|
FLASH MRI
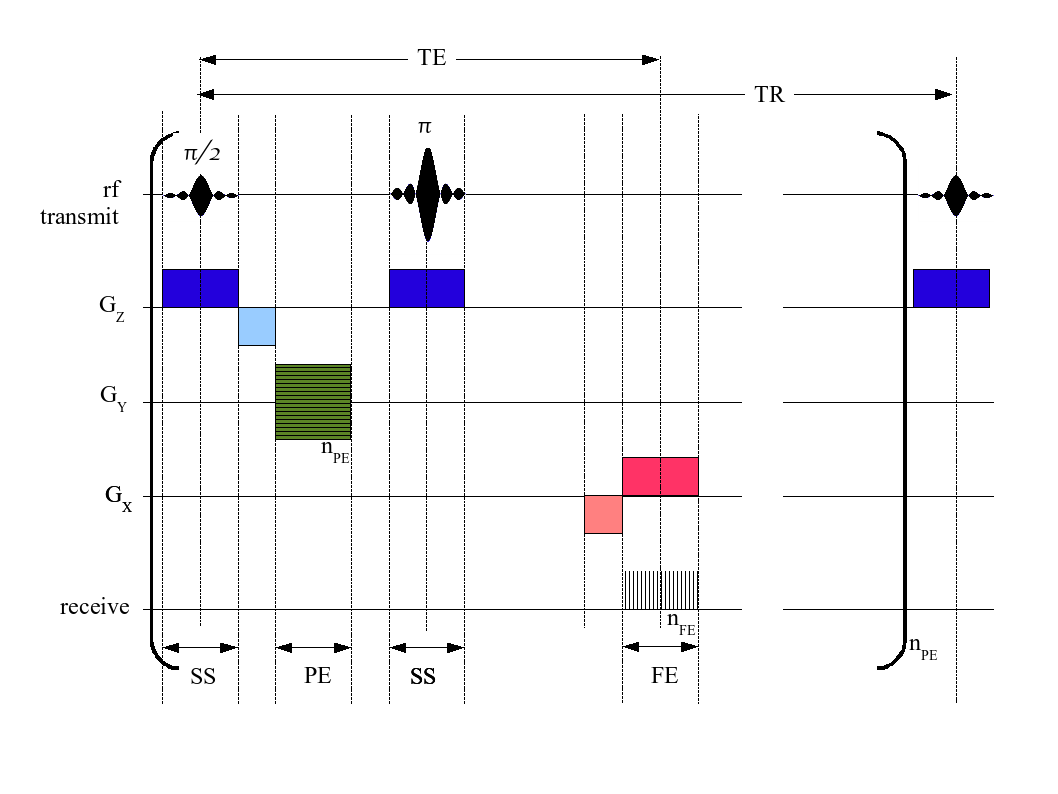
Fast low angle shot magnetic resonance imaging (FLASH MRI) is a particular sequence of magnetic resonance imaging. It is a gradient echo sequence which combines a low-flip angle radio-frequency excitation of the nuclear magnetic resonance signal (recorded as a spatially encoded gradient echo) with a short repetition time. It is the generic form of steady-state free precession imaging. Different manufacturers of MRI equipment use different names for this experiment. Siemens uses the name FLASH, General Electric used the name SPGR (Spoiled Gradient Echo), and Philips uses the name CE-FFE-T1 (Contrast-Enhanced Fast Field Echo) or T1-FFE. Depending on the desired contrast, the generic FLASH technique provides spoiled versions that destroy transverse coherences and yield T1 contrast as well as refocused versions (constant phase per repetition) and fully balanced versions (zero phase per repetition) that incorporate transverse coherences into the steady-state signal and offer T1/T2 c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRI Sequence
An MRI sequence in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a particular setting of pulse sequences and pulsed field gradients, resulting in a particular image appearance. A multiparametric MRI is a combination of two or more sequences, and/or including other specialized MRI configurations such as spectroscopy. Spin echo T1 and T2 Each tissue returns to its equilibrium state after excitation by the independent relaxation processes of T1 ( spin-lattice; that is, magnetization in the same direction as the static magnetic field) and T2 ( spin-spin; transverse to the static magnetic field). To create a T1-weighted image, magnetization is allowed to recover before measuring the MR signal by changing the repetition time (TR). This image weighting is useful for assessing the cerebral cortex, identifying fatty tissue, characterizing focal liver lesions, and in general, obtaining morphological information, as well as for post-contrast imaging. To create a T2-weighted image, magnetiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasculature
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek ''kardia'' meaning ''heart'', and from Latin ''vascula'' meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with the ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Some invertebrates such as art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMR In Biomedicine
''NMR in Biomedicine'' is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal published since 1988 by John Wiley & Sons. It publishes original full-length papers, rapid communications, and review articles in which magnetic resonance spectroscopy or imaging methods are used to investigate physiological, biochemical, biophysical, or medical problems. The current editor-in-chief is John R. Griffiths (Cancer Research UK). Highest cited articles The following articles have been cited most frequently: # "The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system - a technical review", 15 (7-8) Nov-Dec 2002: 435–455, Beaulieu C. # "A review of chemical issues in H-1-NMR spectroscopy - n-acetyl-l-aspartate, creatine and choline", 4 (2) Apr 1991: 47–52, Miller BL. # "Fiber tracking: principles and strategies - a technical review", 15 (7-8) Nov-Dec 2002: 468–480, DMori S, van Zijl PCM. # "Inferring microstructural features and the physiological state of tissues from diffusion-weighted images ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal and one of the oldest of its kind. It is also the world's highest-impact academic journal. It was founded in England in 1823. The journal publishes original research articles, review articles ("seminars" and "reviews"), editorials, book reviews, correspondence, as well as news features and case reports. ''The Lancet'' has been owned by Elsevier since 1991, and its editor-in-chief since 1995 has been Richard Horton. The journal has editorial offices in London, New York City, and Beijing. History ''The Lancet'' was founded in 1823 by Thomas Wakley, an English surgeon who named it after the surgical instrument called a lancet (scalpel). Members of the Wakley family retained editorship of the journal until 1908. In 1921, ''The Lancet'' was acquired by Hodder & Stoughton. Elsevier acquired ''The Lancet'' from Hodder & Stoughton in 1991. Impact According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millisecond
A millisecond (from '' milli-'' and second; symbol: ms) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one thousandth (0.001 or 10−3 or 1/1000) of a second and to 1000 microseconds. A unit of 10 milliseconds may be called a centisecond, and one of 100 milliseconds a decisecond, but these names are rarely used. To help compare orders of magnitude of different times, this page lists times between 10−3 seconds and 100 seconds (1 millisecond and one second). ''See also'' times of other orders of magnitude. Examples The Apollo Guidance Computer used metric units internally, with centiseconds used for time calculation and measurement. *1 millisecond (1 ms) – cycle time for frequency 1 kHz; duration of light for typical photo flash strobe; time taken for sound wave to travel about 34 cm; repetition interval of GPS C/A PN code *1 millisecond - time taken for light to travel 204.19 km in a single mode fiber optic cable for a wavelen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orders Of Magnitude
An order of magnitude is an approximation of the logarithm of a value relative to some contextually understood reference value, usually 10, interpreted as the base of the logarithm and the representative of values of magnitude one. Logarithmic distributions are common in nature and considering the order of magnitude of values sampled from such a distribution can be more intuitive. When the reference value is 10, the order of magnitude can be understood as the number of digits in the base-10 representation of the value. Similarly, if the reference value is one of some powers of 2, since computers store data in a binary format, the magnitude can be understood in terms of the amount of computer memory needed to store that value. Differences in order of magnitude can be measured on a base-10 logarithmic scale in “ decades” (i.e., factors of ten). Examples of numbers of different magnitudes can be found at Orders of magnitude (numbers). Definition Generally, the order of magnitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Göttingen
Göttingen (, , ; nds, Chöttingen) is a university city in Lower Saxony, central Germany, the capital of the eponymous district. The River Leine runs through it. At the end of 2019, the population was 118,911. General information The origins of Göttingen lay in a village called ''Gutingi, ''first mentioned in a document in 953 AD. The city was founded northwest of this village, between 1150 and 1200 AD, and adopted its name. In medieval times the city was a member of the Hanseatic League and hence a wealthy town. Today, Göttingen is famous for its old university (''Georgia Augusta'', or "Georg-August-Universität"), which was founded in 1734 (first classes in 1737) and became the most visited university of Europe. In 1837, seven professors protested against the absolute sovereignty of the kings of Hanover; they lost their positions, but became known as the " Göttingen Seven". Its alumni include some well-known historical figures: the Brothers Grimm, Heinrich Ewal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dieter Matthaei
Dieter Matthaei (born 1 February 1949 in Clausthal-Zellerfeld, Germany) is a German radiotherapist and internist. Matthaei studied physics and medicine at the universities of Berlin and Göttingen. In 1977, he received his doctorate from the University of Göttingen. He was from 1983 to 1987 a research associate at the Max-Planck-Institut für biophysikalische Chemie in Göttingen and is now medical specialist for internal medicine in Göttingen. Matthaei worked at the University of Göttingen and at the Max Planck Institute for Nuclear magnetic resonance in biological systems. He was looking for a scientific development of NMR techniques based on magnetic resonance imagery. With Axel Haase and Jens Frahm he succeeded in 1985 with the invention of rapid image proceedings FLASH MRI Fast low angle shot magnetic resonance imaging (FLASH MRI) is a particular sequence of magnetic resonance imaging. It is a gradient echo sequence which combines a low-flip angle radio-frequency exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jens Frahm
Jens Frahm (born 29 March 1951 in Oldenburg, Germany) is a German biophysicist and physicochemist. He is Research Group Leader of the Biomedical NMR group at the Max Planck Institute (MPI) for Multidisciplinary Sciences in Göttingen, Germany (prior to January 1, 2022, at the former MPI for Biophysical Chemistry). Early life and education From 1969 to 1974 Frahm studied physics at the University of Göttingen. His PhD thesis under the guidance of Hans Strehlow at the MPI for Biophysical Chemistry was devoted to the use of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy for a characterization of the molecular dynamics of hydrated ions in complex solutions. He received his PhD degree in 1977 in physical chemistry. Career Early Working as a research assistant at the Göttingen MPI since 1977 Frahm formed an independent research team which focused on the new possibilities offered by spatially resolved NMR and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – discovered in 1974, by Paul Lauter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real-time MRI
Real-time magnetic resonance imaging (RT-MRI) refers to the continuous monitoring ("filming") of moving objects in real time. Because MRI is based on time-consuming scanning of k-space, real-time MRI was possible only with low image quality or low temporal resolution. Using an iterative reconstruction algorithm these limitations have recently been removed: a new method for real-time MRI achieves a temporal resolution of 20 to 30 milliseconds for images with an in-plane resolution of 1.5 to 2.0 mm.M Uecker, S Zhang, D Voit, A Karaus, KD Merboldt, J Frahm (2010a) Real-time MRI at a resolution of 20 ms. NMR Biomed 23: 986-994 Real-time MRI promises to add important information about diseases of the joints and the heart. In many cases MRI examinations may become easier and more comfortable for patients. History 1977/1978 - Raymond Damadian built the first MRI scanner and achieved the first MRI scan of a healthy human body (1977) with the intent of diagnosing cancer. Addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-dimensional
In mathematics, a plane is a Euclidean ( flat), two-dimensional surface that extends indefinitely. A plane is the two-dimensional analogue of a point (zero dimensions), a line (one dimension) and three-dimensional space. Planes can arise as subspaces of some higher-dimensional space, as with one of a room's walls, infinitely extended, or they may enjoy an independent existence in their own right, as in the setting of two-dimensional Euclidean geometry. Sometimes the word ''plane'' is used more generally to describe a two-dimensional surface, for example the hyperbolic plane and elliptic plane. When working exclusively in two-dimensional Euclidean space, the definite article is used, so ''the'' plane refers to the whole space. Many fundamental tasks in mathematics, geometry, trigonometry, graph theory, and graphing are performed in a two-dimensional space, often in the plane. Euclidean geometry Euclid set forth the first great landmark of mathematical thought, an axioma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |