|
Elmer Belt Library Of Vinciana
The Elmer Belt Library of Vinciana is a special collection at the University of California, Los Angeles which focuses on Leonardo da Vinci-- life, art, thought, and enduring cultural influence. It is the most extensive research collection concerning Leonardo in the United States. It was donated to UCLA in several installments between 1961 and 1966 by Dr. Elmer Belt (1893-1980), an internationally recognized urologist; a pioneer in gender affirmation surgery; a strong supporter in the founding of the UCLA School of Medicine; an important public health advocate; and a lifelong bibliophile and book collector. The Elmer Belt Library of Vinciana was officially dedicated in 1966 when UCLA opened in its Dickson Art Center a suite of wood-paneled and antique-filled rooms especially designed to house Belt’s collection. However, in 2002, the Dickson Art Center was transformed into the Broad Art Center, and the Belt Library was removed from its quarters and ultimately its holdings were i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belt 1
Belt may refer to: Apparel * Belt (clothing), a leather or fabric band worn around the waist * Championship belt, a type of trophy used primarily in combat sports * Colored belts, such as a black belt or red belt, worn by martial arts practitioners to signify rank in the kyū ranking system Geology * A synonym for orogen (e.g. orogenic belt) * Greenstone belt * A large-scale linear or curved array of belt of igneous rocks (e.g. Transscandinavian Igneous Belt) * A large-scale linear or curved array of mineral deposits (e.g. Bolivian tin belt) * Metamorphic belt :* Paired metamorphic belts Mechanical and vehicular * Belt (mechanical), a looped strip of material used to link multiple rotating shafts * Conveyor belt, a device for transporting goods along a fixed track * Belt manlift, a device for moving people between floors in a building or grain elevator. * Seat belt, a safety device in automobiles and on the plane * Timing belt, part of an internal combustion engine * Serpenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gian Paolo Lomazzo
Gian Paolo Lomazzo (26 April 1538 – 27 January 1592; his first name is sometimes also given as "Giovan" or "Giovanni") was an Italian artist and writer on art. Praised as a painter, Lomazzo wrote about artistic practice and art theory after blindness compelled him to pursue a different professional path by 1571. Lomazzo's written works were especially influential to second generation Mannerism in Italian art and architecture. Early life Gian Paolo Lomazzo was born in Milan from a family who had emigrated from the town of Lomazzo. His early training was with Giovan Battista della Cerva in Milan. He painted a large ''Allegory of the Lenten Feast'' for ''San Agostino'' in Piacenza (1567). Other works by his hand include an elaborate dome with ''Glory of Angels'' for the Capella Foppa in San Marco in Milan, and the ''Fall of Simon Magus'' in the wall of the chapel. Lomazzo was depicted on a ca. 1560 medal by Annibale Fontana that described him as having been introduced by Merc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francesco Albani
Francesco Albani or Albano (17 March or 17 August 1578 – 4 October 1660) was an Italian Baroque painter who was active in Bologna (1591–1600), Rome (1600–1609), Bologna (1609), Viterbo (1609–1610), Bologna (1610), Rome (1610–1617), Bologna (1618–1660), Mantova (1621–1622), Roma (1623–1625) and Florence (1633). Early years in Bologna Albani was born in Bologna, Italy in 1578. His father was a silk merchant who intended his son to go into his own trade. By the age of twelve, however, he had become an apprentice to the competent mannerist painter Denis Calvaert, in whose studio he met Guido Reni. He soon followed Reni to the so-called "Academy" run by Annibale, Agostino, and Ludovico Carracci. This studio fostered the careers of many painters of the Bolognese school, including Domenichino, Massari, Viola, Lanfranco, Giovanni Francesco Grimaldi, Pietro Faccini, Remigio Cantagallina, and Reni. Mature work in Rome In 1600, Albani moved to Rome to work on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
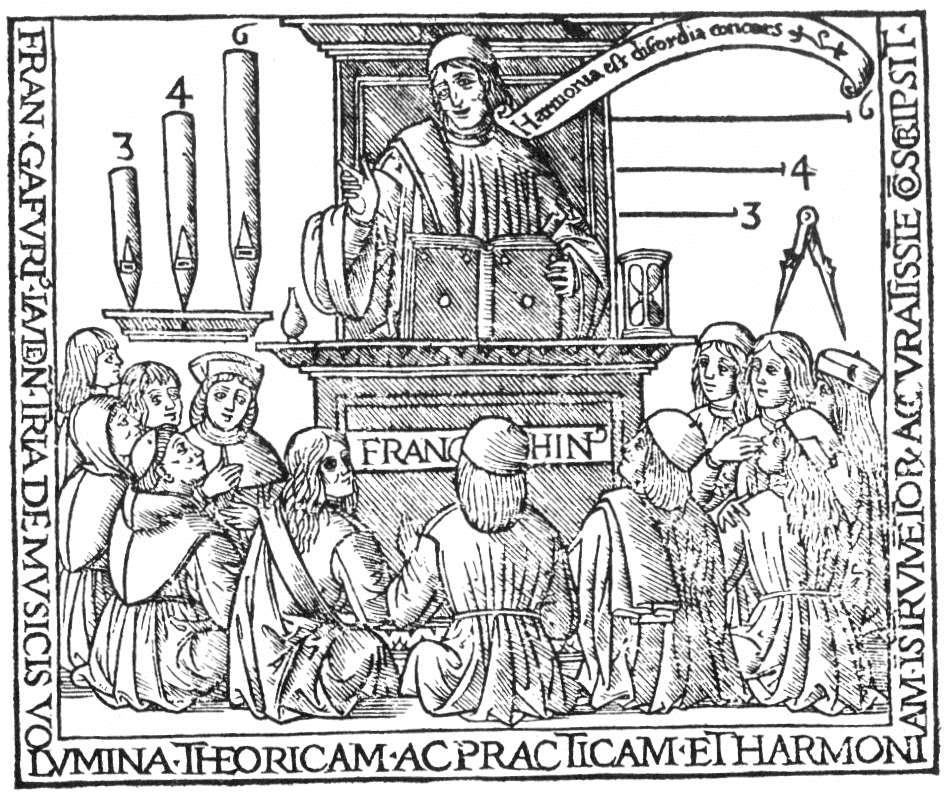
Franchinus Gaffurius
Franchinus Gaffurius (Franchino Gaffurio; 14 January 1451 – 25 June 1522) was an Italian music theorist and composer of the Renaissance. He was an almost exact contemporary of Josquin des Prez and Leonardo da Vinci, both of whom were his personal friends. He was one of the most famous musicians in Italy in the late 15th and early 16th centuries. Life He was born in Lodi to an aristocratic family. Early in life he entered a Benedictine monastery, where he acquired his early musical training; later he became a priest. Later he lived in Mantua and Verona before settling in Milan as the ''maestro di cappella'' at the cathedral there, a position which he accepted in January 1484. During the previous decade the Sforza family, using the composer Gaspar van Weerbeke as a recruiter, had built the choir at their chapel in Milan into one of the largest and most distinguished musical ensembles in Europe: composer-singers such as Alexander Agricola, Loyset Compère and Johannes Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michelangelo Manuscript From 1533
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was inspired by models from classical antiquity and had a lasting influence on Western art. Michelangelo's creative abilities and mastery in a range of artistic arenas define him as an archetypal Renaissance man, along with his rival and elder contemporary, Leonardo da Vinci. Given the sheer volume of surviving correspondence, sketches, and reminiscences, Michelangelo is one of the best-documented artists of the 16th century. He was lauded by contemporary biographers as the most accomplished artist of his era. Michelangelo achieved fame early; two of his best-known works, the ''Pietà'' and ''David'', were sculpted before the age of thirty. Although he did not consider himself a painter, Michelangelo created two of the most influential frescoes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Humani Corporis Fabrica
''De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem'' (Latin, lit. "On the fabric of the human body in seven books") is a set of books on human anatomy written by Andreas Vesalius (1514–1564) and published in 1543. It was a major advance in the history of anatomy over the long-dominant work of Galen, and presented itself as such. The collection of books is based on his Paduan lectures, during which he deviated from common practice by dissecting a corpse to illustrate what he was discussing. Dissections had previously been performed by a barber surgeon under the direction of a doctor of medicine, who was not expected to perform manual labour. Vesalius's ''magnum opus'' presents a careful examination of the organs and the complete structure of the human body. This would not have been possible without the many advances that had been made during the Renaissance, including artistic developments in literal visual representation and the technical development of printing with refined woodcut e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andreas Vesalius
Andreas Vesalius (Latinized from Andries van Wezel) () was a 16th-century anatomist, physician, and author of one of the most influential books on human anatomy, ''De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem'' (''On the fabric of the human body'' ''in seven books''). Vesalius is often referred to as the founder of modern human anatomy. He was born in Brussels, which was then part of the Habsburg Netherlands. He was a professor at the University of Padua (1537–1542) and later became Imperial physician at the court of Emperor Charles V. ''Andreas Vesalius'' is the Latinized form of the Dutch name Andries van Wesel. It was a common practice among European scholars in his time to Latinize their names. His name is also given as ''Andrea Vesalius'', ''André Vésale'', ''Andrea Vesalio'', ''Andreas Vesal'', ''Andrés Vesalio'' and ''Andre Vesale''. Early life and education Vesalius was born as Andries van Wesel to his father Anders van Wesel and mother Isabel Crabbe on 31 December 151 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernardo Bellincioni
Bernardo Bellincioni (1452–1492) was an Italian poet, who began his career in the court of Lorenzo the Magnificent in Florence. In 1483 he was at the House of Gonzaga, Gonzaga court and in 1485 he moved to Milan, where he was the court poet of Ludovico Sforza, the patron of Leonardo da Vinci. He wrote Eulogy, eulogistic sonnets addressed to his patrons and engaged in the usual literary squabbles with other poets, some in the burlesque manner established by Domenico Burchiello, that are a characteristic of the Italian Renaissance. Bellincioni's occasional verse provided the literary clues to elaborate Allegory, allegorical masques and Royal entry, state entries that were highlights of Early Modern court life. On the occasion of the marriage of the heir of Milan Gian Galeazzo Sforza to his cousin Isabella of Aragon, Duchess of Milan, Isabella of Aragon, daughter of the Alfonso II of Naples, King of Naples, Apollo presented the poems that had accompanied the tableaux in a little book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuremberg Chronicle
The ''Nuremberg Chronicle'' is an illustrated encyclopedia consisting of world historical accounts, as well as accounts told through biblical paraphrase. Subjects include human history in relation to the Bible, illustrated mythological creatures, and the histories of important Christian and secular cities from antiquity. Finished in 1493, it was originally written in Latin by Hartmann Schedel, and a German version was translated by Georg Alt. It is one of the best-documented early printed books—an incunabulum—and one of the first to successfully integrate illustrations and text. Latin scholars refer to it as the Liber Chronicarum (''Book of Chronicles'') as this phrase appears in the index introduction of the Latin edition. English-speakers have long referred to it as the ''Nuremberg Chronicle'' after the city in which it was published. German-speakers refer to it as ''Die Schedelsche Weltchronik'' (''Schedel's World History'') in honour of its author. Production Two Nurember ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Battista Passeri
Giovanni Battista Passeri (c. 1610 – 22 April 1679) was an Italian painter of the Baroque period. He was a pupil of the painter Domenichino, as the latter worked at Frascati. He painted genre and still life paintings. Life Born in Rome, Passeri is also known for his volume of artists' biographies, or ''Lives of the painters sculptors, and architects who practiced in Rome, and died between 1641 and 1673'', published in 1773. Passeri became director or president of the Accademia di San Luca in Rome, which once had his portrait of Domenichino, now in Florence. He was also the author of ''Il silenzio, discorso sopra la pittura'' (Rome, 1670) and ''La fantasia, discorso accademico'' (Rome, 1673). These publications are based on Passeri's lectures on art theory, which he delivered between 1662/3 and 1675 at the Accademia di S Luca. Another lecture remained unpublished.Dieter Graf. "Passeri." Grove Art Online. Oxford Art Online. Oxford University Press. Web. 24 Feb. 2016. He d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filippo Baldinucci
Filippo Baldinucci (3 June 1625 – 10 January 1696) was an Italian art historian and biographer. Life Baldinucci is considered among the most significant Florentine biographers/historians of the artists and the arts of the Baroque period. Patronised by the Medici, he aspired to become the new Vasari by renewing and expanding his biographies of artists, to which Baldinucci added lives of French and Flemish artists omitted by Vasari. His most important work was this biographical dictionary of artists, ''Notizie de' professori del disegno da Cimabue in qua'', of which the publication began in 1681 and continued after his death. His biography of Gian Lorenzo Bernini was published in 1682. Baldinucci came from a prominent and wealthy family of the Florentine merchant elite. As well as writing he drew portraits in chalk and modeled in clay; many of his deft and lively chalk portraits of friends are in the collection of the Uffizi. For Cardinal Leopoldo de' Medici, brother of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Pietro Bellori
Giovanni Pietro Bellori (15 January 1613 – 19 February 1696), also known as Giovan Pietro Bellori or Gian Pietro Bellori, was an Italian painter and antiquarian, but, more famously, a prominent biographer of artists of the 17th century, equivalent to Giorgio Vasari in the 16th century. His ''Lives of the Artists'' (''Vite de' Pittori, Scultori et Architetti Moderni''), published in 1672, was influential in consolidating and promoting the theoretical case for classical idealism in art. «Bellori is the "predecessor of Winckelmann" not only as an antiquarian but also as an art theorist. Winckelmann's theory of the "ideally beautiful" as he expounds it in ''Geschichte der Kunst des Altertums'', IV.2.33 ff., thoroughly agrees—except for the somewhat stronger Neoplatonic impact, which is to be explained perhaps more as an influence of Raphael Mengs than as an influence of Shaftesbury—with the content of Bellori's ''Idea'' (to which Winckelmann also owes his acquaintance with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_ca._1590.jpg)