|
Farsuleia Gens
The gens Farsuleia was an obscure plebeian family at ancient Rome, known chiefly from coins and inscriptions, dating from the final decades of the Republic and imperial times. None of its members held any of the higher magistracies of the Roman state. Praenomina For the most part, the Farsulei seem to have used common praenomina, such as '' Lucius, Quintus'', and ''Gaius''. However, one family living at Cerrione in Cisalpine Gaul used such exotic names as ''Niger, Primus'', and ''Tertius''; this seems to have been the habit of the country. Members * Lucius Farsuleius Mensor, ''triumvir monetalis'' in 75 BC, known from a coin depicting Libertas and a pileus, perhaps alluding to the restoration of the powers of the tribunate that year.Eckhel, vol. v., p. 212.''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'', vol. II, p. 1044 ("Lucius Farsuleius Mensor"). * Gaius Farsuleius Strabo, the son of Ptolomaïs, was a soldier in the third legion. He died at the age of twent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plebs
In ancient Rome, the plebeians (also called plebs) were the general body of free Roman citizenship, Roman citizens who were not Patrician (ancient Rome), patricians, as determined by the capite censi, census, or in other words "commoners". Both classes were hereditary. Etymology The precise origins of the group and the term are unclear, but may be related to the Greek, ''plēthos'', meaning masses. In Latin, the word is a grammatical number, singular collective noun, and its genitive is . Plebeians were not a monolithic social class. Those who resided in the city and were part of the four urban tribes are sometimes called the , while those who lived in the country and were part of the 31 smaller rural tribes are sometimes differentiated by using the label . (List of Roman tribes) In ancient Rome In the annalistic tradition of Livy and Dionysius of Halicarnassus, Dionysius, the distinction between patricians and plebeians was as old as Rome itself, instituted by Romulus' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agrarian Law
Agrarian laws (from the Latin ''ager'', meaning "land") were laws among the Romans regulating the division of the public lands, or ''ager publicus''. In its broader definition, it can also refer to the agricultural laws relating to peasants and husbandmen, or to the general farming class of people of any society. Various attempts to reform agrarian laws were part of the socio-political struggle between the patricians and plebeians known as the Conflict of the Orders. Introduction There existed two kinds of land in ancient Rome: private and public land (''ager publicus''), which included common pasture. By the 2nd century BC, wealthy landowners had begun to dominate the agrarian areas of the republic by "renting" large tracts of public land and treating it as if it were private. This began to force out smaller, private farmers with competition; the farmers were forced to move to the cities for this and a number of other factors including battles making living in rural areas danger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnuntum
Carnuntum ( according to Ptolemy) was a Roman legionary fortress ( la, castra legionis) and headquarters of the Roman navy, Pannonian fleet from 50 AD. After the 1st century, it was capital of the Pannonia Superior province. It also became a large city of 50,000 inhabitants. Its impressive remains are situated on the Danube in Lower Austria halfway between Vienna and Bratislava in the Carnuntum Archaeological Park extending over an area of 10 km2 near today's villages of Petronell-Carnuntum and Bad Deutsch-Altenburg. History Military history Carnuntum first occurs in history during the reign of Augustus (6 AD), when Tiberius made it his base of operations as a Roman fort () in the campaigns against Maroboduus (Marbod). Legio XV Significant Romanisation happened when the town was selected as the garrison of the Legio XV Apollinaris, Legio XV before 14 AD. A few years later, it became the centre of the Roman fortifications along the Danube from Vindobona (now Vienna) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio XV Apollinaris
Legio XV Apollinaris ("Apollo's Fifteenth Legion") was a legion of the Imperial Roman army. It was recruited by Octavian in 41/40 BC. The emblem of this legion was probably a picture of Apollo, or of one of his holy animals. XV ''Apollinaris'' is sometimes confused with two other legions with the same number: An earlier unit which was commanded by Julius Caesar and met its end in North Africa in 49 BC, and a later unit that was present at the Battle of Philippi on the side of the Second Triumvirate and then sent east. History Octavianus (later Emperor Augustus) raised XV ''Apollinaris'' in order to end the occupation of Sicily by Sextus Pompeius, who was threatening Rome's grain supply. After the Battle of Actium, where the legion probably gained its epitaph ''Apollinaris'', it was sent to garrison Illyricum, where it probably remained until 6 BC, though it might have seen action in the Cantabrian Wars. In 6 AD, ''Apollinaris'' was part of the huge campaign by Tiberius ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisalpine Gaul
Cisalpine Gaul ( la, Gallia Cisalpina, also called ''Gallia Citerior'' or ''Gallia Togata'') was the part of Italy inhabited by Celts (Gauls) during the 4th and 3rd centuries BC. After its conquest by the Roman Republic in the 200s BC it was considered geographically part of Roman Italy but remained administratively separated until 42 BC. It was a Roman province from c. 81 BC until 42 BC, when it was ''de jure'' merged into Roman Italy as indicated in Caesar's unpublished acts (''Acta Caesaris''). Cisalpine means "on this side of the Alps" (from the perspective of the Romans), as opposed to Transalpine Gaul ("on the far side of the Alps"). Gallia Cisalpina was further subdivided into ''Gallia Cispadana'' and ''Gallia Transpadana'', i.e. its portions south and north of the Po River, respectively. The Roman province of the 1st century BC was bounded on the north and west by the Alps, in the south as far as Placentia by the river Po, and then by the Apennines and the river ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germania Inferior
Germania Inferior ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the fourth century, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Agrippinensis (modern-day Cologne). Geography According to Ptolemy (2.9), Germania Inferior included the Rhine from its mouth up to the mouth of the ''Obringa'', a river identified with either the Aar or the Moselle. The territory included modern-day Luxembourg, the southern Netherlands, part of Belgium, and part of North Rhine-Westphalia in Germany, west of the Rhine. The principal settlements of the province were Castra Vetera and Colonia Ulpia Traiana (both near Xanten), Coriovallum (Heerlen), Albaniana ( Alphen aan den Rijn), Lugdunum Batavorum (Katwijk), Forum Hadriani (Voorburg), Ulpia Noviomagus Batavorum (Nijmegen), Traiectum (Utrecht), Atuatuca Tungrorum (Tongeren), Bona (Bonn), and Colonia Agrippinensis (Cologne), the capital of Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechernich
Mechernich (, ksh, Meischernisch) is a town in the district of Euskirchen in the south of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located in the "Naturpark Nordeifel" in the Eifel hills, approx. 15 km south-west of Euskirchen and 55 km from Cologne. Mechernich is a former mining town and had, in 2009, its 700-years celebration of foundation. Its local football club is called TUS Mechernich. Districts Mechernich has the following districts: Antweiler, Berg, Bergbuir, Bergheim, Bescheid, Bleibuir, Breitenbenden, Denrath, Dreimühlen, Eicks, Eiserfey, , Floisdorf, , Glehn, Harzheim, Heufahrtshütte, Holzheim, Hostel, , Kallmuth, Katzvey, Kommern, Kommern-Süd, Lessenich, Lorbach, Lückerath, Mechernich, Obergartzem, Rissdorf, Roggendorf, Satzvey (Satzvey Castle), Schaven, Schützendorf, Strempt, Urfey, Voißel, Vollem, Vussem, Wachendorf, Weiler am Berge, Weißenbrunnen, Weyer and Wielspütz. Mining tour A tour takes p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satzvey
Mechernich (, ksh, Meischernisch) is a town in the district of Euskirchen in the south of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located in the "Naturpark Nordeifel" in the Eifel hills, approx. 15 km south-west of Euskirchen and 55 km from Cologne. Mechernich is a former mining town and had, in 2009, its 700-years celebration of foundation. Its local football club is called TUS Mechernich. Districts Mechernich has the following districts: Antweiler, Berg, Bergbuir, Bergheim, Bescheid, Bleibuir, Breitenbenden, Denrath, Dreimühlen, Eicks, Eiserfey, , Floisdorf, , Glehn, Harzheim, Heufahrtshütte, Holzheim, Hostel, , Kallmuth, Katzvey, Kommern, Kommern-Süd, Lessenich, Lorbach, Lückerath, Mechernich, Obergartzem, Rissdorf, Roggendorf, Satzvey (Satzvey Castle), Schaven, Schützendorf, Strempt, Urfey, Voißel, Vollem, Vussem, Wachendorf, Weiler am Berge, Weißenbrunnen, Weyer and Wielspütz. Mining tour A tour takes place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capena
Capena (until 1933 called Leprignano) is a town and ''comune'' in the Metropolitan City of Rome, Lazio region (central Italy). The town has borrowed its modern name from a pre-Roman and Roman settlement that was to its north. Geography Capena is located north of Rome (as the crow flies), above the valley of the Tiber. The old quarter stands on a hill overlooking the valley of the Fosso di Morlupo to the west, while the modern district extends into the eastern plain. The neighbouring towns are Castelnuovo di Porto, Civitella San Paolo, Fiano Romano, Monterotondo, Morlupo and Rignano Flaminio. History Ancient era The original Capena occupied the plateau of a nowadays uninhabited hill called La Civitucola, which is about northeast of a post station on the ancient ''Via Flaminia''. Its territory was known in ancient times as the ''Ager Capenas'', which was a Falisci, Faliscan area adjacent (and culturally allied) to Etruria. It is frequently mentioned alongside of Veii, Falerii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
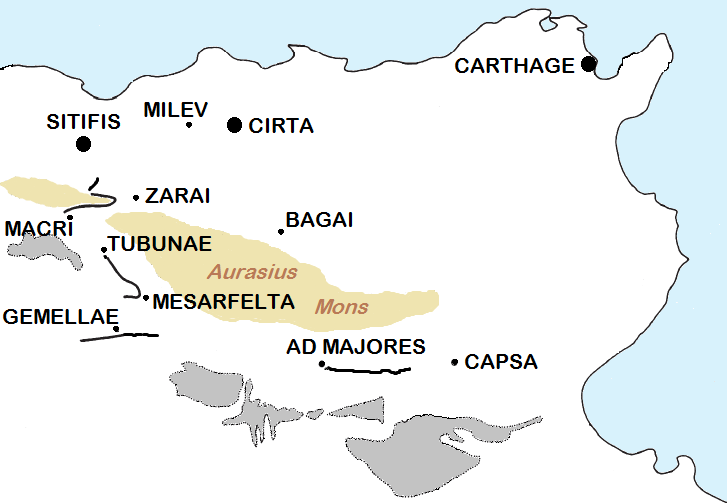
Cirta
Cirta, also known by various other names in antiquity, was the ancient Berber and Roman settlement which later became Constantine, Algeria. Cirta was the capital city of the Berber kingdom of Numidia; its strategically important port city was Russicada. Although Numidia was a key ally of the ancient Roman Republic during the Punic Wars (264–146BC), Cirta was subject to Roman invasions during the 2nd and 1st centuriesBC. Eventually it fell under Roman dominion during the time of Julius Caesar. Cirta was then repopulated with Roman colonists by Caesar and Augustus and was surrounded by the autonomous territory of a " Confederation of four free Roman cities" (with Chullu, Russicada, and Milevum), ruled initially by Publius Sittius. The city was destroyed in the beginning of the 4thcentury and was rebuilt by the Roman emperor Constantine the Great, who gave his name to the newly constructed city, Constantine. The Vandals damaged Cirta, but emperor reconquered and improved th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numidia
Numidia ( Berber: ''Inumiden''; 202–40 BC) was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians located in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up modern-day Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisia, Libya, and some parts of Morocco. The polity was originally divided between the Massylii in the east and the Masaesyli in the west. During the Second Punic War (218–201 BC), Masinissa, king of the Massylii, defeated Syphax of the Masaesyli to unify Numidia into one kingdom. The kingdom began as a sovereign state and later alternated between being a Roman province and a Roman client state. Numidia, at its largest extent, was bordered by Mauretania to the west, at the Moulouya River, Africa Proconsularis to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the north, and the Sahara to the south. It was one of the first major states in the history of Algeria and the Berbers. History Independence The Greek historians referred to these peoples as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa (Roman Province)
Africa Proconsularis was a Roman province on the northern African coast that was established in 146 BC following the defeat of Carthage in the Third Punic War. It roughly comprised the territory of present-day Tunisia, the northeast of Algeria, and the coast of western Libya along the Gulf of Sirte. The territory was originally inhabited by Berber people, known in Latin as ''Mauri'' indigenous to all of North Africa west of Egypt; in the 9th century BC, Phoenicians built settlements along the Mediterranean Sea to facilitate shipping, of which Carthage rose to dominance in the 8th century BC until its conquest by the Roman Republic. It was one of the wealthiest provinces in the western part of the Roman Empire, second only to Italy. Apart from the city of Carthage, other large settlements in the province were Hadrumetum (modern Sousse, Tunisia), capital of Byzacena, and Hippo Regius (modern Annaba, Algeria). History Rome's first province in northern Africa was established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |