|
Fallacies Of Definition
Fallacies of definition are the various ways in which definitions can fail to explain terms. The phrase is used to suggest an analogy with an informal fallacy. Definitions may fail to have merit, because they are overly broad,Gibbon, Guy (2013). ''Critically Reading the Theory and Methods of Archaeology: An Introductory Guide''. Rowman & Littlefield. .Potter, Karl H. (1991). ''Presuppositions of India's Philosophies'', p.87. Motilal Banarsidass. . "Under-extension", "over-extension", and "mutual exclusion".Chakraborti, Chhanda (2007). ''Logic: Informal, Symbolic and Inductive'', p.54-5. PHI Learning. . "Too wide", "too narrow", "incomprehensible", and "conflicting". overly narrow, or incomprehensible; or they use obscure or ambiguous language, contain mutually exclusive parts, or (perhaps most commonly) are circular.Schipper, Edith Watson and Schuh, Edward (1960). ''A First Course in Modern Logic'', p.24. Routledge. "Incongruous", "circular", "negative", and "obscure or figurative" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Definition
A definition is a statement of the meaning of a term (a word, phrase, or other set of symbols). Definitions can be classified into two large categories: intensional definitions (which try to give the sense of a term), and extensional definitions (which try to list the objects that a term describes).Lyons, John. "Semantics, vol. I." Cambridge: Cambridge (1977). p.158 and on. Another important category of definitions is the class of ostensive definitions, which convey the meaning of a term by pointing out examples. A term may have many different senses and multiple meanings, and thus require multiple definitions. In mathematics, a definition is used to give a precise meaning to a new term, by describing a condition which unambiguously qualifies what the mathematical term is and is not. Definitions and axioms form the basis on which all of modern mathematics is to be constructed. Basic terminology In modern usage, a definition is something, typically expressed in words, that at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analogy
Analogy is a comparison or correspondence between two things (or two groups of things) because of a third element that they are considered to share. In logic, it is an inference or an argument from one particular to another particular, as opposed to deduction, induction, and abduction. It is also used where at least one of the premises, or the conclusion, is general rather than particular in nature. It has the general form ''A is to B as C is to D''. In a broader sense, analogical reasoning is a cognitive process of transferring some information or meaning of a particular subject (the analog, or source) onto another (the target); and also the linguistic expression corresponding to such a process. The term analogy can also refer to the relation between the source and the target themselves, which is often (though not always) a similarity, as in the biological notion of analogy. Analogy plays a significant role in human thought processes. It has been argued that analogy li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Informal Fallacy
Informal fallacies are a type of incorrect argument in natural language. The source of the error is not just due to the ''form'' of the argument, as is the case for formal fallacies, but can also be due to their ''content'' and ''context''. Fallacies, despite being incorrect, usually ''appear'' to be correct and thereby can seduce people into accepting and using them. These misleading appearances are often connected to various aspects of natural language, such as ambiguous or vague expressions, or the assumption of implicit premises instead of making them explicit. Traditionally, a great number of informal fallacies have been identified, including the fallacy of equivocation, the fallacy of amphiboly, the Fallacy of composition, fallacies of composition and Fallacy of division, division, the false dilemma, the fallacy of begging the question, the ad hominem fallacy and the appeal to ignorance. There is no general agreement as to how the various fallacies are to be grouped into cate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Definition Of Inflammable Liquid
*
{{disambiguation ...
Circular may refer to: * The shape of a circle * ''Circular'' (album), a 2006 album by Spanish singer Vega * Circular letter (other), a document addressed to many destinations ** Government circular, a written statement of government policy **Circulaire * Circular reasoning, a type of logical fallacy * Circular reference *Circular Quay, Australia *Circular Park, Armenia See also * Circular DNA (other) * Circular Line (other) * Circularity (other) Circularity may refer to: *Circular definition *Circular economy *Circular reasoning Circular reasoning (, "circle in proving"; also known as circular logic) is a fallacy, logical fallacy in which the reasoner begins with what they are trying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Definition
A circular definition is a type of definition that uses the term(s) being defined as part of the description or assumes that the term(s) being described are already known. There are several kinds of circular definition, and several ways of characterising the term: pragmatic, lexicographic and linguistic Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds .... Circular definitions are related to circular reasoning in that they both involve a self-referential approach. Circular definitions may be unhelpful if the audience must either already know the meaning of the key term, or if the term to be defined is used in the definition itself. In linguistics, a circular definition is a description of the meaning of a lexeme that is constructed using one or more synonymous lexemes that are al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Begging The Question
In classical rhetoric and logic, begging the question or assuming the conclusion (Latin: ) is an informal fallacy that occurs when an argument's premises assume the truth of the conclusion. Historically, begging the question refers to a fault in a dialectical argument in which the speaker assumes some premise that has not been demonstrated to be true. In modern usage, it has come to refer to an argument in which the premises assume the conclusion without supporting it. This makes it an example of circular reasoning.Herrick (2000) 248. Some examples are: *“Wool sweaters are better than nylon jackets as fall attire because wool sweaters have higher wool content". ** The claim in this quote is that wool sweaters are better than nylon jackets as fall attire. However, the justification of this claim begs the question because it ''presupposes'' that wool sweaters are better than nylon jackets: in other words, wool sweaters are better than nylon jackets because wool is better than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhombi
In plane Euclidean geometry, a rhombus (: rhombi or rhombuses) is a quadrilateral whose four sides all have the same length. Another name is equilateral quadrilateral, since equilateral means that all of its sides are equal in length. The rhombus is often called a "diamond", after the Diamonds (suit), diamonds suit in playing cards which resembles the projection of an Octahedron#Orthogonal projections, octahedral diamond, or a lozenge (shape), lozenge, though the former sometimes refers specifically to a rhombus with a 60° angle (which some authors call a calisson after calisson, the French sweet—also see Polyiamond), and the latter sometimes refers specifically to a rhombus with a 45° angle. Every rhombus is simple polygon, simple (non-self-intersecting), and is a special case of a parallelogram and a Kite (geometry), kite. A rhombus with right angles is a square. Etymology The word "rhombus" comes from , meaning something that spins, which derives from the verb , roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
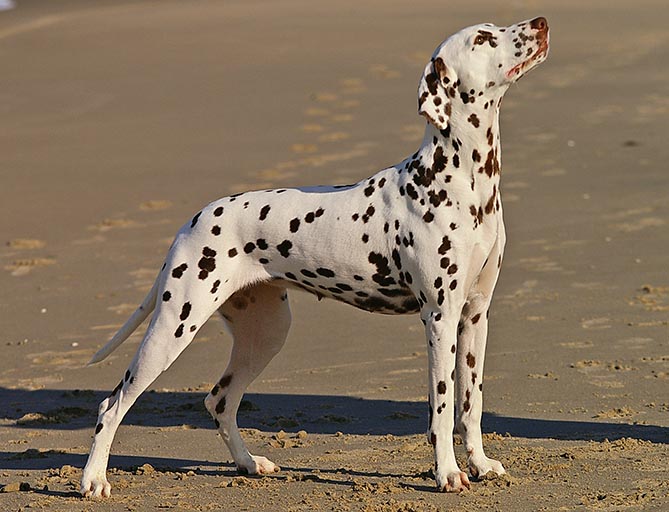
Dalmatian (dog)
The Dalmatian is a dog breed, breed of dog with a white coat marked with dark-coloured spots. Originally bred as a hunting dog, it was also used as a carriage dog and also known as fire dogs in its early days while firefighters were still using horse-drawn carriages. This led to them being known as fire dogs. The origins of this breed can be traced back to Croatia and its historical region of Dalmatia. It is thought that early ancestors of the breed were certain breeds of Pointer dog, pointers and a spotted Great Dane. Today, it is a popular pet and many enthusiasts enter Dalmatians into kennel club competitions. Characteristics Body The Dalmatian is a muscular dog with excellent endurance and stamina. When fully grown, according to the American Kennel Club (AKC) breed standard, it stands from tall. Coat Dalmatian puppies are born with plain white coats and their first spots usually appear within 10 days; however, spots may be visible on their skin from birth. They con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambiguous
Ambiguity is the type of meaning in which a phrase, statement, or resolution is not explicitly defined, making for several interpretations; others describe it as a concept or statement that has no real reference. A common aspect of ambiguity is uncertainty. It is thus an attribute of any idea or statement whose intended meaning cannot be definitively resolved, according to a rule or process with a finite number of steps. (The prefix '' ambi-'' reflects the idea of " two", as in "two meanings"). The concept of ambiguity is generally contrasted with vagueness. In ambiguity, specific and distinct interpretations are permitted (although some may not be immediately obvious), whereas with vague information it is difficult to form any interpretation at the desired level of specificity. Linguistic forms Lexical ambiguity is contrasted with semantic ambiguity. The former represents a choice between a finite number of known and meaningful context-dependent interpretations. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Figurative Language
The distinction between literal and figurative language exists in all natural languages; the phenomenon is studied within certain areas of language analysis, in particular stylistics, rhetoric, and semantics. *Literal language is the usage of words exactly according to their direct, straightforward, or conventionally accepted meaning (linguistics), meanings: their denotation. *Figurative (or non-literal) language is the usage of words in addition to, or deviating beyond, their conventionally accepted definitions in order to convey a more complex meaning or achieve a heightened effect. This is done by language-users presenting words in such a way that their audience equates, compares, or associates the words with normally unrelated meanings. A common intended effect of figurative language is to elicit audience responses that are especially emotional (like excitement, shock, laughter, etc.), aesthetic, or intellectual. The Ancient Greece, ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle, and lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Johnson
Samuel Johnson ( – 13 December 1784), often called Dr Johnson, was an English writer who made lasting contributions as a poet, playwright, essayist, moralist, literary critic, sermonist, biographer, editor, and lexicographer. The ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' calls him "arguably the most distinguished man of letters in English history". Born in Lichfield, Staffordshire, he attended Pembroke College, Oxford, until lack of funds forced him to leave. After working as a teacher, he moved to London and began writing for ''The Gentleman's Magazine''. Early works include '' Life of Mr Richard Savage'', the poems ''London'' and '' The Vanity of Human Wishes'' and the play '' Irene''. After nine years of effort, Johnson's '' A Dictionary of the English Language'' appeared in 1755, and was acclaimed as "one of the greatest single achievements of scholarship". Later work included essays, an annotated '' The Plays of William Shakespeare'', and the apologue '' The Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It shares Anglo-Scottish border, a land border with Scotland to the north and England–Wales border, another land border with Wales to the west, and is otherwise surrounded by the North Sea to the east, the English Channel to the south, the Celtic Sea to the south-west, and the Irish Sea to the west. Continental Europe lies to the south-east, and Ireland to the west. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the population was 56,490,048. London is both List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, the largest city and the Capital city, capital. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic. It takes its name from the Angles (tribe), Angles, a Germanic peoples, Germanic tribe who settled du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |