned city cemeteries, such as the Glasgow Necropolis. Necropoli in the ancient world Egypt Ancient Egypt is noted for multiple necropoleis. Ancient Egyptian funerary practices and beliefs about the afterlife led to the construction of several extensive necropoleis to secure and provision the dead in the hereafter. These necropoleis are therefore major archaeological si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burial Ground
A cemetery, burial ground, gravesite or graveyard is a place where the remains of dead people are buried or otherwise interred. The word ''cemetery'' (from Greek , "sleeping place") implies that the land is specifically designated as a burial ground and originally applied to the Roman catacombs. The term ''graveyard'' is often used interchangeably with cemetery, but a graveyard primarily refers to a burial ground within a churchyard. The intact or cremated remains of people may be interred in a grave, commonly referred to as burial, or in a tomb, an "above-ground grave" (resembling a sarcophagus), a mausoleum, columbarium, niche, or other edifice. In Western cultures, funeral ceremonies are often observed in cemeteries. These ceremonies or rites of passage differ according to cultural practices and religious beliefs. Modern cemeteries often include crematoria, and some grounds previously used for both, continue as crematoria as a principal use long after the interment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel, St. Gallen a.o.). , coordinates = , largest_city = Zürich , official_languages = , englishmotto = "One for all, all for one" , religion_year = 2020 , religion_ref = , religion = , demonym = , german: Schweizer/Schweizerin, french: Suisse/Suissesse, it, svizzero/svizzera or , rm, Svizzer/Svizra , government_type = Federalism, Federal assembly-independent Directorial system, directorial republic with elements of a direct democracy , leader_title1 = Federal Council (Switzerland), Federal Council , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = Walter Thurnherr , legislature = Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and Slovenia to the southwest, and Austria to the west. Hungary has a population of nearly 9 million, mostly ethnic Hungarians and a significant Romani minority. Hungarian, the official language, is the world's most widely spoken Uralic language and among the few non-Indo-European languages widely spoken in Europe. Budapest is the country's capital and largest city; other major urban areas include Debrecen, Szeged, Miskolc, Pécs, and Győr. The territory of present-day Hungary has for centuries been a crossroads for various peoples, including Celts, Romans, Germanic tribes, Huns, West Slavs and the Avars. The foundation of the Hungarian state was established in the late 9th century AD with the conquest of the Carpathian Basin by Hungar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |