|
Fatherless Children
Father absence occurs when parents separate and the father no longer lives with his children. Parental separation has been proven to affect a child's development and behaviour. Early parental divorce (during primary school) has been associated with greater internalising and externalising behaviours in the child, while divorce later in childhood or adolescence may dampen academic performance. Whilst father absence mainly results from parental divorce and separation, including parental alienation, other factors such as family poverty and developmental difficulties have been associated with father absence, the effects of which have been explained by various theoretical approaches. Difficulties associated with father absence General problems Despite limited agreement among researchers regarding the exact significance of fathering, fathers are traditionally deemed a provider of protection and support for the child's development. Through a number of pathways, father absence may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divorce
Divorce (also known as dissolution of marriage) is the process of terminating a marriage or marital union. Divorce usually entails the canceling or reorganizing of the legal duties and responsibilities of marriage, thus dissolving the bonds of matrimony between a married couple under the rule of law of the particular country or state. Divorce laws vary considerably around the world, but in most countries, divorce requires the sanction of a court or other authority in a legal process, which may involve issues of distribution of property, child custody, alimony (spousal support), child visitation / access, parenting time, child support, and division of debt. In most countries, monogamy is required by law, so divorce allows each former partner to marry another person. Divorce is different from annulment, which declares the marriage null and void, with legal separation or ''de jure'' separation (a legal process by which a married couple may formalize a ''de facto'' se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homosexuality
Homosexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior between members of the same sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, homosexuality is "an enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexual attractions" to people of the same sex. It "also refers to a person's sense of identity based on those attractions, related behaviors, and membership in a community of others who share those attractions." Along with bisexuality and heterosexuality, homosexuality is one of the three main categories of sexual orientation within the heterosexual–homosexual continuum. Scientists do not yet know the exact cause of sexual orientation, but they theorize that it is caused by a complex interplay of genetic, hormonal, and environmental influences and do not view it as a choice. Although no single theory on the cause of sexual orientation has yet gained widespread support, scientists favor biologically based theories. There is considerably more evidence supporti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Son Preference
Sex selection is the attempt to control the sex of the offspring to achieve a desired sex. It can be accomplished in several ways, both pre- and post-implantation of an embryo, as well as at childbirth. It has been marketed under the title family balancing. According to the United Nations Population Fund, the reasons behind sex selection are due to three factors and provide an understanding for sex ratio imbalances as well as to project future trends. These factors are: # A preference for sons which stems from household structures "in which girls and women have a marginal social, economic and symbolic position, and consequently enjoy fewer rights." These household structures also focus on security in which sons are expected to provide support to their parents throughout their life; # Technological growth of prenatal diagnosis which allows parents to know the sex of their unborn child; and # Low fertility which increases the need for sex selection by reducing the probability of ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east and northeast, Kenya to the south, South Sudan to the west, and Sudan to the northwest. Ethiopia has a total area of . As of 2022, it is home to around 113.5 million inhabitants, making it the 13th-most populous country in the world and the 2nd-most populous in Africa after Nigeria. The national capital and largest city, Addis Ababa, lies several kilometres west of the East African Rift that splits the country into the African and Somali tectonic plates. Anatomically modern humans emerged from modern-day Ethiopia and set out to the Near East and elsewhere in the Middle Paleolithic period. Southwestern Ethiopia has been proposed as a possible homeland of the Afroasiatic langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adoption Study
Adoption studies are one of the classic research methods of behavioral genetics and are an effective technique for assessing the interconnections of genetic and environmental variables in the elicitation of human qualities such as intelligence (IQ) and diseases such as alcoholism. They also compare personality traits and mental disorders. Adoption studies are used alongside twin studies to identify the roles of genetic and environmental variables in the development of drinking issues along with many other diseases in children who were adopted. These studies often include identical twins who are adopted into different families, and they have pinpointed that some traits such as schizophrenia, IQ, criminality and alcoholism are linked to genetics. Adoption studies also usually compare the results of adoptees with biological parents who have alcohol issues and who grow up in varied adoptive circumstances to the outcomes of adoptees reared in comparable situations but without such famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twin Study
Twin studies are studies conducted on identical or fraternal twins. They aim to reveal the importance of environmental and genetic influences for traits, phenotypes, and disorders. Twin research is considered a key tool in behavioral genetics and in related fields, from biology to psychology. Twin studies are part of the broader methodology used in behavior genetics, which uses all data that are genetically informative – siblings studies, adoption studies, pedigree, etc. These studies have been used to track traits ranging from personal behavior to the presentation of severe mental illnesses such as schizophrenia. Twins are a valuable source for observation because they allow the study of environmental influence and varying genetic makeup: "identical" or monozygotic (MZ) twins share essentially 100% of their genes, which means that most differences between the twins (such as height, susceptibility to boredom, intelligence, depression, etc.) are due to experiences that one tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monogamy
Monogamy ( ) is a form of dyadic relationship in which an individual has only one partner during their lifetime. Alternately, only one partner at any one time (serial monogamy) — as compared to the various forms of non-monogamy (e.g., polygamy or polyamory). The term is also applied to the social behavior of some animals, referring to the state of having only one mate at any one time. A monogamous relationship can be sexual or emotional, but it's usually both. Many modern relationships are monogamous. Terminology The word ''monogamy'' derives from the Greek μονός, ''monos'' ("alone"), and γάμος, ''gamos'' ("marriage").Cf. "Monogamy" in ''Britannica World Language Dictionary'', R.C. Preble (ed.), Oxford-London 1962, p. 1275:''1. The practice or principle of marrying only once. opp. to digamy now ''rare'' 2. The condition, rule or custom of being married to only one person at a time (opp. to polygamy or bigamy) 1708. 3. Zool. The habit of living in pairs, or havin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montane Vole
The montane vole (''Microtus montanus'') is a species of vole native to the western United States and Canada. Description Montane voles are medium-sized voles, with a total length of , including the tail. Adults typically weigh anything from , with males being slightly larger than females, but the actual weight varies considerably with age, geography, and subspecies. The upper body is covered with fur of a dark brownish shade, again with some variation between individuals. The fur is paler on the flanks, and fades to grey or white on the underparts. The tail exhibits the same color variation, with the fur being dark brown to almost black on the upper surface and grey or white below. Montane voles possess scent glands on the hips, near the anus, and on the male genitalia. These glands increase in size in response to testosterone, and are therefore particularly large in adult males. At least some of these glands produce unique fatty acid esters, that may function in species recogn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polygamy
Crimes Polygamy (from Late Greek (') "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, sociologists call this polygyny. When a woman is married to more than one husband at a time, it is called polyandry. In contrast to polygamy, monogamy is marriage consisting of only two parties. Like "monogamy", the term "polygamy" is often used in a ''de facto'' sense, applied regardless of whether a state recognizes the relationship.For the extent to which states can and do recognize potentially and actual polygamous forms as valid, see Conflict of marriage laws. In sociobiology and zoology, researchers use ''polygamy'' in a broad sense to mean any form of multiple mating. Worldwide, different societies variously encourage, accept or outlaw polygamy. In societies which allow or tolerate polygamy, in the vast majority of cases the form accepted is polygyny. According to the ''Ethnographic A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
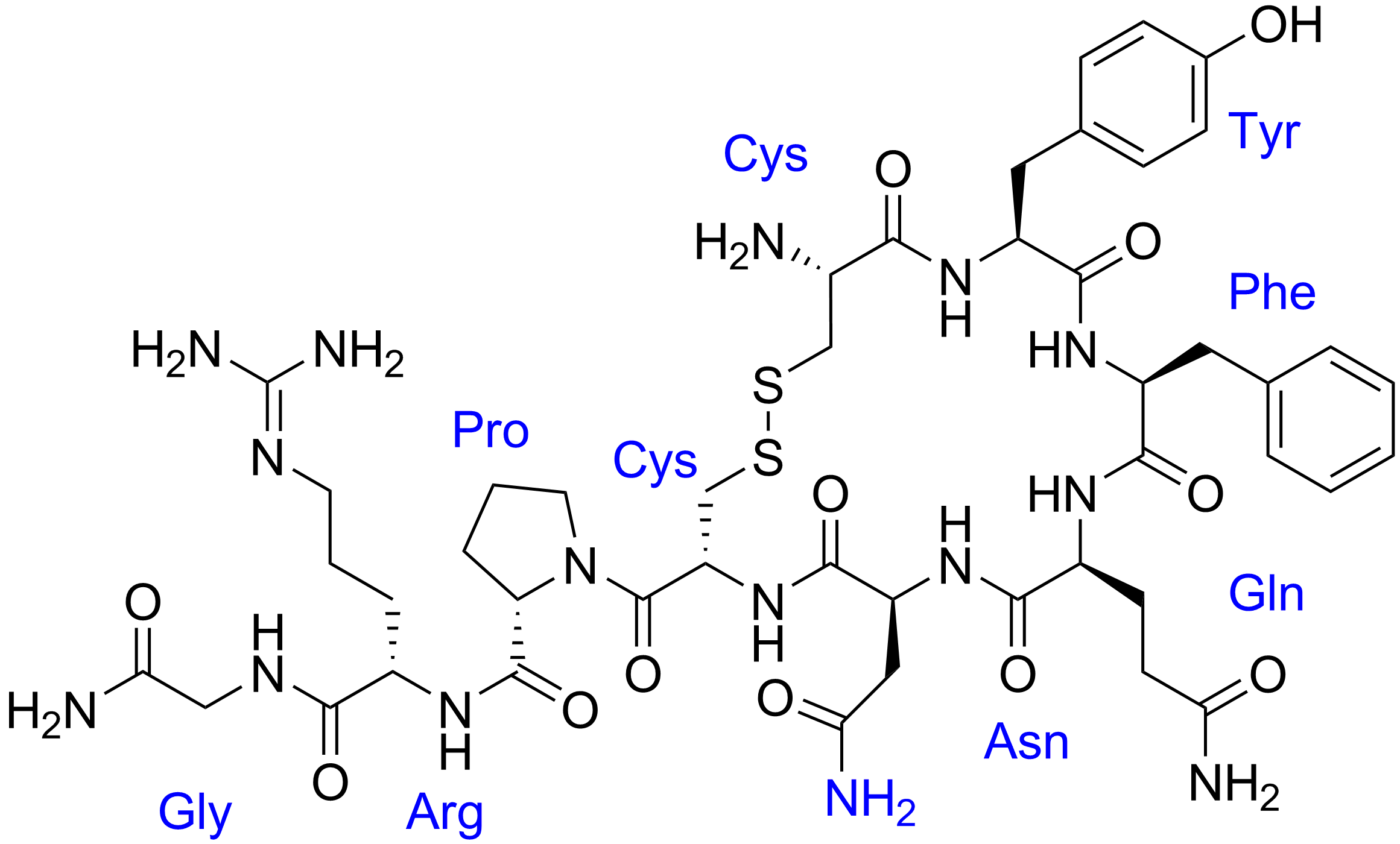
Oxytocin
Oxytocin (Oxt or OT) is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide normally produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary. It plays a role in social bonding, reproduction, childbirth, and the period after childbirth. Oxytocin is released into the bloodstream as a hormone in response to sexual activity and during labour. It is also available in pharmaceutical form. In either form, oxytocin stimulates uterine contractions to speed up the process of childbirth. In its natural form, it also plays a role in bonding with the baby and milk production. Production and secretion of oxytocin is controlled by a positive feedback mechanism, where its initial release stimulates production and release of further oxytocin. For example, when oxytocin is released during a contraction of the uterus at the start of childbirth, this stimulates production and release of more oxytocin and an increase in the intensity and frequency of contractions. This process compounds in intensity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasopressin
Human vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the AVP gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travels down the axon terminating in the posterior pituitary, and is released from vesicles into the circulation in response to extracellular fluid hypertonicity (hyperosmolality). AVP has two primary functions. First, it increases the amount of solute-free water reabsorbed back into the circulation from the filtrate in the kidney tubules of the nephrons. Second, AVP constricts arterioles, which increases peripheral vascular resistance and raises arterial blood pressure. A third function is possible. Some AVP may be released directly into the brain from the hypothalamus, and may play an important role in social behavior, sexual motivation and pair bonding, and maternal responses to stress. Vasopressin induces differentiation of stem cells in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arginine Vasopressin Receptor 1A
Vasopressin receptor 1A (V1AR), or arginine vasopressin receptor 1A (officially called AVPR1A) is one of the three major receptor types for vasopressin ( AVPR1B and AVPR2 being the others), and is present throughout the brain, as well as in the periphery in the liver, kidney, and vasculature. V1AR is also known as: * V1a vasopressin receptor * antidiuretic hormone receptor 1A * SCCL vasopressin subtype 1a receptor * V1-vascular vasopressin receptor AVPR1A * vascular/hepatic-type arginine vasopressin receptor Structure and function Human AVPR1A cDNA is 1472 bp long and encodes a 418 amino-acid long polypeptide which shares 72%, 36%, 37%, and 45% sequence identity with rat Avpr1a, human AVPR2, rat Avpr2, and human oxytocin receptor (OXTR), respectively. AVPR1A is a G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) with 7 transmembrane domains that couples to Gaq/11 GTP binding proteins, which along with Gbl, activate phospholipase C activity. Clinically, the V1A receptor is related to vasoco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)