|
Exercise Book
An exercise book or composition book is a notebook that is used in schools to copy down schoolwork and notes. A student will usually have a different exercise book for each separate lesson or subject. The exercise book format is different for some subjects: for the majority of subjects, the exercise book will contain ruled paper, lined paper with a margin (typography), margin, but for other subjects such as mathematics education, mathematics, the exercise book will contain graph paper, squared paper to aid in the drawing of graphs, tables or other diagrams. Exercise books may act as a primary record of students' learning efforts. For younger pupils, books are often collected at the end of each lesson for review, scoring, or grading. Loose worksheets may be pasted into the book so that they are bound with other work. In some schools, exercise books may be colour-coded depending on the subject. For example, Biology might be green and Algebra blue. The exercise book was also ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staple (fastener)
A staple is a type of two-pronged fastener, usually metal, used for joining or binding materials together. Large staples might be used with a hammer or staple gun for masonry, roofing, corrugated boxes and other heavy-duty uses. Smaller staples are used with a stapler to attach pieces of paper together; such staples are a more permanent and durable fastener for paper documents than the paper clip. Etymology The word "staple" originated in the late thirteenth Century, from Old English ''stapol'', meaning "post, pillar". The word's first usage in the paper-fastening sense is attested from 1895. History In ancient times, the staple had several different functions. Large metal staples dating from the 6th century BC have been found in the masonry works of the Persian empire (ancient Iran). For the construction of the Pasargadae and later Ka'ba-ye Zartosht, these staples, which are known as "dovetail" or "swallowtail" staples, were used for tightening stones together. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiral Notebook
A notebook (also known as a notepad, writing pad, drawing pad, or legal pad) is a book or stack of paper pages that are often ruled and used for purposes such as note-taking, journaling or other writing, drawing, or scrapbooking. History Early history During the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries, notebooks were often made by hand at home by drawing on them into gatherings that were then bound at a later date. The pages were blank and every notekeeper had to make ruled lines across the paper. Making and keeping notebooks was such an important information-management technique that children learned its skills in school. Legal pad According to a legend, Thomas W. Holley of Holyoke, Massachusetts, invented the legal pad around the year 1888 when he innovated the idea to collect all the sortings, various sorts of sub-standard paper scraps from various factories, and stitch them together in order to sell them as pads at an affordable and fair price. In about 1900, the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loose Leaf
A loose leaf is a piece of paper of any kind that is not bound in place, or available on a continuous roll, and may be punched so as to be organized in a ring binder. Loose leaf paper may be sold as free sheets, or made up into notepads, where perforations or glue allow them to be removed easily. "Leaf" in many languages refers to a sheet or page of paper, as in Folio, ''as in feuille de papier'' (French), ''hoja de papel'' (Spanish), ''foglio di carta'' (Italian). Description "Loose leaf" describes any kind of paper or book that is available in single sheets, unbound. Its "leaves", or sheets, are "loose" and not bound in notebook or book form. ''However'', it seems "loose leaf" in the USA's Midwest (and this entry) refers most specifically to a lined and punched paper, or ruled paper, a school supply also known as "binder paper" that can be sorted in a loose leaf binder. This may be a typical 3 ring binder but "loose leaves" of other types can also go in a date book, address b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punctuation
Punctuation (or sometimes interpunction) is the use of spacing, conventional signs (called punctuation marks), and certain typographical devices as aids to the understanding and correct reading of written text, whether read silently or aloud. Another description is, "It is the practice, action, or system of inserting points or other small marks into texts in order to aid interpretation; division of text into sentences, clauses, etc., by means of such marks." In written English, punctuation is vital to disambiguate the meaning of sentences. For example: "woman, without her man, is nothing" (emphasizing the importance of men to women), and "woman: without her, man is nothing" (emphasizing the importance of women to men) have very different meanings; as do "eats shoots and leaves" (which means the subject consumes plant growths) and "eats, shoots, and leaves" (which means the subject eats first, then fires a weapon, and then leaves the scene). Truss, Lynne (2003). '' Eats, Shoots ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammar
In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraints, a field that includes domains such as phonology, morphology, and syntax, often complemented by phonetics, semantics, and pragmatics. There are currently two different approaches to the study of grammar: traditional grammar and theoretical grammar. Fluent speakers of a language variety or ''lect'' have effectively internalized these constraints, the vast majority of which – at least in the case of one's native language(s) – are acquired not by conscious study or instruction but by hearing other speakers. Much of this internalization occurs during early childhood; learning a language later in life usually involves more explicit instruction. In this view, grammar is understood as the cognitive information underlying a specific instance of language prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiplication Table
In mathematics, a multiplication table (sometimes, less formally, a times table) is a mathematical table used to define a multiplication operation for an algebraic system. The decimal multiplication table was traditionally taught as an essential part of elementary arithmetic around the world, as it lays the foundation for arithmetic operations with base-ten numbers. Many educators believe it is necessary to memorize the table up to 9 × 9. History In pre-modern time The oldest known multiplication tables were used by the Babylonians about 4000 years ago. However, they used a base of 60. The oldest known tables using a base of 10 are the Chinese decimal multiplication table on bamboo strips dating to about 305 BC, during China's Warring States period. The multiplication table is sometimes attributed to the ancient Greek mathematician Pythagoras (570–495 BC). It is also called the Table of Pythagoras in many languages (for example French, Italian and Russian), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metric System
The metric system is a system of measurement that succeeded the decimalised system based on the metre that had been introduced in France in the 1790s. The historical development of these systems culminated in the definition of the International System of Units (SI) in the mid-20th century, under the oversight of an international standards body. Adopting the metric system is known as '' metrication''. The historical evolution of metric systems has resulted in the recognition of several principles. Each of the fundamental dimensions of nature is expressed by a single base unit of measure. The definition of base units has increasingly been realised from natural principles, rather than by copies of physical artefacts. For quantities derived from the fundamental base units of the system, units derived from the base units are used—e.g., the square metre is the derived unit for area, a quantity derived from length. These derived units are coherent, which means that they inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial System
The imperial system of units, imperial system or imperial units (also known as British Imperial or Exchequer Standards of 1826) is the system of units first defined in the British Weights and Measures Act 1824 and continued to be developed through a series of Weights and Measures Acts and amendments. The imperial system developed from earlier English units as did the related but differing system of customary units of the United States. The imperial units replaced the Winchester Standards, which were in effect from 1588 to 1825. The system came into official use across the British Empire in 1826. By the late 20th century, most nations of the former empire had officially adopted the metric system as their main system of measurement, but imperial units are still used alongside metric units in the United Kingdom and in some other parts of the former empire, notably Canada. The modern UK legislation defining the imperial system of units is given in the Weights and Measures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cap Line
In typography, cap height is the height of a capital letter above the baseline for a particular typeface.http://pfaedit.sourceforge.net/glossary.html Glossary of (some) Typographic Terms It specifically is the height of capital letters that are flat—such as H or I—as opposed to round letters such as O, or pointed letters like A, both of which may display overshoot. The height of the small letters is the x-height. See also * Body height (typography) In digital typography, the body height refers to the distance between the top of the tallest letterform to the bottom of the lowest one. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baseline (typography)
In European and West Asian typography and penmanship, the baseline is the line upon which most letters ''sit'' and below which descenders extend. In the example to the right, the letter 'p' has a descender; the other letters sit on the (red) baseline. Most, though not all, typefaces are similar in the following ways as regards the baseline: * capital letters sit on the baseline. The most common exceptions are the J and Q. *Lining figures (see Arabic numerals) sit on the baseline. *The following text figures have descenders: 3 4 5 7 9. *The following lowercase letters have descenders: g j p q y. * Glyphs with rounded lower and upper extents (0 3 6 8 c C G J o O Q) dip very slightly below the baseline ("overshoot") to create the optical illusion that they sit on the baseline, and rise above the x-height or capital height to create the illusion that they have the same height as flat glyphs (such as those for H x X 1 5 7). Peter Karow's ''Digital Typefaces'' suggests that typica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
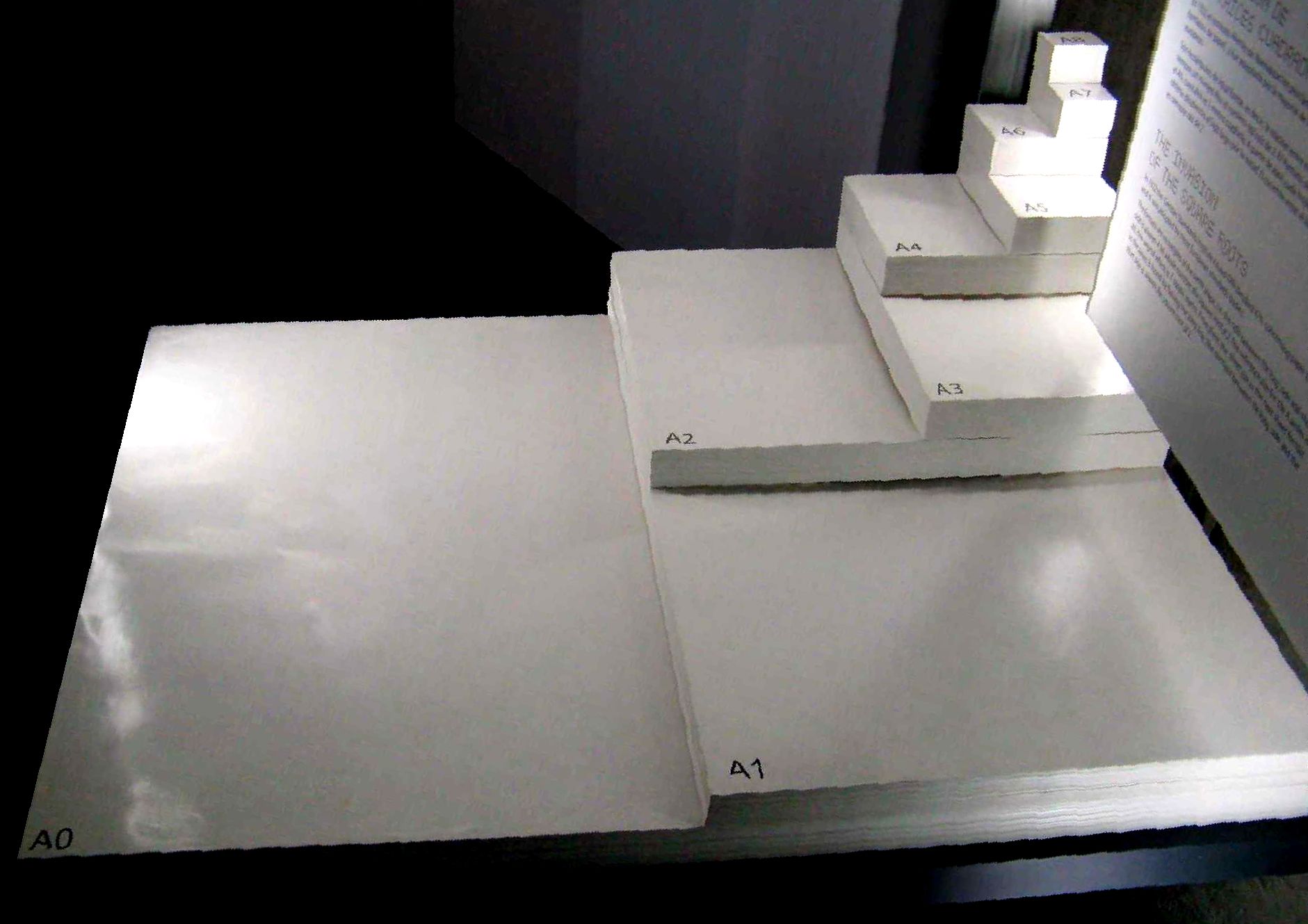
ISO 216
ISO 216 is an international standard for paper sizes, used around the world except in North America and parts of Latin America. The standard defines the "A", "B" and "C" series of paper sizes, including A4, the most commonly available paper size worldwide. Two supplementary standards, ISO 217 and ISO 269, define related paper sizes; the ISO 269 "C" series is commonly listed alongside the A and B sizes. All ISO 216, ISO 217 and ISO 269 paper sizes (except some envelopes) have the same aspect ratio, , within rounding to millimetres. This ratio has the unique property that when cut or folded in half widthways, the halves also have the same aspect ratio. Each ISO paper size is one half of the area of the next larger size in the same series. Dimensions of A, B and C series History The oldest known mention of the advantages of basing a paper size on an aspect ratio of is found in a letter written on 25 October 1786 by the German scientist Georg Christoph Lichtenberg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |