|
FAM46C Paralog Table
Protein FAM46C also known as family with sequence similarity 46, member C is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''FAM46C'' gene at locus 1p12 spanning base pairs from 118,148,556 to 118,171,011. Summary FAM46C is a protein of unknown function consisting of 391 amino acid residues that are translated from a messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) consisting of 5720 base pairs. FAM46C was initially sequenced as part of the Full-length long Japan genomic sequencing project. FAM46C is found on chromosome 1 at the locus 1p12 FAM46C contains one domain of unknown function, DUF1693, and as such has been placed in the DUF1693 protein family. This family has been established as a part of the Nucleotidyltransferase superfamily and contains 4 nematode prion-like proteins. FAM46C was placed into group XXV of the nucleotidyltransferase superfamily along with 3 other ''Homo sapiens'' FAM46 proteins ( A, B, D). It has been suggested that FAM46C may be functionally involved with the Type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testicle
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, primarily testosterone. The release of testosterone is regulated by luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary gland. Sperm production is controlled by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary gland and by testosterone produced within the gonads. Structure Appearance Males have two testicles of similar size contained within the scrotum, which is an extension of the abdominal wall. Scrotal asymmetry, in which one testicle extends farther down into the scrotum than the other, is common. This is because of the differences in the vasculature's anatomy. For 85% of men, the right testis hangs lower than the left one. Measurement and volume The volume of the testicle can be estimated by palpating it and compari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clustal
Clustal is a computer program used for multiple sequence alignment in bioinformatics. The software and its algorithms have gone through several iterations, with ClustalΩ (Omega) being the latest version . It is available as standalone software, via a Clustal#External links, web interface, and through a server hosted by the European Bioinformatics Institute. Clustal has been an important bioinformatic software, with two of its academic publications amongst the top 100 papers cited of all time, according to Nature (journal), Nature in 2014. History Version history * Clustal: The original software for multiple sequence alignments, created by Desmond G. Higgins, Des Higgins in 1988, was based on deriving a guide tree from pairwise sequences of Amino acid, amino acids or Nucleotide, nucleotides. * ClustalV: The second generation of Clustal, released in 1992. It introduced the ability to create new alignments from existing alignments in a process known as phylogenetic tree re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FAM46C Ortholog Unrooted Tree
Protein FAM46C also known as family with sequence similarity 46, member C is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''FAM46C'' gene at locus 1p12 spanning base pairs from 118,148,556 to 118,171,011. Summary FAM46C is a protein of unknown function consisting of 391 amino acid residues that are translated from a messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) consisting of 5720 base pairs. FAM46C was initially sequenced as part of the Full-length long Japan genomic sequencing project. FAM46C is found on chromosome 1 at the locus 1p12 FAM46C contains one domain of unknown function, DUF1693, and as such has been placed in the DUF1693 protein family. This family has been established as a part of the Nucleotidyltransferase superfamily and contains 4 nematode prion-like proteins. FAM46C was placed into group XXV of the nucleotidyltransferase superfamily along with 3 other ''Homo sapiens'' FAM46 proteins ( A, B, D). It has been suggested that FAM46C may be functionally involved with the Type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyre
Phyre and Phyre2 (Protein Homology/AnalogY Recognition Engine; pronounced as ''fire'') are free web-based services for protein structure prediction. Phyre is among the most popular methods for protein structure prediction having been cited over 1,500 times. Like other remote homology recognition techniques (see protein threading), it is able to regularly generate reliable protein models when other widely used methods such as PSI-BLAST cannot. Phyre2 has been designed to ensure a user-friendly interface for users inexpert in protein structure prediction methods. Its development is funded by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council. Description The Phyre and Phyre2 servers predict the three-dimensional structure of a protein sequence using the principles and techniques of homology modeling. Because the structure of a protein is more conserved in evolution than its amino acid sequence, a protein sequence of interest (the target) can be modeled with reasonable accu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ortholog Table
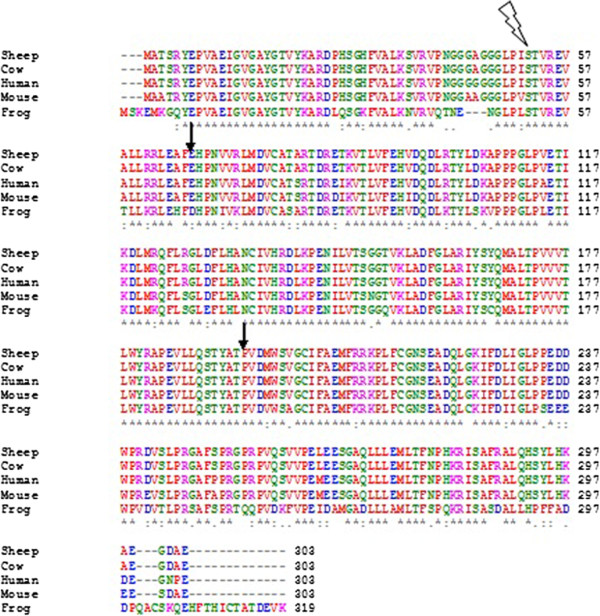
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal (or lateral) gene transfer event (xenologs). Homology among DNA, RNA, or proteins is typically inferred from their nucleotide or amino acid sequence similarity. Significant similarity is strong evidence that two sequences are related by evolutionary changes from a common ancestral sequence. Alignments of multiple sequences are used to indicate which regions of each sequence are homologous. Identity, similarity, and conservation The term "percent homology" is often used to mean "sequence similarity”, that is the percentage of identical residues (''percent identity''), or the percentage of residues conserved with similar physicochemical properties (''p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FAM46C Paralog Table
Protein FAM46C also known as family with sequence similarity 46, member C is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''FAM46C'' gene at locus 1p12 spanning base pairs from 118,148,556 to 118,171,011. Summary FAM46C is a protein of unknown function consisting of 391 amino acid residues that are translated from a messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) consisting of 5720 base pairs. FAM46C was initially sequenced as part of the Full-length long Japan genomic sequencing project. FAM46C is found on chromosome 1 at the locus 1p12 FAM46C contains one domain of unknown function, DUF1693, and as such has been placed in the DUF1693 protein family. This family has been established as a part of the Nucleotidyltransferase superfamily and contains 4 nematode prion-like proteins. FAM46C was placed into group XXV of the nucleotidyltransferase superfamily along with 3 other ''Homo sapiens'' FAM46 proteins ( A, B, D). It has been suggested that FAM46C may be functionally involved with the Type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placozoa
Placozoa ( ; ) is a phylum of free-living (non-parasitic) marine invertebrates. They are blob-like animals composed of aggregations of cells. Moving in water by ciliary motion, eating food by Phagocytosis, engulfment, reproducing by Fission (biology), fission or budding, placozoans are described as "the simplest animals on Earth." Structural and molecular analyses have supported them as among the most basal animals, thus, constituting a primitive metazoan phylum. The first known placozoan, ''Trichoplax adhaerens'', was discovered in 1883 by the German zoologist Franz Eilhard Schulze (1840–1921).F. E. Schulze "''Trichoplax adhaerens'' n. g., n. s.", ''Zoologischer Anzeiger'' (Elsevier, Amsterdam and Jena) 6 (1883), p. 92. Describing the uniqueness, another German, Karl Gottlieb Grell (1912–1994), erected a new phylum, Placozoa, for it in 1971. Remaining a monotypic phylum for over a century, new species began to be added since 2018. So far, three other extant species have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichoplax
''Trichoplax adhaerens'' is one of the four named species in the phylum Placozoa. The others are ''Hoilungia hongkongensis'', ''Polyplacotoma mediterranea'' and ''Cladtertia collaboinventa''. Placozoa is a basal group of multicellular animals, possible relatives of Cnidaria. ''Trichoplax'' are very flat organisms commonly less than 4 mm in diameter, lacking any organs or internal structures. They have two cellular layers: the top epitheloid layer is made of ciliated "cover cells" flattened toward the outside of the organism, and the bottom layer is made up of cylinder cells that possess cilia used in locomotion, and gland cells that lack cilia. Between these layers is the fibre syncytium, a liquid-filled cavity strutted open by star-like fibres. ''Trichoplax'' feed by absorbing food particles—mainly microbes—with their underside. They generally reproduce asexually, by dividing or budding, but can also reproduce sexually. Though ''Trichoplax'' has a small genome in comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |