|
Faculty Of Medicine, University Of Kelaniya
The Faculty of Medicine of the University of Kelaniya located in Ragama, is one of eleven state medical schools in Sri Lanka. It is on a 35-acre (140,000 m2) campus at Ragama, and the faculty began classes with the admission of 120 students in September 1991. Before that it was called the North Colombo Medical College (NCMC). Overview The faculty has 1120 MBBS undergraduate students, 400 Speech and Hearing Sciences students and 73 Occupational Therapy students on its roll. This includes some foreign students, mainly from other South Asian countries, who have been admitted on a self-financing basis. The faculty also welcomes students for elective appointments and many students from medical schools in Europe, United States and Australia have spent their elective periods here. The faculty has a full range of academic departments consisting of about 145 academic staff members, including 23 professors. They are complemented by over 60 visiting staff, including consultants who are b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Kelaniya
Pannaya Parisujjhati , mottoeng = Self-purification is by insight , established = 1875 Vidyalankara Pirivena1959 Vidyalankara University , type = Public , endowment = , administrative_staff = 1000 full-time equivalent academic staff, 637 non-academic , chancellor = Kollupitiye Mahinda Sangharakkhitha Thera , vice_chancellor = Nilanthi De Silva , students = , undergrad = , postgrad = , doctoral = , other = , city = Kelaniya , state = , country = Sri Lanka , coordinates = , free_label = , free = , colours = , mascot = , campus = Suburban , affiliations = University Grants Commission (Sri Lanka), Association of Commonwealth Universiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Air Theatre
Regent's Park Open Air Theatre is an open-air theatre in Regent's Park in central London. The theatre Established in 1932, Regent’s Park Open Air Theatre is one of the largest theatres in London (1,256 seats) and is situated in Queen Mary’s Gardens in Regent’s Park, one of London’s Royal Parks. The theatre’s annual 18-week season is attended by over 140,000 people each year. In 2017, the theatre was named London Theatre of the Year in The Stage Awards, and received the Highly Commended Award for London Theatre of the Year in 2021. Awards †also for ''The Crucible'' The Venue's History In 1932 The New Theatre (now the Noel Coward) was left without a show after the early closure of a play by Mussolini. Robert Atkins and Sydney Carroll presented a ‘black and white’ production of Twelfth Night which subsequently transferred to a makeshift theatre in Regents Park, thus establishing Regent’s Park Open Air Theatre. Many stars of the future have performed at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library And Computer Center, Faculty Of Medicine, University Of Kelaniya
A library is a collection of materials, books or media that are accessible for use and not just for display purposes. A library provides physical (hard copies) or digital access (soft copies) materials, and may be a physical location or a virtual space, or both. A library's collection can include printed materials and other physical resources in many formats such as DVD, CD and cassette as well as access to information, music or other content held on bibliographic databases. A library, which may vary widely in size, may be organized for use and maintained by a public body such as a government; an institution such as a school or museum; a corporation; or a private individual. In addition to providing materials, libraries also provide the services of librarians who are trained and experts at finding, selecting, circulating and organizing information and at interpreting information needs, navigating and analyzing very large amounts of information with a variety of resources. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre Clinical Building, Faculty Of Medicine, University Of Kelaniya
Pre or PRE may refer to: Places *Preston railway station, UK National Rail code PRE *Prince Edward station, on Hong Kong's MTR People *Steve Prefontaine (1951–1975), an American runner nicknamed "Pre" Arts, entertainment, and media *Pre (band), British band *Public Radio East, regional network for NPR Technology *…, HTML element for pre-formatted text *Microphone preamplifier *Palm Pre, a smartphone *Partial redundancy elimination, computer compiler optimization *Personal Rescue Enclosure, for spacecraft Other uses *Andalusian horse or ''Pura Raza Española'' *Proportionate reduction of error Proportionate reduction of error (PRE) is the gain in precision of predicting dependent variable y from knowing the independent variable x (or a collection of multiple variables). It is a goodness of fit The goodness of fit of a statistical model ..., in statistics See also * {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
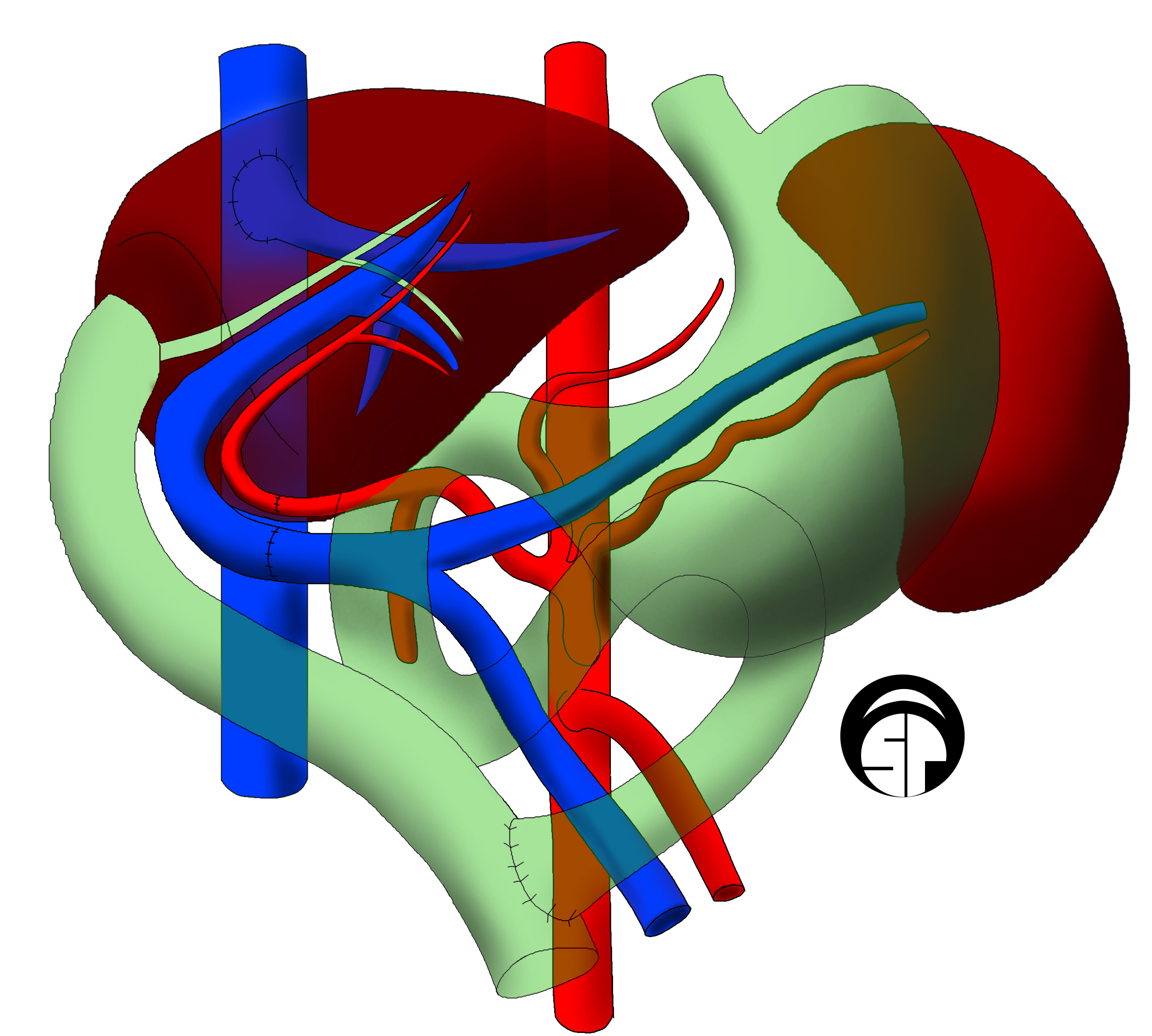
Liver Transplantation
Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a diseased liver with the healthy liver from another person (allograft). Liver transplantation is a treatment option for end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure, although availability of donor organs is a major limitation. The most common technique is orthotopic transplantation, in which the native liver is removed and replaced by the donor organ in the same anatomic position as the original liver. The surgical procedure is complex, requiring careful harvest of the donor organ and meticulous implantation into the recipient. Liver transplantation is highly regulated, and only performed at designated transplant medical centers by highly trained transplant physicians and supporting medical team. The duration of the surgery ranges from 4 to 18 hours depending on outcome. Favorable outcomes require careful screening for eligible recipient, as well as a well-calibrated live or cadaveric donor match. Medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Medicine
Molecular medicine is a broad field, where physical, chemical, biological, bioinformatics and medical techniques are used to describe molecular structures and mechanisms, identify fundamental molecular and genetic errors of disease, and to develop molecular interventions to correct them. The molecular medicine perspective emphasizes cellular and molecular phenomena and interventions rather than the previous conceptual and observational focus on patients and their organs. History In November 1949, with the seminal paper, " Sickle Cell Anemia, a Molecular Disease", in ''Science'' magazine, Linus Pauling, Harvey Itano and their collaborators laid the groundwork for establishing the field of molecular medicine. In 1956, Roger J. Williams wrote ''Biochemical Individuality'', a prescient book about genetics, prevention and treatment of disease on a molecular basis, and nutrition which is now variously referred to as individualized medicine and orthomolecular medicine. Another paper in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disability Studies
Disability studies is an academic discipline that examines the meaning, nature, and consequences of disability. Initially, the field focused on the division between "impairment" and "disability," where impairment was an impairment of an individual's mind or body, while disability was considered a social constructionism, social construct. This premise gave rise to two distinct models of disability: the Social model of disability, social and medical model of disability, medical models of disability. In 1999 the social model was universally accepted as the model preferred by the field. However, in recent years, the division between the social and medical models has been challenged. Additionally, there has been an increased focus on interdisciplinary research. For example, recent investigations suggest using "cross-sectional markers of stratification" may help provide new insights on the non-random distribution of risk factors capable of acerbating disablement processes. Disability stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Health
International health, also called ''geographic medicine'', '' international medicine'', or ''global health'', is a field of health care, usually with a public health emphasis, dealing with health across regional or national boundaries. One subset of international medicine, travel medicine, prepares travelers with immunizations, prophylactic medications, preventive techniques such as bednets and residual pesticides, in-transit care, and post-travel care for exotic illnesses. International health, however, more often refers to health personnel or organizations from one area or nation providing direct health care, or health sector development, in another area or nation. It is this sense of the term that is explained here. More recently, public health experts have become interested in global processes that impact on human health. Globalization and health, for example, illustrates the complex and changing sociological environment within which the determinants of health and disease expre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Centre
A cultural center or cultural centre is an organization, building or complex that promotes culture and arts. Cultural centers can be neighborhood community arts organizations, private facilities, government-sponsored, or activist-run. Asia * Central Cultural Center (CCC), Bangladesh * Bahman Cultural Center, Tehran, Iran * Bangkok Art and Culture Centre, Bangkok, Thailand * Beigang Cultural Center, Yunlin, Taiwan * Bentara Budaya Jakarta, Jakarta, Indonesia * Bentara Budaya Yogyakarta, Yogyakarta, Indonesia * Cultural Center of the Philippines, Philippines * Hong Kong Cultural Centre, Hong Kong, China * Japanese Cultural Center, Taipei, Taiwan * Kaohsiung Cultural Center, Kaohsiung, Taiwan * Keelung Cultural Center, Keelung, Taiwan * Ketagalan Culture Center, Taipei, Taiwan * King Abdulaziz Center for World Culture, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia * Kohima Capital Cultural Center, Kohima, Nagaland * Korean Cultural Center, Seoul, Korea * Sheikh Abdullah Al-Salem Cultural Centre, Kuwai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janaka De Silva
Janaka de Silva Fellow of the Royal College of Physicians, FRCP Fellow of the National Academy of Sciences of Sri Lanka , FNASSL is a Sri Lankan physician and academic. He is Professor Emeritus of Medicine at the University of Kelaniya. Janaka de Silva was educated at Royal College, Colombo and holds degrees from the universities of Colombo and Oxford. He had his higher specialist clinical training at the John Radcliffe Hospital. De Silva was Professor and Chair of Medicine at the University of Kelaniya from 1996-2022, and in 1997, he succeeded Carlo Fonseka as Dean of Medicine, a post he held for nine years. He was also Director of the Postgraduate Institute of Medicine (PGIM), University of Colombo from 2014-2020, and a member of the University Grants Commission (Sri Lanka), University Grants Commission from 2008-2011. Before becoming its Director he chaired a number of boards in the PGIM, where he and colleagues established the first formal training programme for gastroentero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlo Fonseka
Carlo Fonseka ( si, කාලෝ ෆොන්සේකා ''Kālō Fonsēkā''; 4 March 1933 – 2 September 2019) was a Sri Lankan physician, academic and political activist. He was a former dean of the Faculty of Medicine, University of Kelaniya and a former president of the Sri Lanka Medical Council. Early life and family Fonseka was born on 4 March 1933 in Colombo, Ceylon. His family were Roman Catholics. He was educated at Maris Stella College, Negombo and St. Joseph's College, Colombo. After school he joined the University of Ceylon's Faculty of Medicine in Colombo in 1955, graduating in 1960 with a first class MBBS degree. Career After graduating Fonseka joined the Colombo General Hospital as an intern under professor K. Rajasuria and senior surgeon Dr. Noel Bartholomeusz. He then joined the base hospital in Mirigama, near his home village of Divulapitiya, as a medical officer. In 1962 Fonseka joined the University of Ceylon's Department of Physiology as a lecturer. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |