|
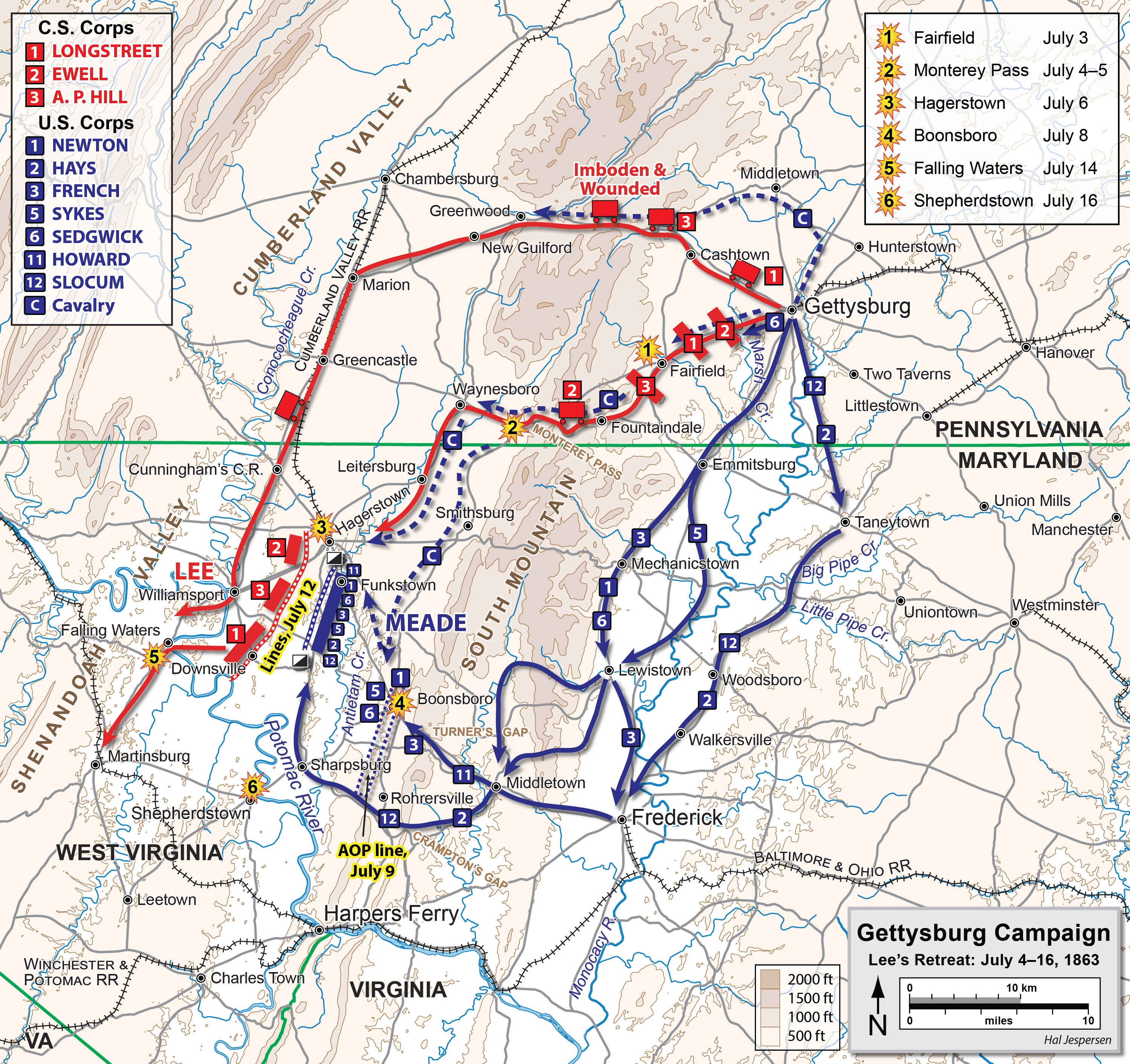
Falling Waters, West Virginia
Falling Waters is a census-designated place (CDP) on the Potomac River in Berkeley County, West Virginia, United States. It is located along Williamsport Pike (US 11) north of Martinsburg. According to the 2010 census, Falling Waters has a population of 876. An 1887 ''Scientific American'' article claimed that the first U.S. railroad was built in Falling Waters in 1814. History The community of Falling Waters was established in 1815. Because of its location between Hagerstown and Martinsburg on the Potomac River, Falling Waters is a predominantly residential community with numerous historic residences, some of which are listed on the National Register of Historic Places. However, recently the community has had a boom in new residential construction as many people use Falling Waters as a bedroom community to commute to cities nearby and as far as Washington, D.C. and Baltimore. Civil War Era Falling Waters was the site of two battles during the American Civil War: * The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census-designated Place
A census-designated place (CDP) is a concentration of population defined by the United States Census Bureau for statistical purposes only. CDPs have been used in each decennial census since 1980 as the counterparts of incorporated places, such as self-governing cities, towns, and villages, for the purposes of gathering and correlating statistical data. CDPs are populated areas that generally include one officially designated but currently unincorporated community, for which the CDP is named, plus surrounding inhabited countryside of varying dimensions and, occasionally, other, smaller unincorporated communities as well. CDPs include small rural communities, edge cities, colonias located along the Mexico–United States border, and unincorporated resort and retirement communities and their environs. The boundaries of any CDP may change from decade to decade, and the Census Bureau may de-establish a CDP after a period of study, then re-establish it some decades later. Most unin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic value". A property listed in the National Register, or located within a National Register Historic District, may qualify for tax incentives derived from the total value of expenses incurred in preserving the property. The passage of the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) in 1966 established the National Register and the process for adding properties to it. Of the more than one and a half million properties on the National Register, 95,000 are listed individually. The remainder are contributing resources within historic districts. For most of its history, the National Register has been administered by the National Park Service (NPS), an agency within the U.S. Department of the Interior. Its goals are to help property owners and inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maidstone-on-the-Potomac
Maidstone-on-the-Potomac is a historic house and farm near Falling Waters, West Virginia. Located on the Potomac River immediately opposite Williamsport, Maryland, the property consists of a tract with a main house dating from c. 1741. The house was built by Evan Watkins, who operated Watkins Ferry on the Potomac, which was used by George Washington and General Edward Braddock. In 1795 the property was sold to Peter Light. The Light family retained the property until 1854, substantially expanding the house. The ferry and house, by now known as Light's Ferry passed to Robert Lemen, who converted the ferry into a cable ferry. In 1861 the ferry was used by Union forces under Captain Abner Doubleday to cross into Virginia for raids. In 1863 Doubleday again crossed the river by fording while pursuing Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia as it advanced on Gettysburg. A month later, following Lee's defeat, 70,000 confederate soldiers crossed at Lemen's Ferry. In the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring Mills High School
