|
Fappi
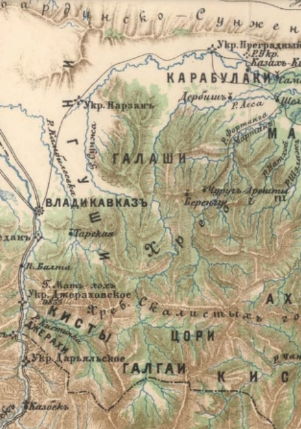
Fappi ( inh, Фаьппи, Fäppi) or Fappi mokhk ( inh, Фаьппи мохк, Fäppi mokhk, lit=Country of Fyappins, links=no), exonym: Kistetia, is a historical region in Ingushetia. Fappi is the territory of historical settlement of the Fyappiy Ingush societies, society. Geography Suleymanov, brought the following boundaries of the historical region in the west with Dzhairakh, in the south with Khevsureti, in the east with Khamkh and Tsori, in the north it went out into a flat plain. The Fyappiy district occupied a significant territory of the Kistin Gorge, Armkhi Gorge and was in contact with the plain in the north. The geography of the initial distribution of this ethnonym A. N. Genko relates “to the west of the Lomeka River (the ancient name of the Terek River)”, covering the entire territory of the modern Republic of Ossetia. History The historical area Fyappiy Mokhk was mentioned as "Kistetia", as well as "Kistia" or "Kistinia". The Georgians, Georgian prince, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fyappiy
The ''Fyappins'' ( inh, фаьппий, fäppiy) were an Ingush subgroup (''society'') that mostly inhabited the mountainous Fappi region of Ingushetia in the Caucasus. Historically they bordered on the west with Dzherakh, on the east with Khamkhins, on the north with Nazranians, and lastly in the south with Gudomakarians. The centre of the society was the fortified village (''aul'') of Erzi or Metskhal. During the 16–17th centuries, part of the ''Fyappins'' migrated to Tusheti, Georgia, due to a lack of land. The descendants of the migrants are known as Bats people. In the 17–18th centuries, another wave of migration accured, to the region of Aukh (modern day Dagestan). In 1733, due to the worry of expansion of Ottoman Turks in the region, ''Fyappins'' tried to establish ties with Kingdom of Kartli. As the Russian Empire started expanding its territories in the Caucasus Region 19th century, Caucasian War broke out. During the war, ''Fyappin'' Society was devasted aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of any geographical feature, and full scope of the term also includes proper names of all cosmographical features. In a more specific sense, the term ''toponymy'' refers to an inventory of toponyms, while the discipline researching such names is referred to as ''toponymics'' or ''toponomastics''. Toponymy is a branch of onomastics, the study of proper names of all kinds. A person who studies toponymy is called ''toponymist''. Etymology The term toponymy come from grc, τόπος / , 'place', and / , 'name'. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' records ''toponymy'' (meaning "place name") first appearing in English in 1876. Since then, ''toponym'' has come to replace the term ''place-name'' in professional discourse among geographers. Topon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingushetia
Ingushetia (; russian: Ингуше́тия; inh, ГӀалгӏайче, Ghalghayče), officially the Republic of Ingushetia,; inh, Гӏалгӏай Мохк, Ghalghay Moxk is a republic of Russia located in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe. The republic is part of the North Caucasian Federal District, and shares land borders with the country of Georgia to its south; and borders the Russian republics of North Ossetia–Alania and Chechnya to its west and east, respectively; while having a border with Stavropol Krai to its north. It also is one of the least-populated republics of Russia at under 500,000. Its capital is the town of Magas, while the largest city is Nazran. At 4,000 square km, in terms of area, the republic is the smallest of Russia's non-city federal subjects. It was established on June 4, 1992, after the Checheno-Ingush Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic was split in two.Law of June 4, 1992Official website of the Republic of IngushetiaSocial-Econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingush Societies
Ingush societies/shahars ( inh, ГIалгIай шахьараш, Ghalghaj šaꜧaraš) were territorial associations of the Ingush based on the geographical association of several villages and intended for conditional administrative-territorial delimitation of the Ingush ethnic group. The formation and functioning of most of them dates back to the late Middle Ages (XVI-XIX centuries). During this period, their boundaries, number and names changed. The names of societies mainly came from the names of the area of their localization, that is, they were based on the geographical principle. Despite the fact that during this period the Ingush lived in relatively closed conditions of mountain gorges, which contributed to more demarcation in terms of territoriality than rallying around a single center, they retained the self-consciousness of a single ethnic group based on a common culture and a single language. Ingush societies in the literature are sometimes called "shahars" ( in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kistin Gorge
Kistin Gorge ( inh, Кистий чӀож) is a gorge of the Armkhi River in the Dzheyrakhsky District of the Republic of Ingushetia. The name of the gorge comes from the historical name of the river Armkhi — Kistinka, which in turn comes from one of the ethnonyms of the Ingush — Kists. Historically, the area where the gorge is located was called " Kistetia". It is mentioned in medieval Georgian sources, in particular, in the work of Vakhushti Bagrationi. History According to the legends, this road was controlled by the Tsurovs and the Yandievs. They "kept guard there and took tribute for the passage". In Russian documents, the name was first mentioned in the first half of the XIX century, in military reports from the period of the Caucasian War, for example, in the Report of the Commander-in-Chief of the Separate Caucasian Caucasian may refer to: Anthropology *Anything from the Caucasus region ** ** ** ''Caucasian Exarchate'' (1917–1920), an ecclesiastical exarc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgians
The Georgians, or Kartvelians (; ka, ქართველები, tr, ), are a nation and indigenous Caucasian ethnic group native to Georgia and the South Caucasus. Georgian diaspora communities are also present throughout Russia, Turkey, Greece, Iran, Ukraine, United States, and European Union. Georgians arose from Colchian and Iberian civilizations of classical antiquity; Colchis was interconnected with the Hellenic world, whereas Iberia was influenced by the Achaemenid Empire until Alexander the Great conquered it. In the 4th century, the Georgians became one of the first to embrace Christianity and now the majority of Georgians are Orthodox Christians, with most following their national autocephalous Georgian Orthodox Church, although there are small Georgian Catholic and Muslim communities as well as a significant number of irreligious Georgians. Located in the Caucasus, on the continental crossroads of Europe and Asia, the High Middle Ages saw Georgian people form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vakhushti Bagrationi
Vakhushti ( ka, ვახუშტი, tr) (1696–1757) was a Georgian royal prince (''batonishvili''), geographer, historian and cartographer. His principal historical and geographic works, ''Description of the Kingdom of Georgia'' and the ''Geographical Atlas'', were inscribed on UNESCO's Memory of the World Register in 2013. Life A natural son of King Vakhtang VI of Kartli (ruled 1716–24), he was born in Tbilisi, 1696. Educated by the brothers Garsevanishvili and a Roman Catholic mission, he was fluent in Greek, Latin, French, Turkish, Russian and Armenian. His name Vakhushti derives from Old Iranian ''vahišta-'' ("paradise", superlative of ''veh'' "good", i.e., "superb, excellent"). Its equivalent in Middle Persian is ''wahišt'' and in New Persian ''behešt''. In 1719 and 1720, he took part in two successive campaigns against the rebel duke (''eristavi'') Shanshe of the Ksani. From August to November 1722, he was a governor of the kingdom during his father's absenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Anton Güldenstädt
Johann Anton Güldenstädt (26 April 1745 in Riga, Latvia – 23 March 1781 in St. Petersburg, Russia) was a Baltic German natural history, naturalist and explorer in Russian service. Güldenstädt lost both his parents early, and from 1763 onwards studied pharmacy, botany and natural history in Berlin. At the age of 22, he obtained his doctorate in medicine at the Viadrina European University, University of Frankfurt in 1767. In the following year, he joined the Russian Academy of Sciences, Russian Imperial Academy of Sciences' expedition sent by Catherine II of Russia to explore the Russian empire's southern frontier. Güldenstädt travelled through Ukraine and the Astrakhan Oblast, Astrakhan region, as well as the northern Caucasus and Georgia (country), Georgia, both of which were almost entirely beyond the borders of the Russian empire. In March 1775 he returned to St Petersburg. The results of the expedition and Güldenstädt's edited expedition journal were published after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumyks
, image = Abdul-Wahab son of Mustafa — a prominent Kumyk architect of the 19th century. , population = near 600,000 , region1 = , pop1 = 503,060 , ref1 = , region2 = , pop2 = 10,000 , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = 718 , ref3 = , langs = Kumyk language , region4 = , pop4 = 1200 , ref4 = , region5 = , pop5 = 481 , ref5 = , region6 = , pop6 = 360 , ref6 = , region7 = , pop7 = 33 , ref7 = [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabardians
The Kabardians ( Highland Adyghe: Къэбэрдей адыгэхэр; Lowland Adyghe: Къэбэртай адыгэхэр; russian: Кабардинцы) or Kabardinians are one of the twelve major Circassian tribes, representing one of the twelve stars on the green-and-gold Circassian flag. They are also commonly known by the plural terms Kabardin, Kebertei, or Kabarday. Along with the Besleney tribe, they speak a distinctive dialect of the Adyghe language. Historically the Kabardians lived in Kabardia, a region of the north Caucasus. In modern times the Kabardians live mostly in the Russian republic of Kabardino-Balkaria, which partly corresponds to the historic region. Despite the Soviet administrative divisions that placed Circassians under four different designations and political units, namely ''Adygeans'' (Adyghe in Adygea), ''Cherkessians'' (Adyghe in Karachay-Cherkessia), ''Kabardians'' (Adyghe in Kabardino-Balkaria), and ''Shapsugians'' (Adyghe in Krasnodar Kra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Georgia
The Kingdom of Georgia ( ka, საქართველოს სამეფო, tr), also known as the Georgian Empire, was a medieval Eurasian monarchy that was founded in circa 1008 AD. It reached its Golden Age of political and economic strength during the reign of King David IV and Queen Tamar the Great from 11th to 13th centuries. Georgia became one of the pre-eminent nations of the Christian East and its pan-Caucasian empire and network of tributaries stretching from Eastern Europe to Anatolia and northern frontiers of Iran, while also maintaining religious possessions abroad, such as the Monastery of the Cross in Jerusalem and the Monastery of Iviron in Greece. It was the principal historical precursor of present-day Georgia. Lasting for several centuries, the kingdom fell to the Mongol invasions in the 13th century, but managed to re-assert sovereignty by the 1340s. The following decades were marked by the Black Death, as well as numerous invasions under the lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etnograficheskoe Obozrenie
''Etnograficheskoe Obozrenie'' (russian: Этнографическое Обозрение, translit=Etnograficheskoe Obozrenie; en, Ethnographic Review) is a peer-reviewed academic journal covering "the study of peoples and cultures of the world". It is published by the N.N. Miklukho-Maklai Institute of Ethnology and Anthropology (Russian Academy of Sciences). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: *Anthropological Literature * EBSCO databases *ERIH PLUS *FRANCIS *Index Islamicus *International Bibliography of the Social Sciences *Modern Language Association Database *Russian Science Citation Index *Scopus History The journal was established in 1889. Its publication, however, was suspended between 1916 and 1926 "due to the turmoil of the revolutionary era" but was resumed in 1926 under the new name ''Этнография (Etnografia)'' which was again changed to ''Советская Этнография (Sovetskaia Etnografia)'' in 1931. Its name was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

