|
Eric Betzig
Robert Eric Betzig (born January 13, 1960) is an American physicist who works as a professor of physics and professor of molecular and cell biology at the University of California, Berkeley. He is also a senior fellow at the Janelia Farm Research Campus in Ashburn, Virginia. Betzig has worked to develop the field of fluorescence microscopy and photoactivated localization microscopy. He was awarded the 2014 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for "the development of super-resolved fluorescence microscopy" along with Stefan Hell and fellow Cornell alumnus William E. Moerner. Early life and education Betzig was born in Ann Arbor, Michigan, in 1960, the son of Helen Betzig and engineer Robert Betzig. Aspiring to work in the aerospace industry, Betzig studied physics at the California Institute of Technology and graduated with a BS degree in 1983. He then went on to study at Cornell University where he was advised by Aaron Lewis and Michael Isaacson. There he obtained an MS degree and a P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Institute Of Technology
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech or CIT)The university itself only spells its short form as "Caltech"; the institution considers other spellings such a"Cal Tech" and "CalTech" incorrect. The institute is also occasionally referred to as "CIT", most notably in its alma mater, but this is uncommon. is a private university, private research university in Pasadena, California. Caltech is ranked among the best and most selective academic institutions in the world, and with an enrollment of approximately 2400 students (acceptance rate of only 5.7%), it is one of the world's most selective universities. The university is known for its strength in science and engineering, and is among a small group of Institute of Technology (United States), institutes of technology in the United States which is primarily devoted to the instruction of pure and applied sciences. The institution was founded as a preparatory and vocational school by Amos G. Throop in 1891 and began ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stefan Hell
Stefan Walter Hell HonFRMS (: born 23 December 1962) is a Romanian-German physicist and one of the directors of the Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry in Göttingen, Germany. He received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2014 "for the development of super-resolved fluorescence microscopy", together with Eric Betzig and William Moerner. Life Born into a Roman Catholic Banat Swabian family in Arad, Romania, he grew up at his parents' home in nearby Sântana. Hell attended primary school there between 1969 and 1977. Andreea Pocotila"Fizicianul premiat cu Nobelul pentru chimie vorbește românește și ține legătura cu mediul științific din țara noastră" ''România Liberă'', October 8, 2014 Subsequently, he attended one year of secondary education at the Nikolaus Lenau High School in Timișoara before leaving with his parents to West Germany in 1978. His father was an engineer and his mother a teacher; the family settled in Ludwigshafen after emigrating. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William L
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ᚹᛁᛚᛃᚨᚺᛖᛚᛗᚨᛉ, ''*Wiljahelmaz'' > German ''Wilhelm'' and Old Norse ᚢᛁᛚᛋᛅᚼᛅᛚᛘᛅᛋ, ''Vilhjálmr''). By regular sound changes, the native, inherited English form of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William O
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ᚹᛁᛚᛃᚨᚺᛖᛚᛗᚨᛉ, ''*Wiljahelmaz'' > German '' Wilhelm'' and Old Norse ᚢᛁᛚᛋᛅᚼᛅᛚᛘᛅᛋ, ''Vilhjálmr''). By regular sound changes, the native, inherited English form of the name shou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Zero
Absolute zero is the lowest limit of the thermodynamic temperature scale, a state at which the enthalpy and entropy of a cooled ideal gas reach their minimum value, taken as zero kelvin. The fundamental particles of nature have minimum vibrational motion, retaining only quantum mechanical, zero-point energy-induced particle motion. The theoretical temperature is determined by extrapolating the ideal gas law; by international agreement, absolute zero is taken as −273.15 degrees on the Celsius scale ( International System of Units), Note: The triple point of water is 0.01 °C, not 0 °C; thus 0 K is −2890.15 °C, not −273.16 °C. which equals −459.67 degrees on the Fahrenheit scale (United States customary units or Imperial units). The corresponding Kelvin and Rankine temperature scales set their zero points at absolute zero by definition. It is commonly thought of as the lowest temperature possible, but it is not the lowest ''enthalpy'' state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
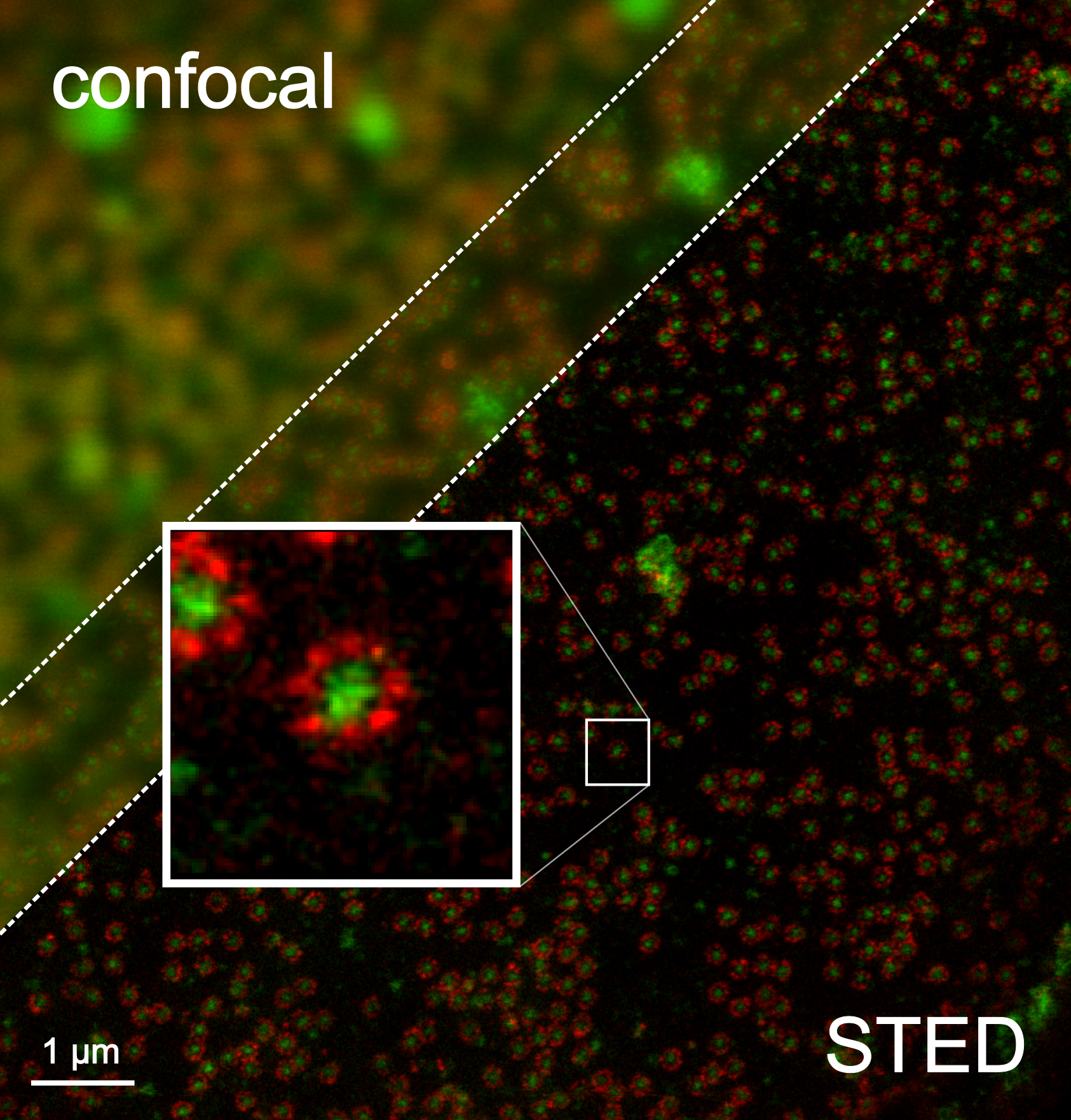
Abbe Limit
The resolution of an optical imaging system a microscope, telescope, or camera can be limited by factors such as imperfections in the lenses or misalignment. However, there is a principal limit to the resolution of any optical system, due to the physics of diffraction. An optical system with resolution performance at the instrument's theoretical limit is said to be diffraction-limited. The diffraction-limited angular resolution of a telescopic instrument is inversely proportional to the wavelength of the light being observed, and proportional to the diameter of its objective's entrance aperture. For telescopes with circular apertures, the size of the smallest feature in an image that is diffraction limited is the size of the Airy disk. As one decreases the size of the aperture of a telescopic lens, diffraction proportionately increases. At small apertures, such as f/22, most modern lenses are limited only by diffraction and not by aberrations or other imperfections in the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984), then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996) and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007), is an American industrial Research and development, research and scientific development S.A. (corporation), company owned by multinational company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, Murray Hill, New Jersey, the company operates several laboratories in the United States and around the world. Researchers working at Bell Laboratories are credited with the development of radio astronomy, the transistor, the laser, the photovoltaic cell, the charge-coupled device (CCD), information theory, the Unix operating system, and the programming languages B (programming language), B, C (programming language), C, C++, S (programming language), S, SNOBOL, AWK, AMPL, and others. Nine Nobel Prizes have been awarded for work completed at Bell Laboratories. Bell Labs had its origin in the complex corporate organizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ProQuest
ProQuest LLC is an Ann Arbor, Michigan-based global information-content and technology company, founded in 1938 as University Microfilms by Eugene B. Power. ProQuest is known for its applications and information services for libraries, providing access to dissertations, theses, ebooks, newspapers, periodicals, historical collections, governmental archives, cultural archives,"Jisc and ProQuest Enable Access to Essential Digital Content" retrieved May 21, 2014 and other aggregated databases. This content was estimated to be around 125 billion digital pages, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineering Physics
Engineering physics, or engineering science, refers to the study of the combined disciplines of physics, mathematics, chemistry, biology, and engineering, particularly computer, nuclear, electrical, electronic, aerospace, materials or mechanical engineering. By focusing on the scientific method as a rigorous basis, it seeks ways to apply, design, and develop new solutions in engineering. Overview Unlike traditional engineering disciplines, engineering science/physics is not necessarily confined to a particular branch of science, engineering or physics. Instead, engineering science/physics is meant to provide a more thorough grounding in applied physics for a selected specialty such as optics, quantum physics, materials science, applied mechanics, electronics, nanotechnology, microfabrication, microelectronics, computing, photonics, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, nuclear engineering, biophysics, control theory, aerodynamics, energy, solid-state physics, etc. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applied Physics
Applied physics is the application of physics to solve scientific or engineering problems. It is usually considered to be a bridge or a connection between physics and engineering. "Applied" is distinguished from "pure" by a subtle combination of factors, such as the motivation and attitude of researchers and the nature of the relationship to the technology or science that may be affected by the work. Applied physics is rooted in the fundamental truths and basic concepts of the physical sciences, but is concerned with the utilization of scientific principles in practical devices and systems, and in the application of physics in other areas of science and high technology. Examples of research and development areas *Accelerator physics * Acoustics *Atmospheric physics *Biophysics * Brain–computer interfacing *Chemical physics *Differentiable programming **Artificial intelligence ** Scientific computing *Engineering physics **Chemical engineering ** Electrical engineering ***E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctor Of Philosophy
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD, Ph.D., or DPhil; Latin: or ') is the most common degree at the highest academic level awarded following a course of study. PhDs are awarded for programs across the whole breadth of academic fields. Because it is an earned research degree, those studying for a PhD are required to produce original research that expands the boundaries of knowledge, normally in the form of a dissertation, and defend their work before a panel of other experts in the field. The completion of a PhD is often a requirement for employment as a university professor, researcher, or scientist in many fields. Individuals who have earned a Doctor of Philosophy degree may, in many jurisdictions, use the title ''Doctor'' (often abbreviated "Dr" or "Dr.") with their name, although the proper etiquette associated with this usage may also be subject to the professional ethics of their own scholarly field, culture, or society. Those who teach at universities or work in academic, edu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master Of Science
A Master of Science ( la, Magisterii Scientiae; abbreviated MS, M.S., MSc, M.Sc., SM, S.M., ScM or Sc.M.) is a master's degree in the field of science awarded by universities in many countries or a person holding such a degree. In contrast to the Master of Arts degree, the Master of Science degree is typically granted for studies in sciences, engineering and medicine and is usually for programs that are more focused on scientific and mathematical subjects; however, different universities have different conventions and may also offer the degree for fields typically considered within the humanities and social sciences. While it ultimately depends upon the specific program, earning a Master of Science degree typically includes writing a thesis. The Master of Science degree was first introduced at the University of Michigan in 1858. One of the first recipients of the degree was De Volson Wood, who was conferred a Master of Science degree at the University of Michigan in 1859. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)