Spring Mills High School is the fourth high school in the Berkeley County, West Virginia school system, which opened in fall of 2013. On opening, the student body was formed from about one-half of the student body of each of Martinsburg High School and Hedgesville High School, which had become overcrowded. The current principal is Mark Salfia. The school was officially dedicated by officials including West Virginia governor Earl Ray Tomblin Earl Ray Tomblin (born March 15, 1952) is an American politician who served as the 35th governor of West Virginia from 2011 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he previously served in the West Virginia Senate from 1980 to 2011 and as pres ... on August 7, 2013. Mascot The school's mascot is the Cardinals and its colors are cardinal red, white, and navy blue. Orchestra Program Spring Mills High is unique in Berkeley County by having an orchestra program. It is home to the Spring Mills High School String Orchestra. Each year, memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Gettysburg
The Battle of Gettysburg () was fought July 1–3, 1863, in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, by Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War. In the battle, Union Major General George Meade's Army of the Potomac defeated attacks by Confederate General Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia, halting Lee's invasion of the North. The battle involved the largest number of casualties of the entire war and is often described as the war's turning point due to the Union's decisive victory and concurrence with the Siege of Vicksburg.Rawley, p. 147; Sauers, p. 827; Gallagher, ''Lee and His Army'', p. 83; McPherson, p. 665; Eicher, p. 550. Gallagher and McPherson cite the combination of Gettysburg and Vicksburg as the turning point. Eicher uses the arguably related expression, " High-water mark of the Confederacy". After his success at Chancellorsville in Virginia in May 1863, Lee led his army through the Shenandoah Valley to begin his second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was the primary military force of the Confederate States of America in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was also the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most often arrayed against the Union Army of the Potomac. Origin The name ''Army of Northern Virginia'' referred to its primary area of operation, as did most Confederate States Army names. The Army originated as the Army of the Potomac, which was organized on June 20, 1861, from all operational forces in northern Virginia. On July 20 and July 21, the Army of the Shenandoah and forces from the District of Harpers Ferry were added. Units from the Army of the Northwest were merged into the Army of the Potomac between March 14 and May 17, 1862. The Army of the Potomac was renamed ''Army of Northern Virginia'' on March 14. The Army of the Peninsula was merged into it on April 12, 1862.Eicher, pp. 889–90. Robert E. Lee's biographer, Douglas S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Armstrong Custer
George Armstrong Custer (December 5, 1839 – June 25, 1876) was a United States Army officer and cavalry commander in the American Civil War and the American Indian Wars. Custer graduated from West Point in 1861 at the bottom of his class, but as the Civil War was just starting, trained officers were in immediate demand. He worked closely with General George B. McClellan and the future General Alfred Pleasonton, both of whom recognized his qualities as a cavalry leader, and he was promoted to brigadier general of volunteers at age 23. Only a few days after his promotion, he fought at the Battle of Gettysburg, where he commanded the Michigan Cavalry Brigade and despite being outnumbered, defeated J. E. B. Stuart's attack at what is now known as the East Cavalry Field. In 1864, he served in the Overland Campaign and in Philip Sheridan's army in the Shenandoah Valley, defeating Jubal Early at Cedar Creek. His division blocked the Army of Northern Virginia's final retreat an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Army
During the American Civil War, the Union Army, also known as the Federal Army and the Northern Army, referring to the United States Army, was the land force that fought to preserve the Union (American Civil War), Union of the collective U.S. state, states. It proved essential to the preservation of the United States as a working, viable republic. The Union Army was made up of the permanent Regular Army (United States), regular army of the United States, but further fortified, augmented, and strengthened by the many temporary units of dedicated United States Volunteers, volunteers, as well as including those who were drafted in to service as Conscription in the United States, conscripts. To this end, the Union Army fought and ultimately triumphed over the efforts of the Confederate States Army in the American Civil War. Over the course of the war, 2,128,948 men enlisted in the Union Army, including 178,895 United States Colored Troops, colored troops; 25% of the white men who s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pickett's Charge
Pickett's Charge (July 3, 1863), also known as the Pickett–Pettigrew–Trimble Charge, was an infantry assault ordered by Confederate General Robert E. Lee against Major General George G. Meade's Union positions on the last day of the Battle of Gettysburg in the commonwealth of Pennsylvania during the Civil War. Confederate troops made a frontal assault towards the center of Union lines, ultimately being repulsed with heavy casualties. Suffering from a lack of preparation and problems from the onset, the attack was a costly mistake that decisively ended Lee's invasion of the north and forced a retreat back to Virginia. The charge is popularly named after Major General George Pickett, one of three Confederate generals (all under the command of Lieutenant General James Longstreet) who led the assault. Pickett's Charge was part of Lee's "general plan" to take Cemetery Hill and the network of roads it commanded. His military secretary, Armistead Lindsay Long, described L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Williamsport
The Battle of Williamsport, also known as the Battle of Hagerstown or Falling Waters, took place from July 6 to July 16, 1863, in Washington County, Maryland, as part of the Gettysburg Campaign of the American Civil War. It is not to be confused with the fighting at Hoke's Run which was also known as the Battle of Falling Waters. During the night of July 4–July 5, Gen. Robert E. Lee's battered Confederate army began its retreat from Gettysburg, moving southwest on the Fairfield Road toward Hagerstown and Williamsport, screened by Maj. Gen. J.E.B. Stuart's cavalry. The Union infantry followed cautiously the next day, converging on Middletown, Maryland. By July 7, Brig. Gen. John D. Imboden stopped Brig. Gen. John Buford's Union cavalry from occupying Williamsport and destroying Confederate trains. On July 6, Brig. Gen. Judson Kilpatrick's cavalry division drove two Confederate cavalry brigades through Hagerstown before being forced to retire by the arrival of the rest of St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Hoke's Run
The Battle of Hoke's Run, also known as the Battle of Falling Waters or Battle of Hainesville, took place on July 2, 1861, in Berkeley County, Virginia (now West Virginia) as part of the Manassas campaign of the American Civil War. Notable as an early engagement of Confederate Colonel Thomas J. Jackson and his Brigade of Virginia Volunteers, nineteen days before their famous nickname would originate, this brief skirmish was hailed by both sides as a stern lesson to the other. Acting precisely upon the orders of a superior officer about how to operate in the face of superior numbers, Jackson's forces resisted General Robert Patterson's Union forces briefly and then slowly retreated over several miles. Battle On July 2, Maj. Gen. Robert Patterson's division crossed the Potomac River near Williamsport, Maryland and marched on the main road to Martinsburg. Near Hoke's Run, the Union brigades of Cols. John J. Abercrombie and George H. Thomas encountered regiments of Col. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |