|
Exact Category
In mathematics, an exact category is a concept of category theory due to Daniel Quillen which is designed to encapsulate the properties of short exact sequences in abelian categories without requiring that morphisms actually possess kernels and cokernels, which is necessary for the usual definition of such a sequence. Definition An exact category E is an additive category possessing a class ''E'' of "short exact sequences": triples of objects connected by arrows : M' \to M \to M''\ satisfying the following axioms inspired by the properties of short exact sequences in an abelian category: * ''E'' is closed under isomorphisms and contains the canonical ("split exact") sequences: :: M' \to M' \oplus M''\to M''; * Suppose M \to M'' occurs as the second arrow of a sequence in ''E'' (it is an admissible epimorphism) and N \to M'' is any arrow in E. Then their pullback exists and its projection to N is also an admissible epimorphism. Dually, if M' \to M occurs as the first arrow of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strictly Full Subcategory
In mathematics, specifically category theory, a subcategory of a category (mathematics), category ''C'' is a category ''S'' whose Object (category theory), objects are objects in ''C'' and whose morphisms are morphisms in ''C'' with the same identities and composition of morphisms. Intuitively, a subcategory of ''C'' is a category obtained from ''C'' by "removing" some of its objects and arrows. Formal definition Let ''C'' be a category. A subcategory ''S'' of ''C'' is given by *a subcollection of objects of ''C'', denoted ob(''S''), *a subcollection of morphisms of ''C'', denoted hom(''S''). such that *for every ''X'' in ob(''S''), the identity morphism id''X'' is in hom(''S''), *for every morphism ''f'' : ''X'' → ''Y'' in hom(''S''), both the source ''X'' and the target ''Y'' are in ob(''S''), *for every pair of morphisms ''f'' and ''g'' in hom(''S'') the composite ''f'' o ''g'' is in hom(''S'') whenever it is defined. These conditions ensure that ''S'' is a category in its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuscripta Mathematica
The Knights of Columbus Vatican Film Library in St. Louis, Missouri is the only collection, outside the Vatican itself, of microfilms of more than 37,000 works from the ''Biblioteca Apostolica Vaticana'', the Vatican Library in Europe. It is located in the Pius XII Memorial Library on the campus of Saint Louis University. History The Library was created by Lowrie J. Daly (1914–2000), with funding from the Knights of Columbus. The goal was to make Vatican and other documents more available to researchers in North America. Microfilming of Vatican manuscripts began in 1951, and according to the Library's website, was the largest microfilming project that had been undertaken up to that date. From 1951 to 1957, twelve million manuscript pages were recorded, from 30,000 different works. This represents approximately 75% of the manuscripts available in the targeted language groups. Other microfilm projects in the 1950s included Jesuit archival material from Rome, archives in both Nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circle Group
In mathematics, the circle group, denoted by \mathbb T or \mathbb S^1, is the multiplicative group of all complex numbers with absolute value 1, that is, the unit circle in the complex plane or simply the unit complex numbers. \mathbb T = \. The circle group forms a subgroup of \mathbb C^\times, the multiplicative group of all nonzero complex numbers. Since \mathbb C^\times is abelian, it follows that \mathbb T is as well. A unit complex number in the circle group represents a rotation of the complex plane about the origin and can be parametrized by the angle measure \theta: \theta \mapsto z = e^ = \cos\theta + i\sin\theta. This is the exponential map for the circle group. The circle group plays a central role in Pontryagin duality and in the theory of Lie groups. The notation \mathbb T for the circle group stems from the fact that, with the standard topology (see below), the circle group is a 1-torus. More generally, \mathbb T^n (the direct product of \mathbb T wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed And Exact Differential Forms
In mathematics, especially vector calculus and differential topology, a closed form is a differential form ''α'' whose exterior derivative is zero (), and an exact form is a differential form, ''α'', that is the exterior derivative of another differential form ''β''. Thus, an ''exact'' form is in the '' image'' of ''d'', and a ''closed'' form is in the ''kernel'' of ''d''. For an exact form ''α'', for some differential form ''β'' of degree one less than that of ''α''. The form ''β'' is called a "potential form" or "primitive" for ''α''. Since the exterior derivative of a closed form is zero, ''β'' is not unique, but can be modified by the addition of any closed form of degree one less than that of ''α''. Because , every exact form is necessarily closed. The question of whether ''every'' closed form is exact depends on the topology of the domain of interest. On a contractible domain, every closed form is exact by the Poincaré lemma. More general questions of this ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Rham Cohomology
In mathematics, de Rham cohomology (named after Georges de Rham) is a tool belonging both to algebraic topology and to differential topology, capable of expressing basic topological information about smooth manifolds in a form particularly adapted to computation and the concrete representation of cohomology classes. It is a cohomology theory based on the existence of differential forms with prescribed properties. On any smooth manifold, every exact form is closed, but the converse may fail to hold. Roughly speaking, this failure is related to the possible existence of "holes" in the manifold, and the de Rham cohomology groups comprise a set of topological invariants of smooth manifolds that precisely quantify this relationship. Definition The de Rham complex is the cochain complex of differential forms on some smooth manifold , with the exterior derivative as the differential: :0 \to \Omega^0(M)\ \stackrel\ \Omega^1(M)\ \stackrel\ \Omega^2(M)\ \stackrel\ \Omega^3(M) \to \cd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torsion-free Abelian Group
