|
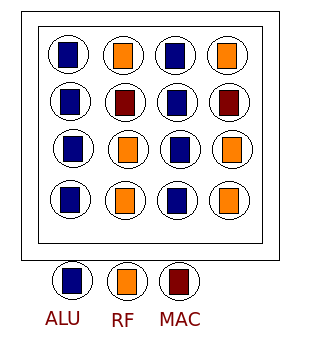
FPOA
A field-programmable object array (FPOA) is a class of programmable logic devices designed to be modified or programmed after manufacturing. They are designed to bridge the gap between ASIC and FPGA. They contain a grid of programmable silicon objects. Arrix range of FPOA contained three types of silicon objects: arithmetic logic units (ALUs), register files (RFs) and multiply-and-accumulate units (MACs). Both the objects and interconnects are programmable. Motivation and history The device was intended to bridge the gap between field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) and application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs). The design goal was to combine the programmability of FPGAs and the performance of ASICs. FPGAs, although programmable, lack performance; they may only be clocked to few hundreds of megahertz and most FPGAs operated below 100 MHz. FPGAs did not offer deterministic timing and the maximum operating frequency depends on the design. ASICs offered good performa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MathStar
MathStar, Inc., was an American, fabless semiconductor company based in Oregon. Founded in Minnesota in 1999, the company moved to the Portland metropolitan area where it remained until it completed a reverse merger with Sajan, Inc. in 2010. MathStar never made a profit after raising $137 million over the lifetime of the company, including via several stock offerings while the company was publicly traded on the NASDAQ market. The company's only product was a field programmable object array (FPOA) chip. History Robert Warren (Bob) Johnson and Douglas Pihl started discussing the formation of a company in 1999 to design a new type of digital signal processors (DSP) microprocessor chip, and founded MathStar the next year and began raising funds. The two founded the company in Minneapolis, Minnesota, and raised $18 million for the venture by September 2000 when they had grown to approximately 15 employees. MathStar's new processor was to be based on using a series of algorithms devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardware Acceleration
Hardware acceleration is the use of computer hardware designed to perform specific functions more efficiently when compared to software running on a general-purpose central processing unit (CPU). Any transformation of data that can be calculated in software running on a generic CPU can also be calculated in custom-made hardware, or in some mix of both. To perform computing tasks more efficiently, generally one can invest time and money in improving the software, improving the hardware, or both. There are various approaches with advantages and disadvantages in terms of decreased latency, increased throughput, and reduced energy consumption. Typical advantages of focusing on software may include greater versatility, more rapid development, lower non-recurring engineering costs, heightened portability, and ease of updating features or patching bugs, at the cost of overhead to compute general operations. Advantages of focusing on hardware may include speedup, reduced power c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AI Accelerator
A neural processing unit (NPU), also known as AI accelerator or deep learning processor, is a class of specialized hardware accelerator or computer system designed to accelerate artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning applications, including artificial neural networks and computer vision. Use Their purpose is either to efficiently execute already trained AI models (inference) or to train AI models. Their applications include algorithms for robotics, Internet of things, and data-intensive or sensor-driven tasks. They are often manycore designs and focus on low-precision arithmetic, novel dataflow architectures, or in-memory computing capability. , a typical AI integrated circuit chip contains tens of billions of MOSFETs. AI accelerators are used in mobile devices such as Apple iPhones and Huawei cellphones, and personal computers such as Intel laptops, AMD laptops and Apple silicon Macs. Accelerators are used in cloud computing servers, including tensor processi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Processing
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be displayed through other media, including a projection on a surface, activation of electronic signals, or digital displays; they can also be reproduced through mechanical means, such as photography, printmaking, or photocopying. Images can also be animated through digital or physical processes. In the context of signal processing, an image is a distributed amplitude of color(s). In optics, the term ''image'' (or ''optical image'') refers specifically to the reproduction of an object formed by light waves coming from the object. A ''volatile image'' exists or is perceived only for a short period. This may be a reflection of an object by a mirror, a projection of a camera obscura, or a scene displayed on a cathode-ray tube. A ''fixed image'', also called a hard copy, is one that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
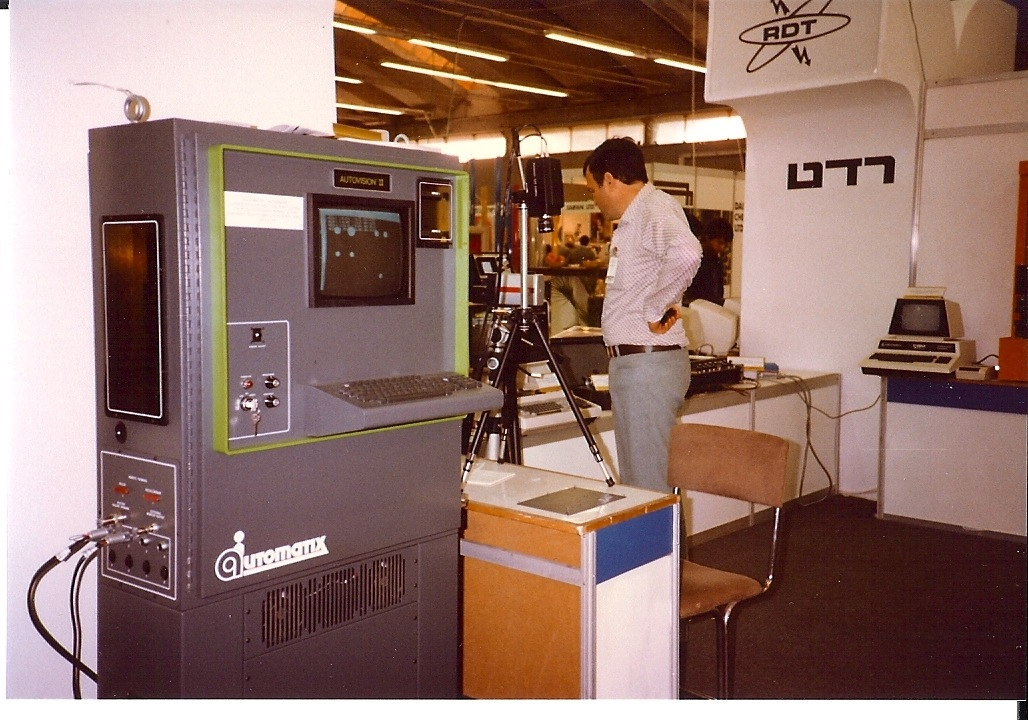
Machine Vision
Machine vision is the technology and methods used to provide image, imaging-based automation, automatic inspection and analysis for such applications as automatic inspection, process control, and robot guidance, usually in industry. Machine vision refers to many technologies, software and hardware products, integrated systems, actions, methods and expertise. Machine vision as a systems engineering discipline can be considered distinct from computer vision, a form of computer science. It attempts to integrate existing technologies in new ways and apply them to solve real world problems. The term is the prevalent one for these functions in industrial automation environments but is also used for these functions in other environment vehicle guidance. The overall machine vision process includes planning the details of the requirements and project, and then creating a solution. During run-time, the process starts with imaging, followed by automated image analysis, analysis of the image a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organ (anatomy), organs and Tissue (biology), tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging. Measurement and recording techniques that are not primarily designed to produce images, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and others, represent other technologies that produce data susceptible to representation as a parameter graph versus time or maps that contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Fourier Transform
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). A Fourier transform converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in the frequency domain and vice versa. The DFT is obtained by decomposing a sequence of values into components of different frequencies. This operation is useful in many fields, but computing it directly from the definition is often too slow to be practical. An FFT rapidly computes such transformations by Matrix decomposition, factorizing the DFT matrix into a product of Sparse matrix, sparse (mostly zero) factors. As a result, it manages to reduce the Computational complexity theory, complexity of computing the DFT from O(n^2), which arises if one simply applies the definition of DFT, to O(n \log n), where is the data size. The difference in speed can be enormous, especially for long data sets where may be in the thousands or millions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avionics
Avionics (a portmanteau of ''aviation'' and ''electronics'') are the Electronics, electronic systems used on aircraft. Avionic systems include communications, Air navigation, navigation, the display and management of multiple systems, and the hundreds of systems that are fitted to aircraft to perform individual functions. These can be as simple as a searchlight for a police helicopter or as complicated as the tactical system for an airborne early warning platform. History The term "avionics" was coined in 1949 by Philip J. Klass, senior editor at ''Aviation Week & Space Technology'' magazine as a portmanteau of "aviation electronics". Radio communication was first used in aircraft just prior to World War I. The first Airborne radio relay, airborne radios were in zeppelins, but the military sparked development of light radio sets that could be carried by heavier-than-air craft, so that aerial reconnaissance biplanes could report their observations immediately in case they we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardware Emulation
In integrated circuit design, hardware emulation is the process of imitating the behavior of one or more pieces of hardware (typically a system under design) with another piece of hardware, typically a special purpose emulation system. The emulation model is usually based on a hardware description language (e.g. Verilog) source code, which is compiled into the format used by emulation system. The goal is normally debugging and functional verification of the system being designed. Often an emulator is fast enough to be plugged into a working target system in place of a yet-to-be-built chip, so the whole system can be debugged with live data. This is a specific case of in-circuit emulation. Sometimes hardware emulation can be confused with hardware devices such as expansion cards with hardware processors that assist functions of software emulation, such as older daughterboards with x86 chips to allow x86 OSes to run on motherboards of different processor families. Introduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field of science that develops methods and Bioinformatics software, software tools for understanding biological data, especially when the data sets are large and complex. Bioinformatics uses biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, data science, computer programming, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret biological data. The process of analyzing and interpreting data can sometimes be referred to as computational biology, however this distinction between the two terms is often disputed. To some, the term ''computational biology'' refers to building and using models of biological systems. Computational, statistical, and computer programming techniques have been used for In silico, computer simulation analyses of biological queries. They include reused specific analysis "pipelines", particularly in the field of genomics, such as by the identification of genes and single nucleotide polymorphis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |