Real-time MRI on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Real-time magnetic resonance imaging (RT-MRI) refers to the continuous monitoring ("filming") of moving objects in real time. Because MRI is based on time-consuming scanning of k-space, real-time MRI was possible only with low image quality or low temporal resolution. Using an iterative reconstruction algorithm these limitations have recently been removed: a new method for real-time MRI achieves a temporal resolution of 20 to 30 milliseconds for images with an in-plane resolution of 1.5 to 2.0 mm.M Uecker, S Zhang, D Voit, A Karaus, KD Merboldt, J Frahm (2010a) Real-time MRI at a resolution of 20 ms. NMR Biomed 23: 986-994
Real-time MRI promises to add important information about diseases of the
 In general, real time MRI relies on gradient echo sequences, efficient k-space sampling, and fast reconstruction methods to speed up the image acquisition process. Gradient echo sequences present shorter echo times since only one RF pulse is required for each sequence. Modern fast-switching gradient coils also require increasing the
In general, real time MRI relies on gradient echo sequences, efficient k-space sampling, and fast reconstruction methods to speed up the image acquisition process. Gradient echo sequences present shorter echo times since only one RF pulse is required for each sequence. Modern fast-switching gradient coils also require increasing the 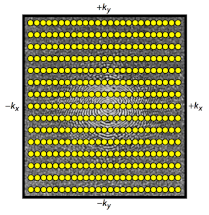
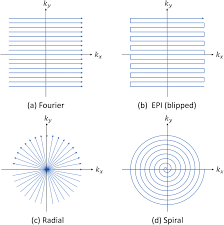 Efficient k-space sampling also decreases data collection time. Rectilinear scanning has become the standard k-space sampling method for MRI. However, the process takes a relatively long time as it samples the entire k-space equally. Because of this delay, other sampling methods are used to capture real-time motion. Single shot echo planar imaging is one extremely fast sampling method in which all of the data for the MR image is collected from one RF pulse. However, it is important to note that the EPI method is still a Cartesian sampling method, like the rectilinear scan, equally sampling the entire k-space. Spiral sampling, like EPI, only requires a single RF pulse to sample the entire k-space. Radial and spiral sampling are also used as methods to efficiently sample the k-space, with spiral also only requiring a single RF pulse to sample the k-space. Both radial and spiral sampling are more efficient than the Cartesian methods because they oversample low frequencies, which allows for general motion capture and better real-time image reconstruction. Thus, radial or spiral sampling of the k-space are now the preferred methods for real-time MRI reconstruction.
Efficient k-space sampling also decreases data collection time. Rectilinear scanning has become the standard k-space sampling method for MRI. However, the process takes a relatively long time as it samples the entire k-space equally. Because of this delay, other sampling methods are used to capture real-time motion. Single shot echo planar imaging is one extremely fast sampling method in which all of the data for the MR image is collected from one RF pulse. However, it is important to note that the EPI method is still a Cartesian sampling method, like the rectilinear scan, equally sampling the entire k-space. Spiral sampling, like EPI, only requires a single RF pulse to sample the entire k-space. Radial and spiral sampling are also used as methods to efficiently sample the k-space, with spiral also only requiring a single RF pulse to sample the k-space. Both radial and spiral sampling are more efficient than the Cartesian methods because they oversample low frequencies, which allows for general motion capture and better real-time image reconstruction. Thus, radial or spiral sampling of the k-space are now the preferred methods for real-time MRI reconstruction.
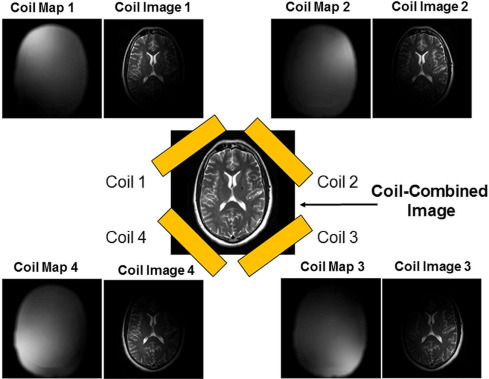 Parallel imaging involves the addition of multiple coils surrounding the target with each coil acquiring a fraction of the total image. Because modern GPUs have parallel processing capabilities, they can reconstruct each portion of the image simultaneously. Therefore, the more coils used, the faster the acquisition of the MR images.
Parallel imaging involves the addition of multiple coils surrounding the target with each coil acquiring a fraction of the total image. Because modern GPUs have parallel processing capabilities, they can reconstruct each portion of the image simultaneously. Therefore, the more coils used, the faster the acquisition of the MR images.
The real-time imaging method proposed by Uecker and colleagues combines radial FLASH MRI,S Zhang, KT Block KT, J Frahm (2010b) Magnetic resonance imaging in real time: Advances using radial FLASH. J Magn Reson Imag 31: 101-109
which offers rapid and continuous data acquisition, motion robustness, and tolerance to undersampling, with an iterative reconstruction, iterative image reconstruction method based on the formulation of image reconstruction as a
M Uecker, S Zhang, J Frahm (2010b) Nonlinear inverse reconstruction for real-time MRI of the human heart using undersampled radial FLASH. Magn Reson Med 63: 1456-1462
By integrating the data from multiple receive coils (i.e. parallel MRI) and exploiting the Redundancy (information theory), redundancy in the time series of images with the use of regularization and

Previous Cardiac mri, cardiac MR (CMR) used cine techniques to capture the periodic motion of the heart. However, this is not feasible for patients with
Related information
of the
Real-time MRI of horn playing (Sarah Willis)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Real-Time Mri Magnetic resonance imaging Medical monitoring Articles containing video clips
Real-time MRI promises to add important information about diseases of the
joint
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw ...
s and the heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon diox ...
. In many cases MRI examinations may become easier and
more comfortable for patients.
History
1977/1978 - Raymond Damadian built the first MRI scanner and achieved the first MRI scan of a healthy human body (1977) with the intent of diagnosing cancer. Additionally, Peter Mansfield develops the echo-planar technique, producing images in seconds and becoming the basis for fast MRIs. 1983 - Introduction of the k-space by D B Twieg 1987 - First real-time MRI of the heart is developed 1997 - Parallel imaging with an RF coil array is introduced by D K Sodickson 1999 - SENSE image reconstruction is introduced by K P Pruessmann 2002 - GRAPPA image reconstruction is introduced by Mark GriswoldPhysical basis
Overview
 In general, real time MRI relies on gradient echo sequences, efficient k-space sampling, and fast reconstruction methods to speed up the image acquisition process. Gradient echo sequences present shorter echo times since only one RF pulse is required for each sequence. Modern fast-switching gradient coils also require increasing the
In general, real time MRI relies on gradient echo sequences, efficient k-space sampling, and fast reconstruction methods to speed up the image acquisition process. Gradient echo sequences present shorter echo times since only one RF pulse is required for each sequence. Modern fast-switching gradient coils also require increasing the slew rate
In electronics, slew rate is defined as the change of voltage or current, or any other electrical quantity, per unit of time. Expressed in SI units, the unit of measurement is volts/ second or amperes/second, but is usually expressed in terms of ...
, allowing for faster changes in gradient echo sequences and decreasing the repetition time.

k-space sampling
 Efficient k-space sampling also decreases data collection time. Rectilinear scanning has become the standard k-space sampling method for MRI. However, the process takes a relatively long time as it samples the entire k-space equally. Because of this delay, other sampling methods are used to capture real-time motion. Single shot echo planar imaging is one extremely fast sampling method in which all of the data for the MR image is collected from one RF pulse. However, it is important to note that the EPI method is still a Cartesian sampling method, like the rectilinear scan, equally sampling the entire k-space. Spiral sampling, like EPI, only requires a single RF pulse to sample the entire k-space. Radial and spiral sampling are also used as methods to efficiently sample the k-space, with spiral also only requiring a single RF pulse to sample the k-space. Both radial and spiral sampling are more efficient than the Cartesian methods because they oversample low frequencies, which allows for general motion capture and better real-time image reconstruction. Thus, radial or spiral sampling of the k-space are now the preferred methods for real-time MRI reconstruction.
Efficient k-space sampling also decreases data collection time. Rectilinear scanning has become the standard k-space sampling method for MRI. However, the process takes a relatively long time as it samples the entire k-space equally. Because of this delay, other sampling methods are used to capture real-time motion. Single shot echo planar imaging is one extremely fast sampling method in which all of the data for the MR image is collected from one RF pulse. However, it is important to note that the EPI method is still a Cartesian sampling method, like the rectilinear scan, equally sampling the entire k-space. Spiral sampling, like EPI, only requires a single RF pulse to sample the entire k-space. Radial and spiral sampling are also used as methods to efficiently sample the k-space, with spiral also only requiring a single RF pulse to sample the k-space. Both radial and spiral sampling are more efficient than the Cartesian methods because they oversample low frequencies, which allows for general motion capture and better real-time image reconstruction. Thus, radial or spiral sampling of the k-space are now the preferred methods for real-time MRI reconstruction.
Parallel imaging
 Parallel imaging involves the addition of multiple coils surrounding the target with each coil acquiring a fraction of the total image. Because modern GPUs have parallel processing capabilities, they can reconstruct each portion of the image simultaneously. Therefore, the more coils used, the faster the acquisition of the MR images.
Parallel imaging involves the addition of multiple coils surrounding the target with each coil acquiring a fraction of the total image. Because modern GPUs have parallel processing capabilities, they can reconstruct each portion of the image simultaneously. Therefore, the more coils used, the faster the acquisition of the MR images.
Gradient-echo sequences
FLASH MRI
While early applications were based on echo planar imaging, which found an important application in real-timefunctional MRI
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area o ...
(rt-fMRI), recent progress is based on iterative reconstruction
Iterative reconstruction refers to iterative algorithms used to reconstruct 2D and 3D images in certain imaging techniques.
For example, in computed tomography an image must be reconstructed from projections of an object. Here, iterative recon ...
and FLASH MRI. J Frahm, A Haase, W Hänicke, KD Merboldt, D Matthaei (1985) Hochfrequenz-Impuls und Gradienten-Impuls-Verfahren zur Aufnahme von schnellen NMR-Tomogrammen unter Benutzung von Gradientenechos. German Patent Application P 35 04 734.8, February 12, 1985 J Frahm, A Haase, D Matthaei (1986) Rapid NMR imaging of dynamic processes using the FLASH technique. Magn Reson Med 3:321-32The real-time imaging method proposed by Uecker and colleagues combines radial FLASH MRI,S Zhang, KT Block KT, J Frahm (2010b) Magnetic resonance imaging in real time: Advances using radial FLASH. J Magn Reson Imag 31: 101-109
which offers rapid and continuous data acquisition, motion robustness, and tolerance to undersampling, with an iterative reconstruction, iterative image reconstruction method based on the formulation of image reconstruction as a
nonlinear
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other ...
inverse problem
An inverse problem in science is the process of calculating from a set of observations the causal factors that produced them: for example, calculating an image in X-ray computed tomography, source reconstruction in acoustics, or calculating th ...
.M Uecker, T Hohage, KT Block, J Frahm (2008) Image reconstruction by regularized nonlinear inversion – Joint estimation of coil sensitivities and image content. Magn Reson Med 60: 674-682M Uecker, S Zhang, J Frahm (2010b) Nonlinear inverse reconstruction for real-time MRI of the human heart using undersampled radial FLASH. Magn Reson Med 63: 1456-1462
By integrating the data from multiple receive coils (i.e. parallel MRI) and exploiting the Redundancy (information theory), redundancy in the time series of images with the use of regularization and
filtering
Filter, filtering or filters may refer to:
Science and technology
Computing
* Filter (higher-order function), in functional programming
* Filter (software), a computer program to process a data stream
* Filter (video), a software component th ...
, this approach enhances the possible degree of data undersampling by one order of magnitude, so that high-quality images may be obtained out of as little as 5 to 10% of the data required for a normal image reconstruction.
Because of the very short echo times (e.g., 1 to 2 millisecond
A millisecond (from '' milli-'' and second; symbol: ms) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one thousandth (0.001 or 10−3 or 1/1000) of a second and to 1000 microseconds.
A unit of 10 milliseconds may be ca ...
s), the method does not suffer from off-resonance effects, so that the images neither exhibit susceptibility artifacts nor rely on fat suppression. While spoiled FLASH sequences offer spin density or T1 contrast, versions with refocused or fully balanced gradients provide access to T2/T1 contrast. The choice of the gradient-echo time (e.g., in-phase vs opposed-phase conditions) further alters the representation of water and fat signals in the images and will allow for separate water/fat movies.
Balanced steady state free precession
Another GRE sequence commonly used in RT-MRI is balanced steady state free precession (bSSFP), as mentioned above with balanced gradients. Steady state free precession involves a repetition time (TR) that is shorter than T2. This prevents the magnetic signal from decaying completely before the next RF pulse is applied, which then establishes a steady state signal over time. The short TR also makes bSSFP ideal for RT-MRI. The equation for peak MR signal in bSSFP is given as: Where is the initial magnetization, and . Thus, the MR signal is proportional to T2/T1. Materials with similar T1 and T2, such as fluids and fat, present high T2/T1 contrast and can have signal intensity up to . The bSSFP signal is also greater than the FLASH signal by a factor of . Due to this strong fluid/tissue contrast, RT-MRI with bSSFP lends itself to cardiac imaging and visualizing blood flow.Image reconstruction
SENSitivity Encoding (SENSE)
Certain image reconstruction algorithms used alongside parallel imaging address the potential issues that can arise from undersampling the k-space. SENSitivity Encoding (SENSE) is a method that reconstructs the partial k-space data from each coil and combines the partial images into the final scan in the spatial domain. Coil sensitivities must first be acquired either before the actual imaging or during the imaging process. During the rest of imaging, the k-space is undersampled to skip every other line, resulting in a ½ FOV. As a two-point example, pixels on the original aliased images can be “unfolded” through the following equations to give the final scan: for two points, and , in the final image. and denote the image signal for the aliased image. and are the sensitivity values for coil 1 at points and , respectively, and and are the sensitivity values for coil 2 at points and , respectively.GeneRalized Autocalibrating Partial Parallel Acquisition (GRAPPA)
Another reconstruction algorithm used is GeneRalized Autocalibrating Partial Parallel Acquisition (GRAPPA). GRAPPA fills in the undersampled k-space data in the k-space domain before reconstructing the final image. Lines through the center of the k-space are fully sampled, typically alongside the actual image, to give the autocalibration signal (ACS) region. Weighing factors are calculated using the ACS, and these factors reflect the coil-specific distortions that each coil applies on the full field-of-view frequency domain. Then, the filled-in k-space data undergoes theinverse Fourier transform In mathematics, the Fourier inversion theorem says that for many types of functions it is possible to recover a function from its Fourier transform. Intuitively it may be viewed as the statement that if we know all frequency and phase information ...
to construct the partial, non-aliased images. These images are then simply combined directly in the spatial domain.
If the k-space data is non-Cartesian, reconstruction is computationally more difficult, since the fast Fourier transform
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). Fourier analysis converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in t ...
(FFT) requires Cartesian values. Typically, k-space data must be resampled into Cartesian coordinates before applying the FFT. GRAPPA can address these issues by obtaining large quantities of calibration data; however, the fastest reconstructions will generally require Cartesian data.
Signal-to-noise ratio
Lastly, within parallel image reconstruction there is another factor to consider, which is the signal to noise ratio ( SNR). The SNR for parallel imaging can be calculated using the following equation: Where is the acceleration factor and is the spatially dependent geometry factor (proportional to the number of coils used or the interactions between coils). Therefore, the more coils used, the faster the imaging process and the more inter-coil interactions; hence, the lower the SNR.Applications

Cardiac MRI
Although applications of real-time MRI cover a broad spectrum ranging from non-medical studies ofturbulent flow
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to a laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between ...
to the noninvasive monitoring of interventional (surgical) procedures, the most important application making use of the new capabilities is cardiovascular
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
imaging.S Zhang, M Uecker, D Voit, KD Merboldt, J Frahm (2010a) Real-time cardiovascular magnetic resonance at high temporal resolution: radial FLASH with nonlinear inverse reconstruction. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 12, 39Previous Cardiac mri, cardiac MR (CMR) used cine techniques to capture the periodic motion of the heart. However, this is not feasible for patients with
arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults ...
, where the cardiac cycle is unpredictable. With the new method it is possible to obtain movies of the beating heart in real time with up to 50 frames per second during free breathing and without the need for a synchronization to the electrocardiogram.I Uyanik, P Lindner, D Shah, N Tsekos I Pavlidis (2013) Applying a Level Set Method for Resolving Physiologic Motions in Free-Breathing and Non-gated Cardiac MRI. FIMH, 2013, A study performed by Laubrock et. al demonstrated that RT-MRI produced higher quality images with a higher SNR than cine CMR with a bSSFP sequence and radial k-space sampling. RT-MRI also removes the need for breath-holding while imaging, leading to a more comfortable experience for the patient as well.
Musculoskeletal MRI
Apart from cardiac MRI other real-time applications deal with functional studies ofjoint
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw ...
kinetics (e.g., temporomandibular joint
In anatomy, the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) are the two joints connecting the jawbone to the skull. It is a bilateral synovial articulation between the temporal bone of the skull above and the mandible below; it is from these bones that it ...
,S Zhang, N Gersdorff, J Frahm (2011) Real-Time Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Temporomandibular Joint Dynamics. The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2011, 5, 1-7, knee
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the human leg, leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest join ...
and the wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal ...
) or address the coordinated dynamics of the articulators such as lips, tongue, soft palate and vocal folds during speaking
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are th ...
(articulatory phonetics
The field of articulatory phonetics is a subfield of phonetics that studies articulation and ways that humans produce speech. Articulatory phoneticians explain how humans produce speech sounds via the interaction of different physiological struct ...
)Niebergall A, Zhang S, Kunay E, Keydana G, Job M, et al. Real-time MRI of Speaking at a Resolution of 33 ms: Undersampled Radial FLASH with Nonlinear Inverse Reconstruction. Magn Reson Med 2010, . or swallowing
Swallowing, sometimes called deglutition in scientific contexts, is the process in the human or animal body that allows for a substance to pass from the mouth, to the pharynx, and into the esophagus, while shutting the epiglottis. Swallowing ...
.Zhang S, Olthoff A and Frahm J. Real-time magnetic resonance imaging of normal swallowing. J Magn Reson Imaging 2011;35:1372-1379. . Musculoskeletal
The human musculoskeletal system (also known as the human locomotor system, and previously the activity system) is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move using their muscular and skeletal systems. The musculoskeletal system prov ...
imaging in particular benefits from real-time observation. Researchers at the NYU Grossman School of Medicine developed a RT-MRI glove for imaging movement of the hand. The glove uses high impedance coils to prevent the generation of eddy currents from rapidly changing magnetic fields and bSSFP for rapid imaging times. High-impedance coils remove the need for specific coil conformations and active gradient shielding.
MRI-guided invasive procedures
Applications ininterventional MRI
Interventional magnetic resonance imaging, also Interventional MRI or IMRI, is the use of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to do interventional radiology procedures.
Because of the lack of harmful effects on the patient and the operator, MR is we ...
, which refers to the monitoring of minimally invasive
Minimally invasive procedures (also known as minimally invasive surgeries) encompass surgical techniques that limit the size of incisions needed, thereby reducing wound healing time, associated pain, and risk of infection. Surgery by definition ...
surgical procedures, are possible by interactively changing parameters such as image position and orientation. This application is particularly helpful when a 3D image of the tissue is needed during surgery. It requires an in-room display for the physician to use during the procedure as well as the use of MRI-safe surgical tools. These include ceramic, plastic, or titanium, which is a paramagnetic
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior, ...
metal. By using bSSFP and parallel imaging with multiple coils, frame rates of 5-10 frames per second have been accomplished, allowing for the visualization of cardiac procedures.
Future directions
Parallel imaging
Parallel imaging coils are available for torso and cardiac imaging, but they are not yet standardized for other body parts. Dynamic coil setups for speech and musculoskeletal imaging are key areas for current research.
Machine learning
Image reconstruction in RT-MRI benefits frommachine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence.
Machine ...
(ML) or deep learning (DL). A nonlinear kernel
Kernel may refer to:
Computing
* Kernel (operating system), the central component of most operating systems
* Kernel (image processing), a matrix used for image convolution
* Compute kernel, in GPGPU programming
* Kernel method, in machine lea ...
, or mapping function, can be developed from the ACS to fill in k-space data and generate the final image. This process as a whole significantly accelerates the MRI process. Image segmentation or identification of lesions can be achieved through machine learning. In deep learning, with a convolutional neural network
In deep learning, a convolutional neural network (CNN, or ConvNet) is a class of artificial neural network (ANN), most commonly applied to analyze visual imagery. CNNs are also known as Shift Invariant or Space Invariant Artificial Neural Netwo ...
, the mapping function can be specified by the network. ML and DL improve image resolution as well as imaging speed.
High-performance, low-field scanners
High-performance, low-field MRI scanners are also an area of development. These scanners operate at relatively low magnetic field strengths, such as 0.35 T or 0.55 T. Many RT-MRI acquisition sequences, such as bSSFP, experience significant off-resonance effects. Off-resonance effects increase linearly with B0 field strength, so minimizing B0 also minimizes these effects that can lead to artifacts and image distortion. This allows for longer TRs, which then opens the door for a wider range of k-space sampling methods and sequence designs. Finally, lower strength MRI scanners will reduce the dangers associated with heating of metallic implants and decrease the cost of MRI.References
External links
Related information
of the
Max Planck Society
The Max Planck Society for the Advancement of Science (german: Max-Planck-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der Wissenschaften e. V.; abbreviated MPG) is a formally independent non-governmental and non-profit association of German research institutes. ...
Real-time MRI of horn playing (Sarah Willis)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Real-Time Mri Magnetic resonance imaging Medical monitoring Articles containing video clips