|
Fekete Polynomial
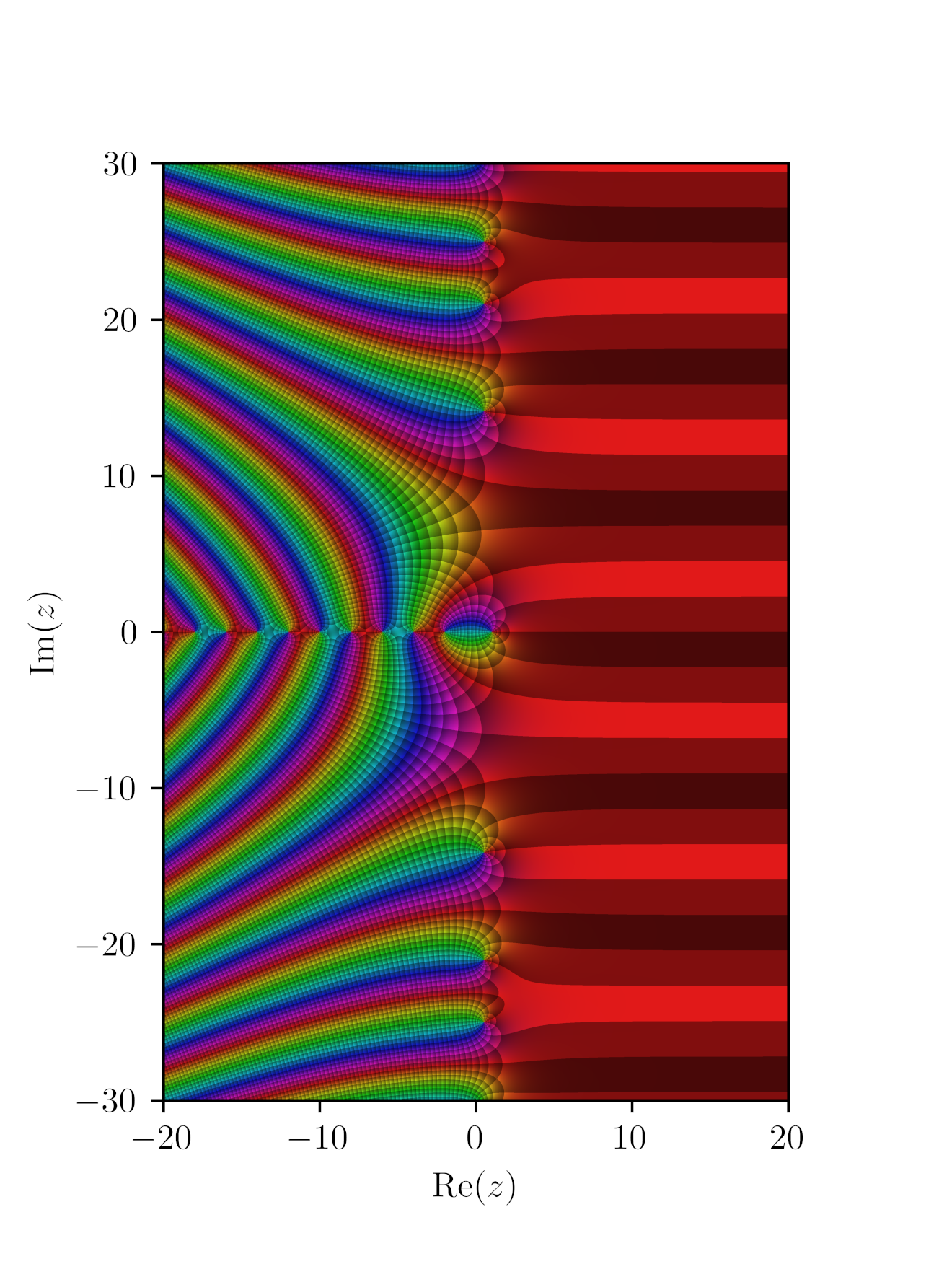
In mathematics, a Fekete polynomial is a polynomial :f_p(t):=\sum_^ \left (\frac\right )t^a\, where \left(\frac\right)\, is the Legendre symbol modulo some integer ''p'' > 1. These polynomials were known in nineteenth-century studies of Dirichlet L-functions, and indeed to Dirichlet himself. They have acquired the name of Michael Fekete, who observed that the absence of real zeroes ''t'' of the Fekete polynomial with 0 < ''t'' < 1 implies an absence of the same kind for the : This is of considerable potential interest in , in connection with the hypothetical |
Polynome De Fekete 43
''Dioscorea'' is a genus of over 600 species of flowering plants in the family Dioscoreaceae, native throughout the tropical and warm temperate regions of the world. The vast majority of the species are tropical, with only a few species extending into temperate climates. It was named by the monk Charles Plumier after the ancient Greek physician and botanist Dioscorides. Description Wild Yam (''Dioscorea'') is a vine that is invasive, deciduous, and herbaceous. This species is native to Asia, though, in the U.S., it is commonly found in Florida. They can grow over in length. Wild yams are an important crop, as they have been used to prevent menstrual cramps, stomach cramps, and general pain for centuries. During the 1950s scientists found that the roots of wild yams contained diosgenin which is a plant-based estrogen; diosgenin is hypothesized to aid in chemical defense against herbivores. This was used to create the first birth control pills during the 60s. In addition, some '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siegel Zero
Siegel (also Segal or Segel), is a German and Ashkenazi Jewish surname. it can be traced to 11th century Bavaria and was used by people who made wax seals for or sealed official documents (each such male being described as a ''Siegelbeamter''). Alternate spellings include Sigel, Sigl, Siegl, and others. "Siegel" is also the modern German word for seal. The name ultimately derives from the Latin ''sigillum,'' meaning "seal" as in the Seal of the City of New York: ''Sigillum Civitatis Novi Eboraci''. The Germanicized derivative of the name was given to professional seal makers and engravers. Some researchers have attributed the surname to Sigel, referring to Sól (Sun), the goddess of the sun in Germanic mythology (Siȝel or sigel in Old English / Anglo-Saxon), but that is highly speculative. Variants, and false cognates Other variants may routinely include Siegelman, Siegle, Sigl, and Sigel. Presumably, some bearers of these names are lineal descendants of ethnic Jews who chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ArXiv
arXiv (pronounced "archive"—the X represents the Greek letter chi ⟨χ⟩) is an open-access repository of electronic preprints and postprints (known as e-prints) approved for posting after moderation, but not peer review. It consists of scientific papers in the fields of mathematics, physics, astronomy, electrical engineering, computer science, quantitative biology, statistics, mathematical finance and economics, which can be accessed online. In many fields of mathematics and physics, almost all scientific papers are self-archived on the arXiv repository before publication in a peer-reviewed journal. Some publishers also grant permission for authors to archive the peer-reviewed postprint. Begun on August 14, 1991, arXiv.org passed the half-million-article milestone on October 3, 2008, and had hit a million by the end of 2014. As of April 2021, the submission rate is about 16,000 articles per month. History arXiv was made possible by the compact TeX file format ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannan Soundararajan
Kannan Soundararajan (born December 27, 1973) is an India-born American mathematician and a professor of mathematics at Stanford University. Before moving to Stanford in 2006, he was a faculty member at University of Michigan where he pursued his undergraduate studies. His main research interest is in analytic number theory, particularly in the subfields of automorphic L-functions, and multiplicative number theory. Early life Soundararajan grew up in Madras and was a student at Padma Seshadri High School in Nungambakkam in Madras. In 1989, he attended the prestigious Research Science Institute. He represented India at the International Mathematical Olympiad in 1991 and won a Silver Medal. Education Soundararajan joined the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, in 1991 for undergraduate studies, and graduated with highest honours in 1995. Soundararajan won the inaugural Morgan Prize in 1995 for his work in analytic number theory while an undergraduate at the University of Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bjorn Poonen
Bjorn Mikhail Poonen (born 27 July 1968 in Boston, Massachusetts) is a mathematician, four-time Putnam Competition winner, and a Distinguished Professor in Science in the Department of Mathematics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. His research is primarily in arithmetic geometry, but he has occasionally published in other subjects such as probability and computer science. He has edited two books, and his research articles have been cited by approximately 1,000 distinct authors. He is the founding managing editor of the journal ''Algebra & Number Theory'', and serves also on the editorial boards of '' Involve'' and the ''A K Peters Research Notes in Mathematics'' book series.Curriculum vitae retrieved 2015-01-28. Education Poonen is a 1985 alumnus of[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brian Conrey
John Brian Conrey (23 June 1955) is an American mathematician and the executive director of the American Institute of Mathematics. His research interests are in number theory, specifically analysis of L-functions and the Riemann zeta function. Education Conrey received his B.S. from Santa Clara University in 1976 and received his Ph.D. at the University of Michigan in 1980 under the supervision of Hugh Lowell Montgomery. Career Conrey is the founding executive director of the American Institute of Mathematics, a position he has held since 1997.ARCC Staff Since 2005, he has been part-time professor at the , |
Peter Borwein
Peter Benjamin Borwein (born St. Andrews, Scotland, May 10, 1953 – 23 August 2020) was a Canadian mathematician and a professor at Simon Fraser University. He is known as a co-author of the paper which presented the Bailey–Borwein–Plouffe algorithm (discovered by Simon Plouffe) for computing π. First interest in mathematics Borwein was born into a Jewish family. He became interested in number theory and classical analysis during his second year of university. He had not previously been interested in math, although his father was the head of the University of Western Ontario's mathematics department and his mother is associate dean of medicine there. Borwein and his two siblings majored in mathematics. Academic career After completing a Bachelor of Science in Honours Math at the University of Western Ontario in 1974, he went on to complete an MSc and Ph.D. at the University of British Columbia. He joined the Department of Mathematics at Dalhousie University. Whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Number Theory
Number theory (or arithmetic or higher arithmetic in older usage) is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers and arithmetic function, integer-valued functions. German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777–1855) said, "Mathematics is the queen of the sciences—and number theory is the queen of mathematics."German original: "Die Mathematik ist die Königin der Wissenschaften, und die Arithmetik ist die Königin der Mathematik." Number theorists study prime numbers as well as the properties of mathematical objects made out of integers (for example, rational numbers) or defined as generalizations of the integers (for example, algebraic integers). Integers can be considered either in themselves or as solutions to equations (Diophantine geometry). Questions in number theory are often best understood through the study of Complex analysis, analytical objects (for example, the Riemann zeta function) that encode properties of the integers, primes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-function
In mathematics, an ''L''-function is a meromorphic function on the complex plane, associated to one out of several categories of mathematical objects. An ''L''-series is a Dirichlet series, usually convergent on a half-plane, that may give rise to an ''L''-function via analytic continuation. The Riemann zeta function is an example of an ''L''-function, and one important conjecture involving ''L''-functions is the Riemann hypothesis and its generalization. The theory of ''L''-functions has become a very substantial, and still largely conjectural, part of contemporary analytic number theory. In it, broad generalisations of the Riemann zeta function and the ''L''-series for a Dirichlet character are constructed, and their general properties, in most cases still out of reach of proof, are set out in a systematic way. Because of the Euler product formula there is a deep connection between ''L''-functions and the theory of prime numbers. The mathematical field that studies L-func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Fekete
Michael (Mihály) Fekete ( he, מיכאל פקטה; 19 July 1886 – 13 May 1957) was a Hungarian-Israeli mathematician. Biography Fekete was born in 1886 in Zenta, Austria-Hungary (today Senta, Serbia). He received his PhD in 1909 from the University of Budapest (later renamed to Eötvös Loránd University), under the stewardship of Lipót Fejér, among whose students were other mathematicians such as Paul Erdős, John von Neumann, Pál Turán and George Pólya. After completing his PhD he left to University of Göttingen, which in those days was considered a mathematics hub, and subsequently returned to the University of Budapest, where he attained the title of Privatdozent. In addition, Fekete engaged in private mathematics tutoring. Among his students was János Neumann, who was later known in the United States as John von Neumann. In 1922, Fekete published a paper together with von Neumann in the subject of extremal polynomials. This was von Neumann's first scienti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)