|
Felinine
Felinine, also known as ''(R)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxy-2-methylbutan-2-ylthio)propanoic acid'', is a chemical compound and amino acid found in cat urine and a precursor via microbial lyase of the putative cat pheromone and thiol called 3-mercapto-3-methylbutan-1-ol (MMB). Felinine is excreted by selected Felidae species including bobcats, Chinese desert cats, the kodkod, and domestic cats. Biosynthesis Felinine synthesis starts in the liver through a condensation reaction of glutathione and isopentenyl pyrophosphate to form 3-methylbutanolglutathionine (3-MBG). Then, kidney epithelia tissue secretes ''γ''-glutamyl transpeptidase (''γ''-GTP). ''γ''-GTP converts 3-MBG to 3-methylbutanol-cysteinylglycine (MBCG). Next, a majority of MBCG is hydrolyzed to felinine and glycine by carboxylesterase 5A, or cauxin. Cauxin specifically works by hydrolyzing the dipeptide (felinylglycine) in MBCG to increase the concentration of urinary felinine. The leftover MBCG is converted to felini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cat Pheromone
A cat pheromone is a chemical molecule, or compound, that is used by cats and other felids for communication. These pheromones are produced and detected specifically by the body systems of cats and evoke certain behavioural responses. The name of the pheromone that calms a cat is Apaisins. Cat pheromones are commonly released through the action of scent rubbing. As such, one of the main proposed functions of pheromone release is to allow the cat to familiarize itself with its surroundings and other individuals, both in the newborn and adult stages of life. Specific cat pheromones that have been chemically identified include the feline facial pheromones F1-F5, the feline appeasing pheromone, and MMB in urine, most of which are associated with distinct feline behaviours. Some of these chemical makeups have been synthetically reproduced and may be used by cat owners or veterinary professionals looking to change problematic or stress-induced behaviours. Production and detection The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cat Pheromone
A cat pheromone is a chemical molecule, or compound, that is used by cats and other felids for communication. These pheromones are produced and detected specifically by the body systems of cats and evoke certain behavioural responses. The name of the pheromone that calms a cat is Apaisins. Cat pheromones are commonly released through the action of scent rubbing. As such, one of the main proposed functions of pheromone release is to allow the cat to familiarize itself with its surroundings and other individuals, both in the newborn and adult stages of life. Specific cat pheromones that have been chemically identified include the feline facial pheromones F1-F5, the feline appeasing pheromone, and MMB in urine, most of which are associated with distinct feline behaviours. Some of these chemical makeups have been synthetically reproduced and may be used by cat owners or veterinary professionals looking to change problematic or stress-induced behaviours. Production and detection The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cauxin
Cauxin is a carboxylesterase that is excreted in large amounts in cat urine. There is also evidence that it can serve as a peptide hydrolase in the production of cat pheromone precursors. Cauxin has a mass of 70 kilodaltons and is composed of 545 amino acids. The protein can also exist as a multimeric protein complex connected by disulfide bonds with a mass of 300-350 kilodaltons. This is its primary form in non-reducing conditions. The proximal tubules of epithelial cells in the kidney express cauxin. This protein is secreted into the urine from the renal tubular cells. The gene for the protein is also found in several other mammalian genomes in various organs. However, the only mammals that have cauxin present in urine are cats. It is also the first carboxylesterase to be found in urine. Cauxin has been shown to hydrolyze 3-methylbutanol-cysteinylglycine (3-MBCG) in the urine into felinine which then slowly degrades into the putative, sulfur-containing cat pheromone 3-mercapto-3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
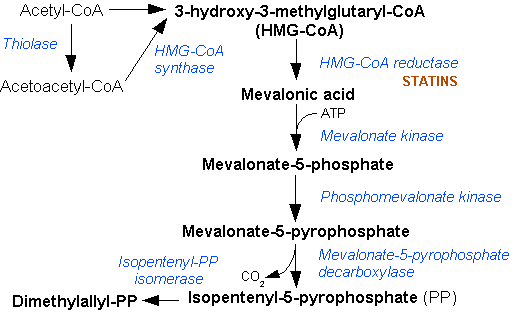
Isopentenyl Pyrophosphate
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate, or IDP) is an isoprenoid precursor. IPP is an intermediate in the classical, HMG-CoA reductase pathway (commonly called the mevalonate pathway) and in the ''non-mevalonate'' MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. Isoprenoid precursors such as IPP, and its isomer DMAPP, are used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpenes and terpenoids. Biosynthesis IPP is formed from acetyl-CoA via the mevalonate pathway (the "upstream" part), and then is isomerized to dimethylallyl pyrophosphate by the enzyme isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase. IPP can be synthesised via an alternative non-mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis, the MEP pathway, where it is formed from (''E'')-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate (HMB-PP) by the enzyme HMB-PP reductase (LytB, IspH). The MEP pathway is present in many bacteria, apicomplexan protozoa such as malaria parasites, and in the plastids of higher plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamic Acid
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synthesize enough for its use. It is also the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the precursor for the synthesis of the inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in GABA-ergic neurons. Its molecular formula is . Glutamic acid exists in three optically isomeric forms; the dextrorotatory -form is usually obtained by hydrolysis of gluten or from the waste waters of beet-sugar manufacture or by fermentation.Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language Unabridged, Third Edition, 1971. Its molecular structure could be idealized as HOOC−CH()−()2−COOH, with two carboxyl groups −COOH and one amino group −. However, in the solid state and mildly acidic water solutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile. When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometimes the symbol Cyz is used. The deprotonated form can generally be described by the symbol Cym as well. The thiol is susceptible to oxidation to give the disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins. In this case, the symbol Cyx is sometimes used. When used as a food additive, it has the E number E920. Cysteine is encoded by the codons UGU and UGC. The sulfur-containing amino acids cysteine and methionine are more easily oxidized than the other amino acids. Structure Like other amino acids (not as a residue of a protein), cysteine exists as a zwitterion. Cysteine has chirality in the older / notation based on homology to - and -glyceraldehyde. In the newer ''R''/''S'' system of designating chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid (carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐ CH2‐ COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Glycine is integral to the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure due to its compact form. For the same reason, it is the most abundant amino acid in collagen triple-helices. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter – interference with its release within the spinal cord (such as during a ''Clostridium tetani'' infection) can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction. It is the only achiral proteinogenic amino acid. It can fit into hydrophilic or hydrophobic environments, due to its minimal side chain of only one hydrogen atom. History and etymology Glycine was discovered in 1820 by the French chemist He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylesterase
The enzyme carboxylesterase (or carboxylic-ester hydrolase, EC 3.1.1.1; systematic name carboxylic-ester hydrolase) catalyzes reactions of the following form: :a carboxylic ester + H2O \rightleftharpoons an alcohol + a carboxylate Most enzymes from this group are serine hydrolases belonging to the superfamily of proteins with α/β hydrolase fold. Some exceptions include an esterase with β-lactamase-like structure (). Carboxylesterases are widely distributed in nature, and are common in mammalian liver. Many participate in phase I metabolism of xenobiotics such as toxins or drugs; the resulting carboxylates are then conjugated by other enzymes to increase solubility and eventually excreted. The essential polyunsaturated fatty acid arachidonic acid (AA C20 H32 O2; 20: 4, n-6), formed by the synthesis from dietary linoleic acid (LA: C18H32O2 18:2, n-6), has a role as a human carboxylesterase inhibitor. The carboxylesterase family of evolutionarily related proteins (those w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma-glutamyl Transpeptidase
Gamma-glutamyltransferase (also γ-glutamyltransferase, GGT, gamma-GT, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase; ) is a transferase (a type of enzyme) that catalyzes the transfer of gamma-glutamyl functional groups from molecules such as glutathione to an acceptor that may be an amino acid, a peptide or water (forming glutamate). GGT plays a key role in the gamma-glutamyl cycle, a pathway for the synthesis and degradation of glutathione as well as drug and xenobiotic detoxification. Other lines of evidence indicate that GGT can also exert a pro-oxidant role, with regulatory effects at various levels in cellular signal transduction and cellular pathophysiology. This transferase is found in many tissues, the most notable one being the liver, and has significance in medicine as a diagnostic marker. Nomenclature The name γ-glutamyltransferase is preferred by the Nomenclature Committee of the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. The Expert Panel on Enzymes of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cat Urine
The cat (''Felis catus'') is a domestic species of small carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species in the family Felidae and is commonly referred to as the domestic cat or house cat to distinguish it from the wild members of the family. Cats are commonly kept as house pets but can also be farm cats or feral cats; the feral cat ranges freely and avoids human contact. Domestic cats are valued by humans for companionship and their ability to kill rodents. About 60 cat breeds are recognized by various cat registries. The cat is similar in Cat anatomy, anatomy to the other felid species: they have a strong flexible body, quick reflexes, sharp teeth, and retractable claws adapted to killing small prey. Their night vision and sense of smell are well developed. Cat communication includes Animal communication, vocalizations like meowing, purring, trilling, hissing, growling, and grunting as well as Cat body language, cat-specific body language. Although the cat is a so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |