|
False Position Method
In mathematics, the ''regula falsi'', method of false position, or false position method is a very old method for solving an equation with one unknown; this method, in modified form, is still in use. In simple terms, the method is the trial and error technique of using test ("false") values for the variable and then adjusting the test value according to the outcome. This is sometimes also referred to as "guess and check". Versions of the method predate the advent of algebra and the use of equations. As an example, consider problem 26 in the Rhind papyrus, which asks for a solution of (written in modern notation) the equation . This is solved by false position. First, guess that to obtain, on the left, . This guess is a good choice since it produces an integer value. However, 4 is not the solution of the original equation, as it gives a value which is three times too small. To compensate, multiply (currently set to 4) by 3 and substitute again to get , verifying that the solution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
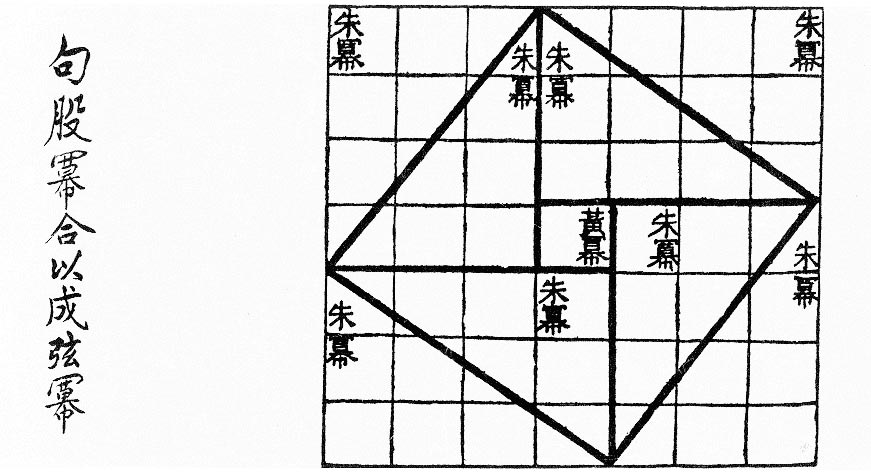
Chinese Mathematics
Mathematics emerged independently in China by the 11th century BCE. The Chinese independently developed a real number system that includes significantly large and negative numbers, more than one numeral system (base 2, binary and base 10, decimal), algebra, geometry, number theory and trigonometry. Since the Han dynasty, as diophantine approximation being a prominent numerical method, the Chinese made substantial progress on polynomial evaluation. Algorithms like regula falsi and expressions like simple continued fractions are widely used and have been well-documented ever since. They deliberately find the principal nth root, ''n''th root of positive numbers and the zero of a function, roots of equations. The major texts from the period, ''The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art'' and the ''Book on Numbers and Computation'' gave detailed processes for solving various mathematical problems in daily life. All procedures were computed using a counting board in both texts, and they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Inheritance Jurisprudence
Islamic Inheritance jurisprudence is a field of Islamic jurisprudence () that deals with inheritance, a topic that is prominently dealt with in the Qur'an. It is often called ''Mīrāth'' (, literally "inheritance"), and its branch of Islamic law is technically known as ''ʿilm al-farāʾiḍ'' (, "the science of the ordained quotas"). Inheritance and the Qur'an The Qur'an introduced a number of different rights and restrictions on matters of inheritance, including what were at that time general improvements to the treatment of women and family life. The Qur'an also presented efforts to fix the laws of inheritance, and thus forming a complete legal system. This development was in contrast to pre-Islamic societies where rules of inheritance varied considerably. They do, however, also differ from ongoing secular changes since that time, up to, though principally in, the modern era. Furthermore, the Qur'an introduced additional heirs that were not entitled inheritance in pre-Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics In Medieval Islam
Mathematics during the Golden Age of Islam, especially during the 9th and 10th centuries, was built upon syntheses of Greek mathematics (Euclid, Archimedes, Apollonius) and Indian mathematics (Aryabhata, Brahmagupta). Important developments of the period include extension of the place-value system to include decimal fractions, the systematised study of algebra and advances in geometry and trigonometry. The medieval Islamic world underwent significant developments in mathematics. Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwārizmī played a key role in this transformation, introducing algebra as a distinct field in the 9th century. Al-Khwārizmī's approach, departing from earlier arithmetical traditions, laid the groundwork for the arithmetization of algebra, influencing mathematical thought for an extended period. Successors like Al-Karaji expanded on his work, contributing to advancements in various mathematical domains. The practicality and broad applicability of these mathematical metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euclidean Geometry
Euclidean geometry is a mathematical system attributed to ancient Greek mathematics, Greek mathematician Euclid, which he described in his textbook on geometry, ''Euclid's Elements, Elements''. Euclid's approach consists in assuming a small set of intuitively appealing axioms (postulates) and deducing many other propositions (theorems) from these. One of those is the parallel postulate which relates to parallel lines on a Euclidean plane. Although many of Euclid's results had been stated earlier,. Euclid was the first to organize these propositions into a logic, logical system in which each result is ''mathematical proof, proved'' from axioms and previously proved theorems. The ''Elements'' begins with plane geometry, still taught in secondary school (high school) as the first axiomatic system and the first examples of mathematical proofs. It goes on to the solid geometry of three dimensions. Much of the ''Elements'' states results of what are now called algebra and number theory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west; Cyprus lies a short distance from the coastline. Lebanon has a population of more than five million and an area of . Beirut is the country's capital and largest city. Human habitation in Lebanon dates to 5000 BC. From 3200 to 539 BC, it was part of Phoenicia, a maritime civilization that spanned the Mediterranean Basin. In 64 BC, the region became part of the Roman Empire and the subsequent Byzantine Empire. After the seventh century, it Muslim conquest of the Levant, came under the rule of different Islamic caliphates, including the Rashidun Caliphate, Rashidun, Umayyad Caliphate, Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid. The 11th century saw the establishment of Christian Crusader states, which fell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baalbek
Baalbek (; ; ) is a city located east of the Litani River in Lebanon's Beqaa Valley, about northeast of Beirut. It is the capital of Baalbek-Hermel Governorate. In 1998, the city had a population of 82,608. Most of the population consists of Shi'a Islam in Lebanon, Shia Muslims, followed by Sunni Islam in Lebanon, Sunni Muslims and Christianity in Lebanon, Christians; in 2017, there was also a large presence of Refugees of the Syrian civil war, Syrian refugees. Baalbek has a history that dates back at least 11,000 years, encompassing significant periods such as Prehistory of Lebanon, Prehistoric, Canaanite, Hellenistic period, Hellenistic, and Phoenicia under Roman rule, Roman eras. After Alexander the Great conquered the city in 334 BCE, he renamed it Heliopolis (, Greek language, Greek for "Sun City"). The city flourished under Roman rule. However, it underwent transformations during the Historiography of the Christianization of the Roman Empire, Christianization period and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world. Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years. In the 9th century BCE, the Assyrians made written references to Arabs as inhabitants of the Levant, Mesopotamia, and Arabia. Throughout the Ancient Near East, Arabs established influential civilizations starting from 3000 BCE onwards, such as Dilmun, Gerrha, and Magan (civilization), Magan, playing a vital role in trade between Mesopotamia, and the History of the Mediterranean region, Mediterranean. Other prominent tribes include Midian, ʿĀd, and Thamud mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, Bible and Quran. Later, in 900 BCE, the Qedarites enjoyed close relations with the nearby Canaan#Canaanites, Canaanite and Aramaeans, Aramaean states, and their territory extended from Lower Egypt to the Southern Levant. From 1200 BCE to 110 BCE, powerful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qusta Ibn Luqa
Qusta ibn Luqa, also known as Costa ben Luca or Constabulus (820912) was a Melkite Christian physician, philosopher, astronomer, mathematician and translator. He was born in Baalbek. Travelling to parts of the Byzantine Empire, he brought back Greek language, Greek texts and translated them into Arabic language, Arabic. Personal life Qusta ibn Luqa al-Ba'albakki originated from Baalbek (or Heliopolis of Phoenicia, Heliopolis), now in Lebanon. A Melkite Christian, he was born in 820 and flourished in Baghdad. He was a philosopher, physician, mathematician and astronomer. He died in Armenia, possibly in around 912. Translations Qusta ibn Luqa produced, personally revised, or supervised the translations of a number of works. These include works by Diophantus, Theodosius of Bithynia's ''Theodosius%27 Spherics, Spherics'', ''On Days and Nights'', and ''On the places of habitation'', Autolycus of Pitane, Autolycus's ''On the moving sphere'' and ''On Risings and Settings'', Hypsicles's ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq. The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western European nations in the early 20th century as a replacement of the term Near East (both were in contrast to the Far East). The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions. Since the late 20th century, it has been criticized as being too Eurocentrism, Eurocentric. The region includes the vast majority of the territories included in the closely associated definition of West Asia, but without the South Caucasus. It also includes all of Egypt (not just the Sinai Peninsula, Sinai) and all of Turkey (including East Thrace). Most Middle Eastern countries (13 out of 18) are part of the Arab world. The list of Middle Eastern countries by population, most populous countries in the region are Egypt, Turkey, and Iran, whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Kamil
Abū Kāmil Shujāʿ ibn Aslam ibn Muḥammad Ibn Shujāʿ ( Latinized as Auoquamel, , also known as ''Al-ḥāsib al-miṣrī''—lit. "The Egyptian Calculator") (c. 850 – c. 930) was a prominent Egyptian mathematician during the Islamic Golden Age. He is considered the first mathematician to systematically use and accept irrational numbers as solutions and coefficients to equations. His mathematical techniques were later adopted by Fibonacci, thus allowing Abu Kamil an important part in introducing algebra to Europe. Abu Kamil made important contributions to algebra and geometry. He was the first Islamic mathematician to work easily with algebraic equations with powers higher than x^2 (up to x^8), and solved sets of non-linear simultaneous equations with three unknown variables. He illustrated the rules of signs for expanding the multiplication (a \pm b)(c \pm d). He wrote all problems rhetorically, and some of his books lacked any mathematical notation beside those of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptians
Egyptians (, ; , ; ) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian identity is closely tied to Geography of Egypt, geography. The population is concentrated in the Nile Valley, a small strip of cultivable land stretching from the Cataracts of the Nile, First Cataract to the Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean and enclosed by desert both to the Eastern Desert, east and to the Western Desert (North Africa), west. This unique geography has been the basis of the DNA history of Egypt, development of Egyptian society since Ancient Egypt, antiquity. The daily language of the Egyptians is a continuum of the local variety of Arabic, varieties of Arabic; the most famous dialect is known as Egyptian Arabic or ''Masri''. Additionally, a sizable minority of Egyptians living in Upper Egypt speak Sa'idi Arabic. Egyptians are predominantly adherents of Sunni Islam with a small Shia minority and a significant proportion who follow native Sufi tariqah, orders.Hoffman, Val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |