|
Fabio Pacucci
Fabio Pacucci is an Italian theoretical astrophysicist and science educator, currently at Harvard University and at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. He is widely known for his contributions to the study of black holes, in particular the first population of black holes formed in the Universe and high redshift quasars. He discovered the only two candidate direct collapse black holes known so far, and he was in the team that discovered the farthest lensed quasar known. Pacucci is also a science educator, engaged in public talks on astronomy and science in general. Since 2018 he is a collaborator of TED in developing educational videos about science. The four videos released so far were watched by millions of people worldwide and translated into 25 languages. Education and career Fabio Pacucci was born in 1988 in Apulia, a region in the southern part of Italy. He received his B.Sc. in Physics and his M.Sc. in Astronomy and Astrophysics at the Sapienza University of Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apulia
it, Pugliese , population_note = , population_blank1_title = , population_blank1 = , demographics_type1 = , demographics1_footnotes = , demographics1_title1 = , demographics1_info1 = , demographics1_title2 = , demographics1_info2 = , demographics1_title3 = , demographics1_info3 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +01:00 , timezone1_DST = CEST , utc_offset1_DST = +02:00 , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code_type = ISO 3166 code , area_code = IT-75 , blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €76.6 billion (2018) , blank1_name_sec1 = GDP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 = €19,000 (2018) , blank2_name_sec1 = HDI (2018) , blank2_info_sec1 = 0.845 · 18th of 21 , blank_name_sec2 = NUTS Region , blank_info_sec2 = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronology Of The Universe
The chronology of the universe describes the history and future of the universe according to Big Bang cosmology. Research published in 2015 estimates the earliest stages of the universe's existence as taking place 13.8 billion years ago, with an uncertainty of around 21 million years at the 68% confidence level. The Planck Collaboration in 2015 published the estimate of 13.799 ± 0.021 billion years ago (68% confidence interval). See PDF: page 32, Table 4, Age/Gyr, last column. Outline Chronology in five stages For the purposes of this summary, it is convenient to divide the chronology of the universe since it originated, into five parts. It is generally considered meaningless or unclear whether time existed before this chronology: The very early universe The first picosecond (10−12) of cosmic time. It includes the Planck epoch, during which currently established laws of physics may not apply; the emergence in stages of the four known fundamental interactions or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21st-century Italian Astronomers
The 1st century was the century spanning AD 1 ( I) through AD 100 ( C) according to the Julian calendar. It is often written as the or to distinguish it from the 1st century BC (or BCE) which preceded it. The 1st century is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period. The 1st century also saw the appearance of Christianity. During this period, Europe, North Africa and the Near East fell under increasing domination by the Roman Empire, which continued expanding, most notably conquering Britain under the emperor Claudius (AD 43). The reforms introduced by Augustus during his long reign stabilized the empire after the turmoil of the previous century's civil wars. Later in the century the Julio-Claudian dynasty, which had been founded by Augustus, came to an end with the suicide of Nero in AD 68. There followed the famous Year of Four Emperors, a brief period of civil war and instability, which was finally brought to an end by Vespasian, ninth Roman emperor, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Astrophysicists
Italian(s) may refer to: * Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries ** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom ** Italian language, a Romance language *** Regional Italian, regional variants of the Italian language ** Languages of Italy, languages and dialects spoken in Italy ** Italian culture, cultural features of Italy ** Italian cuisine, traditional foods ** Folklore of Italy, the folklore and urban legends of Italy ** Mythology of Italy, traditional religion and beliefs Other uses * Italian dressing, a vinaigrette-type salad dressing or marinade * Italian or Italian-A, alternative names for the Ping-Pong virus, an extinct computer virus See also * * * Italia (other) * Italic (other) * Italo (other) * The Italian (other) * Italian people (other) Italian people may refer to: * in terms of ethnicity: all ethnic Italians, in and outside of Italy * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Harvard Gazette
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and one of the most prestigious and highly ranked universities in the world. The university is composed of ten academic faculties plus Harvard Radcliffe Institute. The Faculty of Arts and Sciences offers study in a wide range of undergraduate and graduate academic disciplines, and other faculties offer only graduate degrees, including professional degrees. Harvard has three main campuses: the Cambridge campus centered on Harvard Yard; an adjoining campus immediately across Charles River in the Allston neighborhood of Boston; and the medical campus in Boston's Longwood Medical Area. Harvard's endowment is valued at $50.9 billion, making it the wealthiest academic institution in the world. Endowment inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
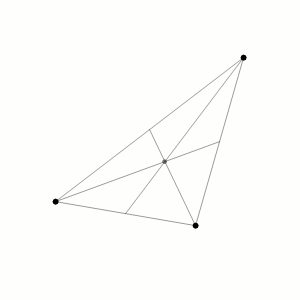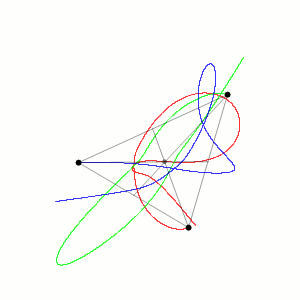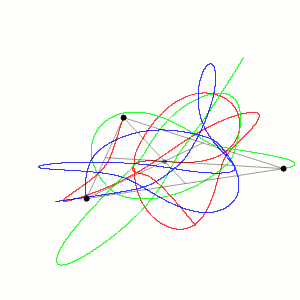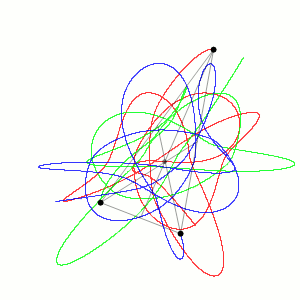
Three-body Problem
In physics and classical mechanics, the three-body problem is the problem of taking the initial positions and velocities (or momenta) of three point masses and solving for their subsequent motion according to Newton's laws of motion and Newton's law of universal gravitation. The three-body problem is a special case of the n-body problem, -body problem. Unlike two-body problems, no general closed-form solution exists, as the resulting dynamical system is chaos theory, chaotic for most initial conditions, and numerical methods are generally required. Historically, the first specific three-body problem to receive extended study was the one involving the Moon, Earth, and the Sun. In an extended modern sense, a three-body problem is any problem in classical mechanics Classical mechanics is a physical theory describing the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of machinery, and astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. For o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawking Radiation
Hawking radiation is theoretical black body radiation that is theorized to be released outside a black hole's event horizon because of relativistic quantum effects. It is named after the physicist Stephen Hawking, who developed a theoretical argument for its existence in 1974. Hawking radiation is a purely kinematic effect that is generic to Lorentzian geometries containing event horizons or local apparent horizons. Hawking radiation reduces the mass and rotational energy of black holes and is therefore also theorized to cause black hole evaporation. Because of this, black holes that do not gain mass through other means are expected to shrink and ultimately vanish. For all except the smallest black holes, this would happen extremely slowly. The radiation temperature is inversely proportional to the black hole's mass, so micro black holes are predicted to be larger emitters of radiation than larger black holes and should dissipate faster. Overview Black holes are astrophysica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avi Loeb
Abraham "Avi" Loeb ( he, אברהם (אבי) לייב; born February 26, 1962) is an Israeli-American theoretical physicist who works on astrophysics and cosmology. Loeb is the Frank B. Baird Jr. Professor of Science at Harvard University. He had been the longest serving chair of Harvard's Department of Astronomy (2011–2020), founding director of Harvard's Black Hole Initiative (since 2016) and director of the Institute for Theory and Computation (since 2007) within the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Loeb is a fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, the American Physical Society, and the International Academy of Astronautics. In July 2018, he was appointed as chair of the Board on Physics and Astronomy (BPA) of the National Academies, which is the Academies' forum for issues connected with the fields of physics and astronomy, including oversight of their decadal surveys. In June 2020, Loeb was sworn in as a member of the President's Council o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiaohui Fan
Xiaohui Fan (born 9 December 1971 in Beijing, China) is an American astronomer, and full professor at University of Arizona. He is widely known for his studies on quasars, extremely bright supermassive black holes, detected primarily at high redshift. In 2003, Fan was named to ''Popular Science'' magazine's annual Brilliant Ten list for developing methods to investigate distant quasars. Since 2001, he was a pioneer in the detection and discovery of high-redshift quasars, introducing new techniques and practically inventing the field. Using these quasars, he has shown that supermassive black holes with masses up to 10 million solar masses existed within one billion years after the big bang. In 2019, he led an international team of astronomers that discovered the farthest lensed quasar thus far, the very first in the epoch of reionization. In 2021, his team announced the discovery of the most distant and oldest known quasar, QSO J0313–1806. Education He graduated from Nanjing U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reionization
In the fields of Big Bang theory and cosmology, reionization is the process that caused matter in the universe to reionize after the lapse of the " dark ages". Reionization is the second of two major phase transitions of gas in the universe (the first is recombination). While the majority of baryonic matter in the universe is in the form of hydrogen and helium, reionization usually refers strictly to the reionization of hydrogen, the element. It is believed that the primordial helium also experienced the same phase of reionization changes, but at different points in the history of the universe. This is usually referred to as helium reionization. Background The first phase change of hydrogen in the universe was recombination, which occurred at a redshift ''z'' = 1089 (379,000 years after the Big Bang), due to the cooling of the universe to the point where the rate of recombination of electrons and protons to form neutral hydrogen was higher than the reionizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
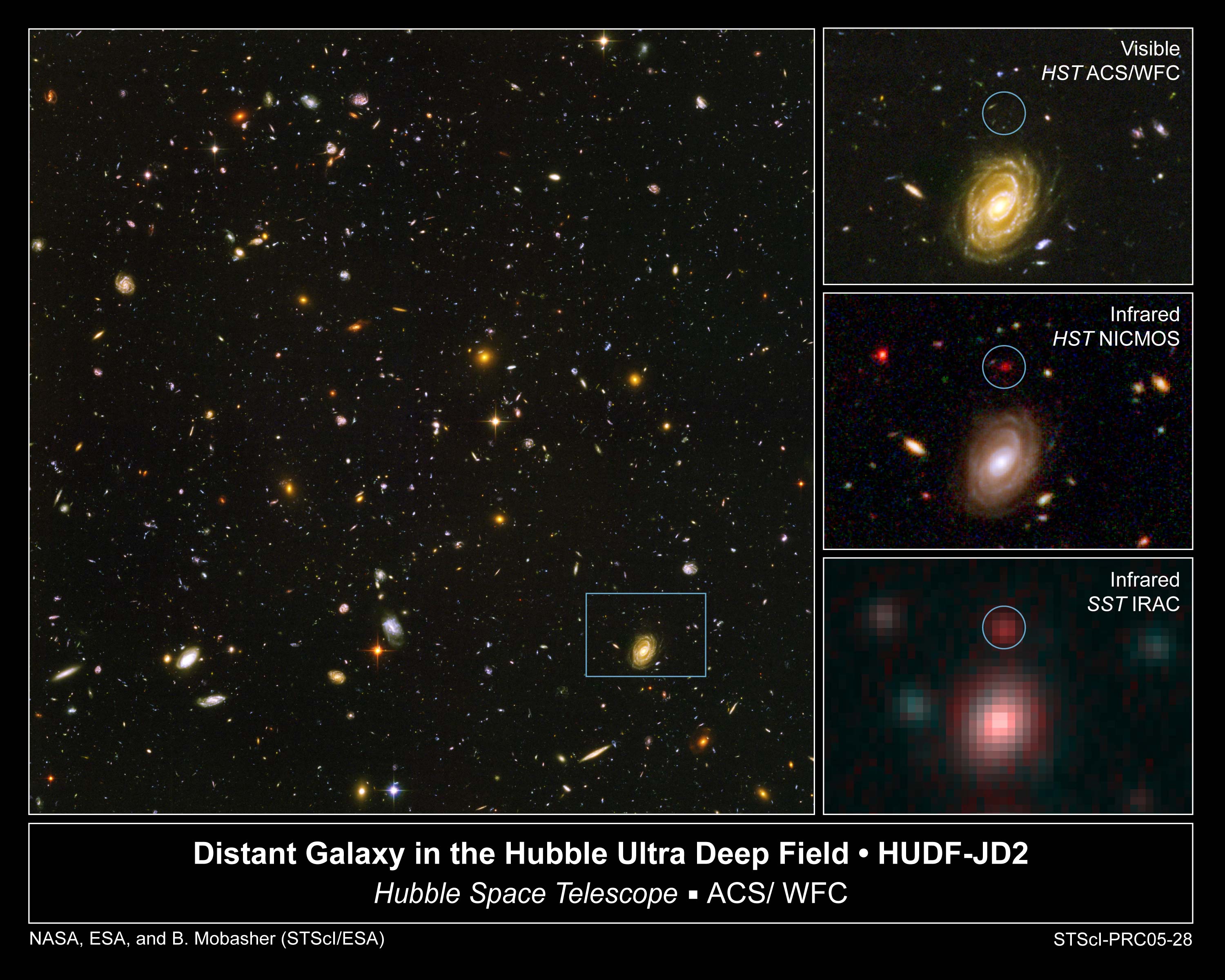
Spitzer Space Telescope
The Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), was an infrared space telescope launched in 2003. Operations ended on 30 January 2020. Spitzer was the third space telescope dedicated to infrared astronomy, following IRAS (1983) and ISO (1995–1998). It was the first spacecraft to use an Earth-trailing orbit, later used by the Kepler planet-finder. The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments were no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera continued to operate with the same sensitivity as before the helium was exhausted, and continued to be used into early 2020 in the Spitzer Warm Mission. During the warm mission, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)