In mathematics, specifically in abstract algebra, a torsion-free abelian group is an abelian group which has no non-trivial torsion elements; that is, a group in which the group operation is commutative and the identity element is the only element with finite order. While finitely generated abelian groups are completely classified, not much is known about infinitely generated abelian groups, even in the torsion-free countable case. Definitions An abelian group \langle G, + ,0\rangle is said to be torsion-free if no element other than the identity e is of finite order. Explicitly, for any n > 0, the only element x \in G for which nx = 0 is x = 0. A natural example of a torsion-free group is \langle \mathbb Z,+,0\rangle , as only the integer 0 can be added to itself finitely many times to reach 0. More generally, the free abelian group \mathbb Z^r is torsion-free for any r \in \mathbb N. An important step in the proof of the classification of finitely generated abelia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motivation
Motivation is the reason for which humans and other animals initiate, continue, or terminate a behavior at a given time. Motivational states are commonly understood as forces acting within the agent that create a disposition to engage in goal-directed behavior. It is often held that different mental states compete with each other and that only the strongest state determines behavior. This means that we can be motivated to do something without actually doing it. The paradigmatic mental state providing motivation is desire. But various other states, such as beliefs about what one ought to do or intentions, may also provide motivation. Motivation is derived from the word 'motive', which denotes a person's needs, desires, wants, or urges. It is the process of motivating individuals to take action in order to achieve a goal. The psychological elements fueling people's behavior in the context of job goals might include a desire for money. Various competing theories have been proposed co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoneda Lemma
In mathematics, the Yoneda lemma is arguably the most important result in category theory. It is an abstract result on functors of the type ''morphisms into a fixed object''. It is a vast generalisation of Cayley's theorem from group theory (viewing a group as a miniature category with just one object and only isomorphisms). It allows the embedding of any locally small category into a category of functors (contravariant set-valued functors) defined on that category. It also clarifies how the embedded category, of representable functors and their natural transformations, relates to the other objects in the larger functor category. It is an important tool that underlies several modern developments in algebraic geometry and representation theory. It is named after Nobuo Yoneda. Generalities The Yoneda lemma suggests that instead of studying the locally small category \mathcal , one should study the category of all functors of \mathcal into \mathbf (the category of sets with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abelian Group
In mathematics, an abelian group, also called a commutative group, is a group in which the result of applying the group operation to two group elements does not depend on the order in which they are written. That is, the group operation is commutative. With addition as an operation, the integers and the real numbers form abelian groups, and the concept of an abelian group may be viewed as a generalization of these examples. Abelian groups are named after early 19th century mathematician Niels Henrik Abel. The concept of an abelian group underlies many fundamental algebraic structures, such as fields, rings, vector spaces, and algebras. The theory of abelian groups is generally simpler than that of their non-abelian counterparts, and finite abelian groups are very well understood and fully classified. Definition An abelian group is a set A, together with an operation \cdot that combines any two elements a and b of A to form another element of A, denoted a \cdot b. The symbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
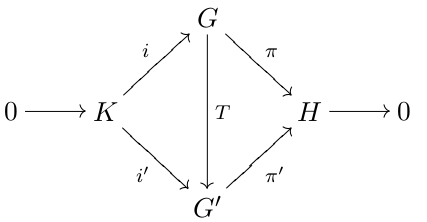
Extension (algebra)
In mathematics, a group extension is a general means of describing a group (mathematics), group in terms of a particular normal subgroup and quotient group. If Q and N are two groups, then G is an extension of Q by N if there is a short exact sequence :1\to N\;\overset\;G\;\overset\;Q \to 1. If G is an extension of Q by N, then G is a group, \iota(N) is a normal subgroup of G and the quotient group G/\iota(N) is isomorphic to the group Q. Group extensions arise in the context of the extension problem, where the groups Q and N are known and the properties of G are to be determined. Note that the phrasing "G is an extension of N by Q" is also used by some. Since any finite group G possesses a maximal normal subgroup N with simple group, simple factor group G/N, all finite groups may be constructed as a series of extensions with finite simple groups. This fact was a motivation for completing the classification of finite simple groups. An extension is called a central extension if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Additive Functor
In mathematics, specifically in category theory, a preadditive category is another name for an Ab-category, i.e., a category that is enriched over the category of abelian groups, Ab. That is, an Ab-category C is a category such that every hom-set Hom(''A'',''B'') in C has the structure of an abelian group, and composition of morphisms is bilinear, in the sense that composition of morphisms distributes over the group operation. In formulas: f\circ (g + h) = (f\circ g) + (f\circ h) and (f + g)\circ h = (f\circ h) + (g\circ h), where + is the group operation. Some authors have used the term ''additive category'' for preadditive categories, but here we follow the current trend of reserving this term for certain special preadditive categories (see below). Examples The most obvious example of a preadditive category is the category Ab itself. More precisely, Ab is a closed monoidal category. Note that commutativity is crucial here; it ensures that the sum of two group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |