FPOA on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A field-programmable object array (FPOA) is a class of
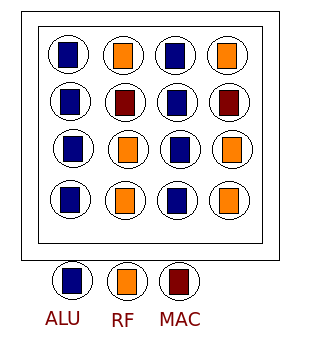 FPOAs have a core grid of silicon objects or core objects. These objects are connected through a synchronous interconnect. Each core object also has a supporting structures for clock synchronization, BIST and the like. The core is surrounded by peripheral circuitry that contains memory and I/O. An interface circuitry connects the objects to rest of FPOA. Exact number of each type of object and its arrangement are specific to a given family. There are two types of communication: nearest member and "party-line". Nearest member is used to connect a core to nearest core object and party line is used to connect remote objects. There are 8 nearest neighbor interconnects per object and offers transmission speed on one object hop per clock cycle. There are 10 party line interconnect per object that offers transmission speed of four object hops per clock cycle.
FPOAs have a core grid of silicon objects or core objects. These objects are connected through a synchronous interconnect. Each core object also has a supporting structures for clock synchronization, BIST and the like. The core is surrounded by peripheral circuitry that contains memory and I/O. An interface circuitry connects the objects to rest of FPOA. Exact number of each type of object and its arrangement are specific to a given family. There are two types of communication: nearest member and "party-line". Nearest member is used to connect a core to nearest core object and party line is used to connect remote objects. There are 8 nearest neighbor interconnects per object and offers transmission speed on one object hop per clock cycle. There are 10 party line interconnect per object that offers transmission speed of four object hops per clock cycle.
programmable logic device
A programmable logic device (PLD) is an electronic component used to build reconfigurable digital circuits. Unlike digital logic constructed using discrete logic gates with fixed functions, the function of a PLD is undefined at the time of m ...
s designed to be modified or programmed after manufacturing. They are designed to bridge the gap between ASIC
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC ) is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-efficien ...
and FPGA. They contain a grid of programmable silicon objects. Arrix range of FPOA contained three types of silicon objects: arithmetic logic unit
In computing, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a Combinational logic, combinational digital circuit that performs arithmetic and bitwise operations on integer binary numbers. This is in contrast to a floating-point unit (FPU), which operates on ...
s (ALUs), register file
A register file is an array of processor registers in a central processing unit (CPU). The instruction set architecture of a CPU will almost always define a set of registers which are used to stage data between memory and the functional units on ...
s (RFs) and multiply-and-accumulate units (MACs). Both the objects and interconnects are programmable.
Motivation and history
The device was intended to bridge the gap between field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) andapplication-specific integrated circuit
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC ) is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-efficienc ...
s (ASICs). The design goal was to combine the programmability of FPGAs and the performance of ASICs. FPGAs, although programmable, lack performance; they may only be clocked to few hundreds of megahertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in terms of SI base ...
and most FPGAs operated below 100 MHz. FPGAs did not offer deterministic timing and the maximum operating frequency depends on the design. ASICs offered good performance, but they could not be modified and they were very costly. The FPOA had a programmable architecture, deterministic timing, and gigahertz performance. The FPOA was designed by Douglas Pihl who had this idea when working on a DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military. Originally known as the Adva ...
funded project. He founded MathStar in 1997 to manufacture FPOAs and the idea was patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling discl ...
ed in 2004. The first FPOA prototypes were made in 2005 and first batch of FPOA chips were fabricated in 2006.
Architecture
 FPOAs have a core grid of silicon objects or core objects. These objects are connected through a synchronous interconnect. Each core object also has a supporting structures for clock synchronization, BIST and the like. The core is surrounded by peripheral circuitry that contains memory and I/O. An interface circuitry connects the objects to rest of FPOA. Exact number of each type of object and its arrangement are specific to a given family. There are two types of communication: nearest member and "party-line". Nearest member is used to connect a core to nearest core object and party line is used to connect remote objects. There are 8 nearest neighbor interconnects per object and offers transmission speed on one object hop per clock cycle. There are 10 party line interconnect per object that offers transmission speed of four object hops per clock cycle.
FPOAs have a core grid of silicon objects or core objects. These objects are connected through a synchronous interconnect. Each core object also has a supporting structures for clock synchronization, BIST and the like. The core is surrounded by peripheral circuitry that contains memory and I/O. An interface circuitry connects the objects to rest of FPOA. Exact number of each type of object and its arrangement are specific to a given family. There are two types of communication: nearest member and "party-line". Nearest member is used to connect a core to nearest core object and party line is used to connect remote objects. There are 8 nearest neighbor interconnects per object and offers transmission speed on one object hop per clock cycle. There are 10 party line interconnect per object that offers transmission speed of four object hops per clock cycle.
Applications
FPOAs may be used almost anywhere an FPGA is used, broadly in allhardware acceleration
Hardware acceleration is the use of computer hardware designed to perform specific functions more efficiently when compared to software running on a general-purpose central processing unit (CPU). Any transformation of data that can be calcula ...
tasks including digital signal processing
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The digital signals processed in this manner are a ...
, medical imaging, computer vision, speech recognition
Speech recognition is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and computational linguistics that develops methodologies and technologies that enable the recognition and translation of spoken language into text by computers. It is also ...
, cryptography, bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field of science that develops methods and Bioinformatics software, software tools for understanding biological data, especially when the data sets are large and complex. Bioinformatics uses biology, ...
, computer hardware emulation, and aerospace
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial, and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astron ...
. Since FPOAs are built around fast and optimized silicon objects, they offer higher performance in flat field error correction, fast Fourier transform
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). A Fourier transform converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in ...
computation, medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
, machine vision
Machine vision is the technology and methods used to provide image, imaging-based automation, automatic inspection and analysis for such applications as automatic inspection, process control, and robot guidance, usually in industry. Machine vision ...
, image encoding and decoding, video encoding and decoding and artificial intelligence acceleration to name a few.
Development on FPOA
In FPOA we work at silicon object level a higher level than the gate level used in FPGA. This eases the learning curve and also speeds up development. Programming is done in System C. The Arrix family released in 2006 was supported by FPOA design software, which enabled designers to create, verify, program and debug their algorithms on the devices. Summit Design's Visual Elite tool was used for behavioural simulation. MathStar's COAST (COnnection and ASsignment Tool) offered a graphical environment for floor-planning and placement it compiled to an intermediate code that maps to hardware resources. The Object compiler generated the file to be loaded into the FPGA. In 2007 MathStar struck a partnership with mentor graphics and subsequent release use Visual Elite editor from Mentor Graphics for behavioural simulation and functional verification. FPOAs also offered IP core library IP partners included professionals in the video market as well as machine vision market.Present status
MathStar the producer of FPOAs never posted a profit and the company decided to shut down production in May 2008. MathStar was merged into Sajan Inc. in 2010 and Sajan thus acquired MathStar's patent including that of FPOAs. In November 2011, Sajan sold several of MathStar's patent including some on FPOAs to OLK Grun GmbH.References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Field-Programmable Object Array Gate arrays Integrated circuits